Alabama PFAS manufacturing plant creates the climate pollution of 125,000 cars
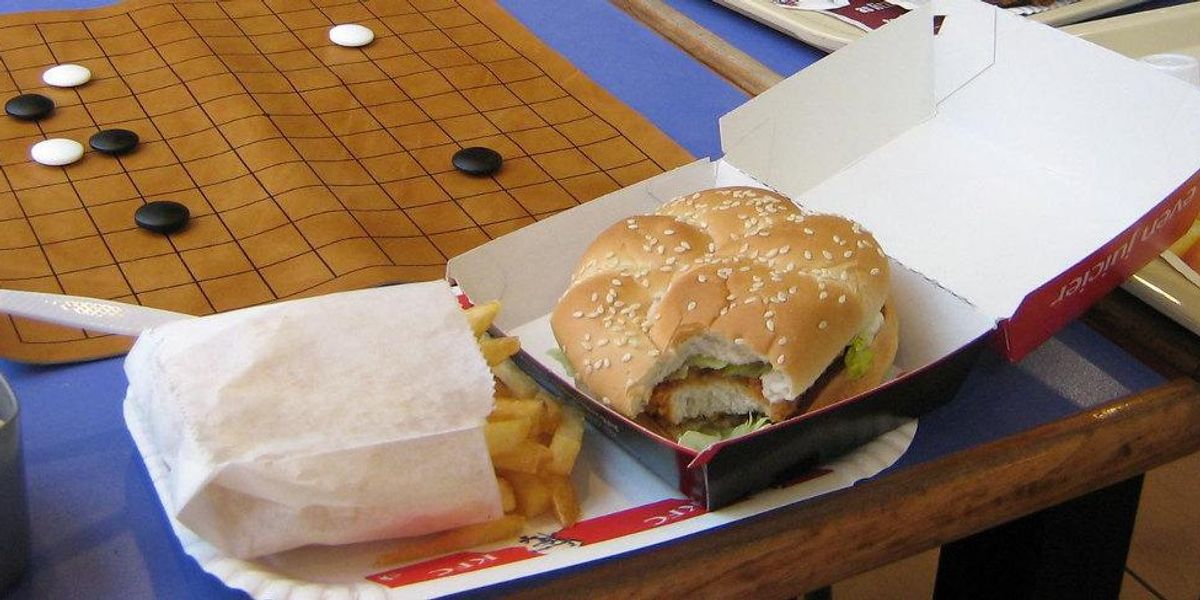
The manufacturing plant responsible for PFAS-coated fast food packaging pumps out loads of a banned ozone-depleting compound along with "forever chemicals."
As evidence mounts that hamburger wrappers and other kinds of grease-proof packaging contaminate food with PFAS, states have started banning the toxic chemicals from food packaging.
Now, a new report provides yet another reason to remove PFAS, or perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, from food wrappers: climate and ozone pollution.
PFAS exposure is linked to immune and developmental system effects, increased risk of preeclampsia in pregnant women, increased risk of kidney and testicular cancers, and higher cholesterol, among other health effects. The Daikin America plant in Decatur, Alabama, which manufactures PFAS used to coat food packaging and textiles, released 240,584 pounds of the ozone-depleting chemical Chlorodifluoromethane (HCFC-22)—the global warming equivalent of one billion pounds of carbon dioxide—in 2019, according to a new report out Thursday from the nonprofit Toxic-Free Future.
Related: Global action on harmful PFAS chemicals is long overdue: Study
While HCFC-22, used in refrigeration, was banned at the start of last year under the Montreal Protocol, companies are still allowed to produce the compound as a byproduct of making other substances. Advocates say the new report highlights the need to close that loophole—and to use PFAS-free food packaging alternatives.
"The entire world is scrambling to reduce greenhouse gas emissions before their damage to our climate is beyond repair, yet we are letting a company dump hundreds of thousands of pounds of hydrochlorofluorocarbons into the atmosphere so that it can produce 'forever chemicals' that poison our communities?" Peggy Shepard, executive director of the nonprofit WE ACT for Environmental Justice, who was not involved in the report, said in a prepared statement. "Where is the justice in that?"
Far-reaching impacts of PFAS production
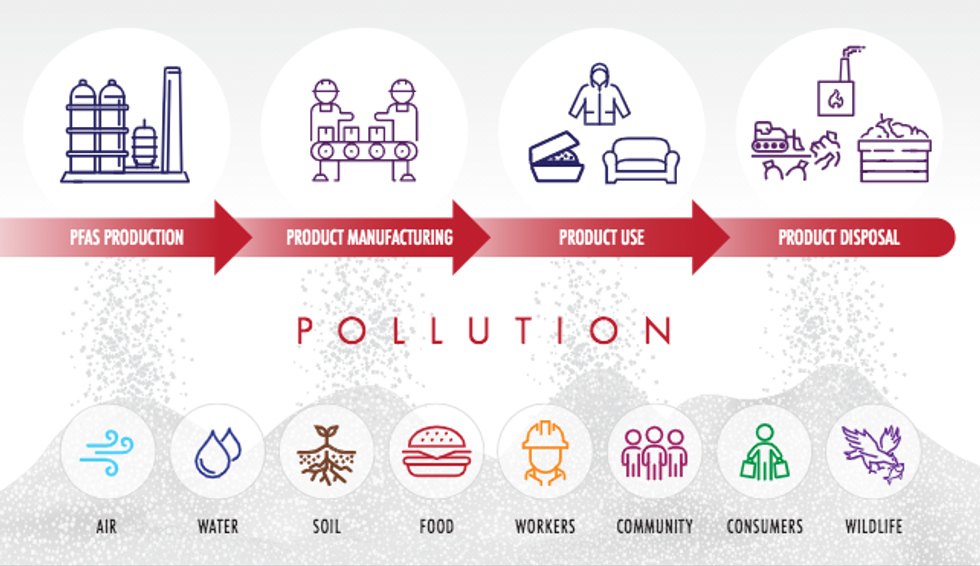
Credit: Path of Toxic Pollution report
The impetus for the study was to learn more about the impacts of PFAS-containing products before they get to consumers or end up in landfills, Erika Schreder, science director of Toxic-Free Future, told EHN. The researchers found that there appears to be only one plant in the U.S. that makes PFAS for fast food packaging coating.
Daikin America, which also emits 55,000 pounds a year of the carcinogen tetrafluoroethylene, is the number two emitter in the country of HCFC-22 after the Chemours chemical manufacturing plant in Louisville, Kentucky, according to the report.
The authors also looked at the upstream pollution from the paper mills that coat food packaging with Daikin's PFAS product, estimating that each mill releases around 180 pounds of PFAS a day into waterways, with an additional 1,260 pounds ending up in sludge at wastewater treatment plants. "We have to remember that whenever PFAS is used, it's part of the drinking water contamination problem," said Schreder, noting that landfills have been a major source of PFAS pollution around the country.
Health problems near PFAS plant
Decatur's PFAS manufacturing plant was originally built in 1961 by 3M, which sold the facility to Daikin America in 2014. Concerns about the plant, and other factories in the industrial area, have been around for decades, Brenda Hampton, a local resident and founder of Concerned Citizens of WMEL Water Authority, told EHN. Hampton and her mother both experienced kidney failure, and residents have come down with unusual forms of cancer and respiratory problems, she said.
Federal health authorities have tied elevated levels of PFAS in residents' blood to drinking water contamination downstream of that and another area plant, with Daikin agreeing to pay the local water authority $5 million in 2017 to help pay for a water filtration system, according to the report.
Last month, an employee at the Daikin America plant died after being exposed to dangerous chemicals on the job, local TV station WAFF-48 reported. Last year, OSHA fined the company $40,482 for alleged hazardous chemical management and respiratory protection violations, according to the new report.
"In this day and time, we should have [jobs and food] out there that won't be as toxic to people," said Hampton.
The report authors issue a number of recommendations, such as manufacturers paying for PFAS cleanup in affected communities, the EPA banning the production of HCFC-22 as an intermediary in PFAS manufacturing, and restaurant chains removing PFAS from food wrappers. With PFAS already banned from food packaging in states including Washington and Connecticut, some chains, like McDonald's, have recently agreed to phase out PFAS-coated packaging.
Daikin did not respond to requests for a comment on the new report.
Banner photo credit: Crispin Semmens/flickr













