Surprise! Unexpected ocean heat waves are becoming the norm
"We are entering a world where history is an unreliable guide for decision-making"
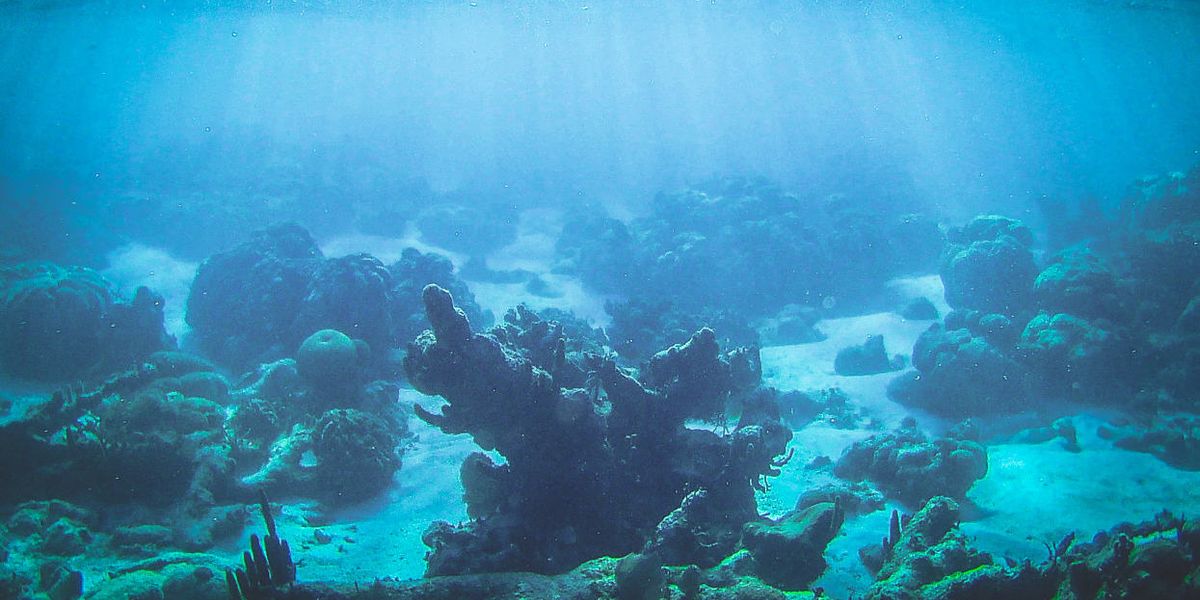
Ocean heat waves, which can push out fish, plankton and other aquatic life, are happening far more frequently than previously thought, according to a study published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Based on historical and lived experience, people expect certain conditions to prevail in the ecosystems they depend upon. Climate change is now introducing strong trends that push conditions beyond historic levels," the authors wrote.
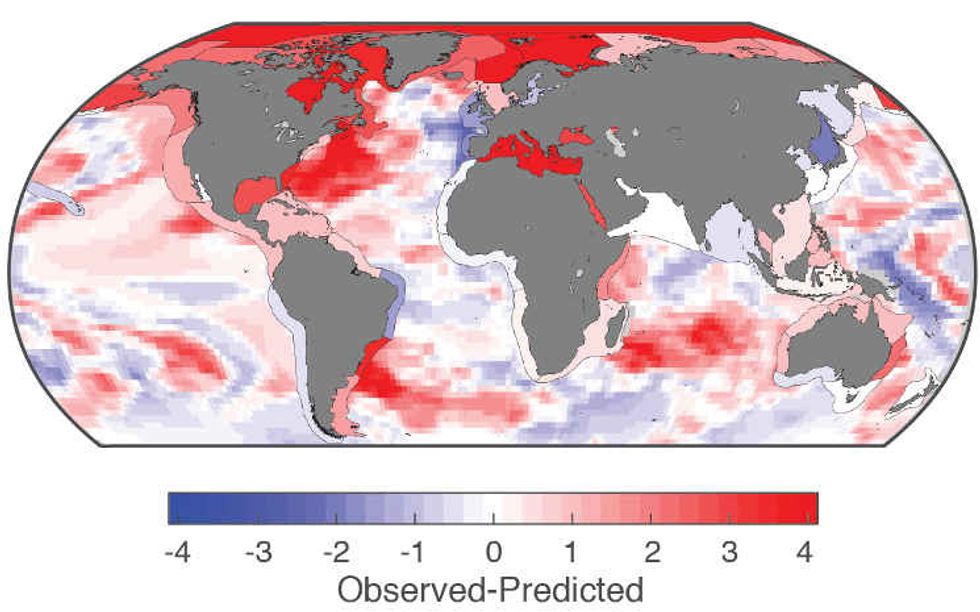
Led by the Gulf of Maine Research Institute, researchers looked at 65 large marine ecosystems around the world over the past 164 years to determine how frequently "surprising" ocean temperatures occur, with surprising defined as an event expected to occur about two times in 100 years, lead author and chief scientific officer at the Gulf of Maine Research Institute Andrew Pershing told EHN via email.
Pershing and colleagues reported that over the past seven years, the planet averaged 12 ecosystems each year experiencing the kind of unusually warm temperatures that someone in the given region would expect to see only a couple times in a century. In 2016 alone there were 23 such events.
"Across the 65 ecosystems we examined, we expected about six or seven of them would experience these 'surprises' each year," Pershing said in a statement.
The results are in line with what scientists continue to warn: oceans are the Earth's largest heat collector. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, more than 90 percent of Earth's warming over the past 50 years has happened in the ocean.
These increasing surprises documented by Pershing and other researchers are happening all over the world—the Arctic, North Atlantic, eastern Pacific, and near Australia—and spell trouble for corals, fish and tiny organisms at the base of the food chain.
While overall warming, not the surprise warming events, has a more profound effect on marine species, the researchers did find, via modeling, that surprise heat waves will decrease biodiversity. They pointed to warming trends in the Tropics as an example, where there is increasingly less coral reef cover and complexity.
Humans need to adapt and plan for these marine heat waves as well, the authors write. "To be successful, human institutions including businesses, communities, management agencies, and governments will need to adopt strategies that look forward rather than backward," they wrote.
As an example of "backward thinking," they pointed to the rapid increase in temperature in the Gulf of Maine and the resulting population collapse in the economic and ecologically vital cod fishery.
"We are entering a world where history is an unreliable guide for decision-making," Pershing said. "In a rapidly changing world, betting that trends will continue is a much better strategy."
See the full study here.