25 zones along the proposed Shell Falcon Pipeline are at risk of explosions due to landslides
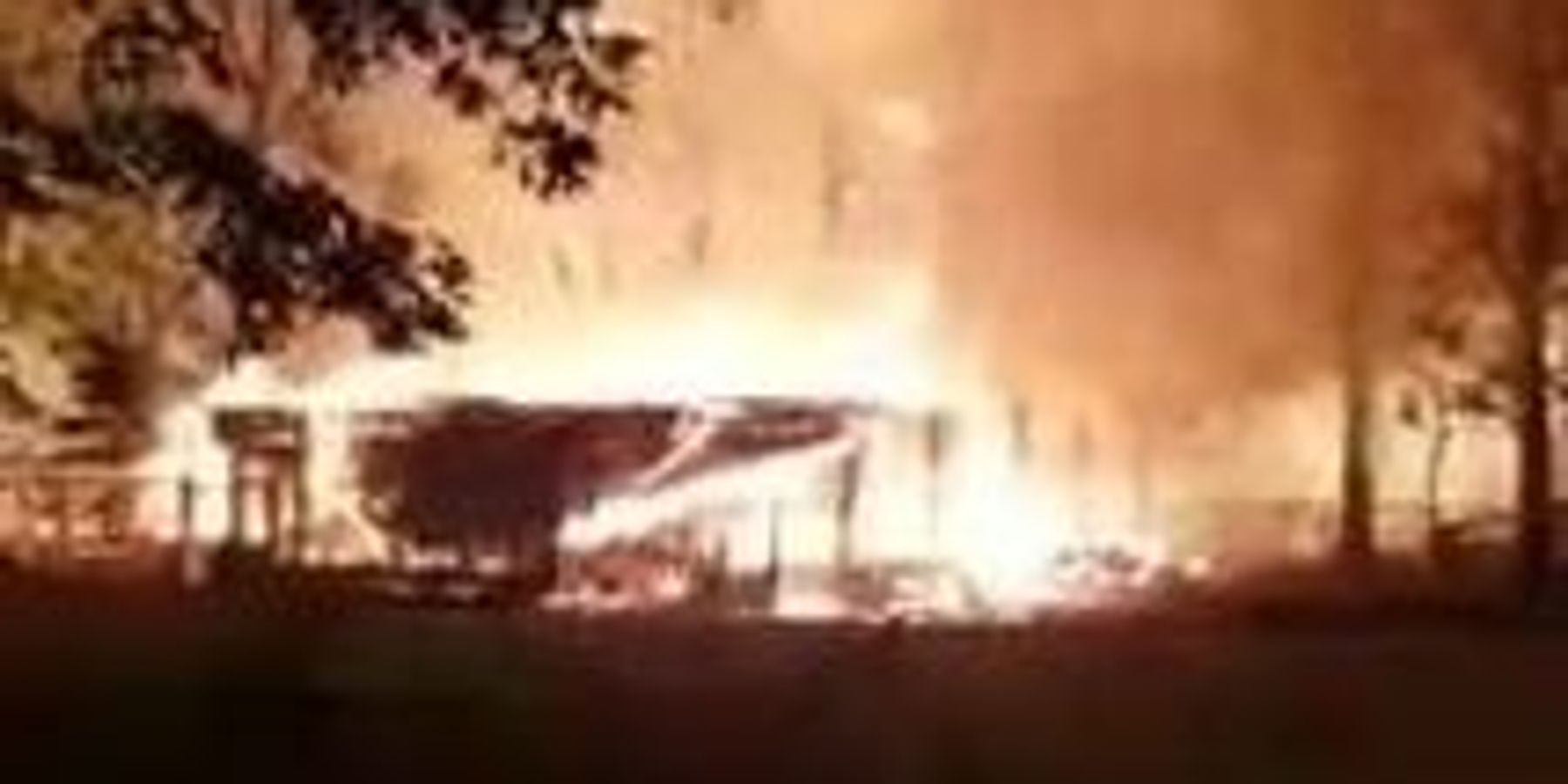
A landslide caused a natural gas pipeline 35 miles west of Pittsburgh to explode on Monday. It wasn't an isolated incident.
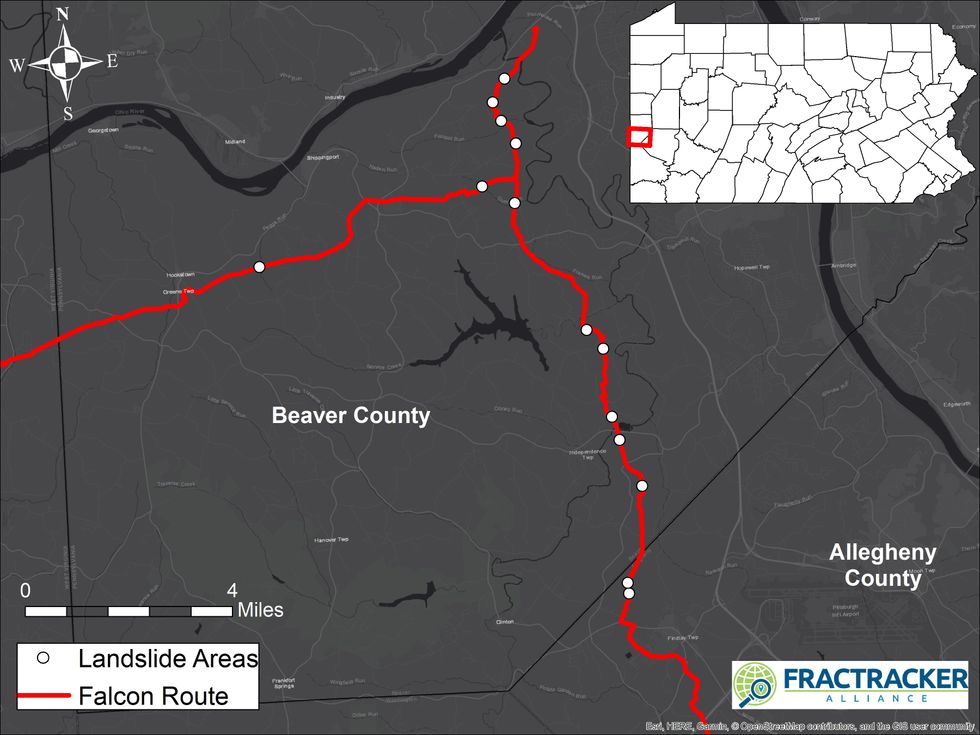
PITTSBURGH—Shell Pipeline Company has identified 25 locations that are prone to landslides in or near the route of its proposed Falcon Ethane Pipeline through Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. Fourteen of those locations are in Southwestern Pennsylvania.
The Falcon Pipeline is just one piece of a massive network of unconventional oil and gas-related infrastructure being built by Shell and its affiliates and business partners in Pennsylvania with the aim of turning the region into a new petrochemical hub. The development has elicited concern from researchers, residents and environmental groups about the increased risk of explosions and spills, as well as the cumulative impact on air and water quality in the region.
Two of the sites identified by Shell as being prone to landslides along the proposed Falcon Pipeline route are in Allegheny County. The other 12 sites are in Beaver County—35 miles west of Pittsburgh—where on Monday a natural gas pipeline not affiliated with Shell exploded, destroying one home, two garages, a barn, and several vehicles. The explosion and subsequent fire didn't result in any serious injuries, but it forced the evacuation of 25 homes, shut down the interstate, and caused the local school district to close for the day.
The explosion, in a brand new section of Energy Transfer Partners' Rover Pipeline, is being attributed to a landslide following heavy rains over the weekend. This isn't the first time a landslide has caused a natural gas pipeline to explode: In June, landslides resulted in the rupture and explosion of a TransCanada natural gas pipeline in Marshall County, West Virginia.
Shell is currently constructing a multi-billion dollar ethane cracker plant in Potter Township, just five miles from the site of the Energy Transfer Pipeline explosion. Shell's proposed Falcon Pipeline would transport large volumes of natural gas and liquids to the ethane cracker plant to be converted into ethylene for use in plastics manufacturing.
In its permit application, Shell identified "landslide risk" areas along the proposed route for the Falcon Pipeline. The FracTracker Alliance, a Pittsburgh-based oil and gas industry watchdog group, has mapped those locations. In Pennsylvania, the 14 landslide-prone areas on or near the proposed pipeline route total 2.1 miles.
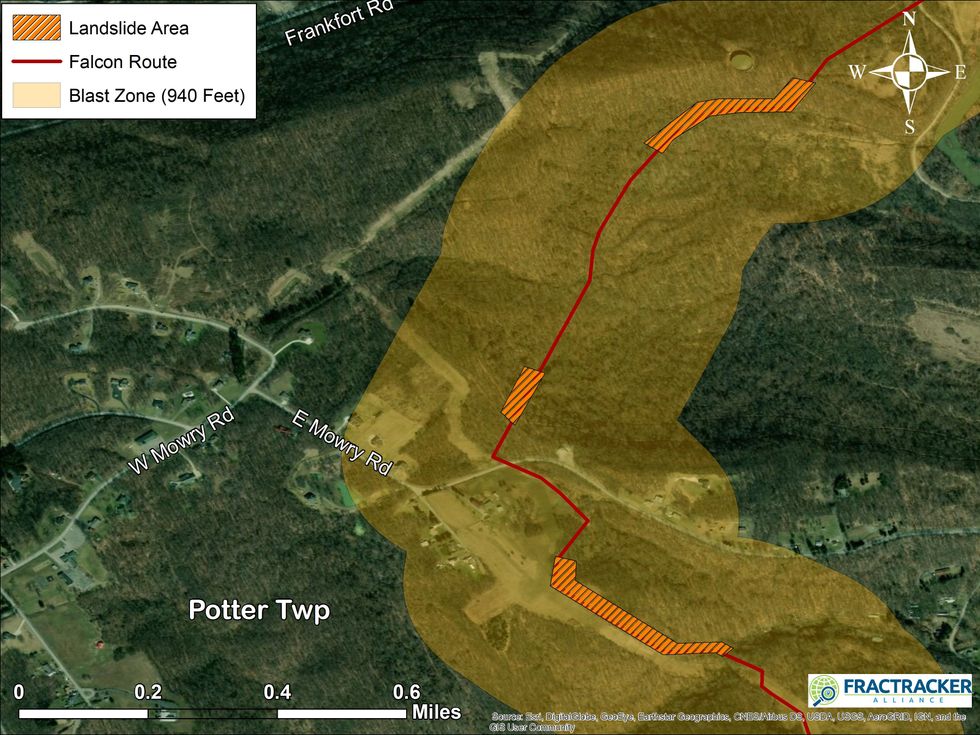
In Potter Township, where the ethane cracker plant is under construction, the Falcon Pipeline would cut through an approximately half-mile long landslide risk zone located about 800 to 1,000 feet from neighborhoods with 20 to 30 homes in them. One house in Potter Township sits 665 feet from a portion of the proposed pipeline route identified as being in a landslide risk zone.
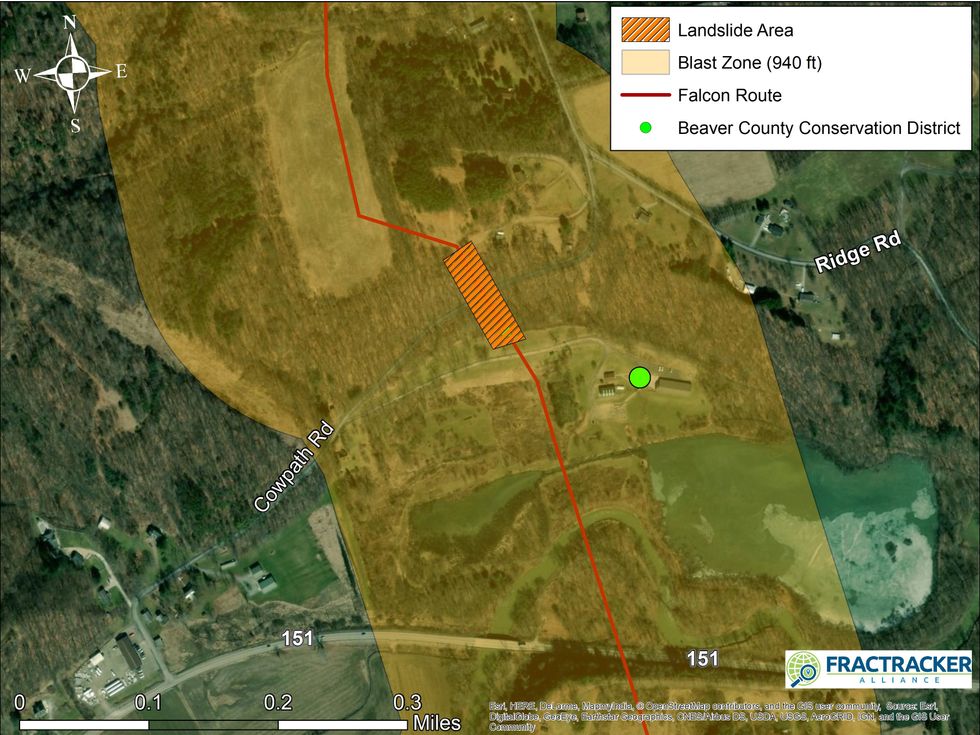
In Independence Township, one home sits 396 feet from a landslide risk zone along the proposed pipeline route.
"According to our analysis, the blast radius for the Falcon pipeline there is about 900 feet, so if there were an accident, all those homes are in the impact radius near the landslide area," Kirk Jalbert, a science and technology researcher and assistant professor at Arizona State University, told EHN. Jalbert previously served on the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection's (DEP) Environmental Justice Advisory Board, and as Manager of Community-Based Research and Engagement for the FracTracker Alliance.
The Pennsylvania DEP found 101 technical deficiencies in Shell's initial Falcon Pipeline application, and Shell has since issued a response to those citations.
"It's possible there are sections of the proposed pipeline route that were moved away from landslide areas in Shell's responses," Jalbert noted, "but it's unlikely that all of them were moved."
Shell did not respond to inquiries about whether the proposed pipeline route has been changed to avoid landslide risk areas.
“I hope this explosion serves as a wake-up call”
On September 6—four days before the Energy Transfer Partners pipeline explosion—local environmental groups held a rally at the Pittsburgh office of the Pennsylvania DEP to urge the agency to deny Shell Pipeline Company's permit application for the Falcon Ethane Pipeline, in part due to concerns over landslide risks.
"We think there are still significant problems with Shell's application for the Falcon pipeline," Matt Mehalik, executive director of environmental advocacy group The Breathe Project, told EHN. "This pipeline would go through a route that's very close to many homes in Southwestern Pennsylvania. I hope this explosion serves as a wake-up call to homeowners about the serious risks associated with Shell's plan."
Record-setting precipitation in 2018 has caused hundreds of landslides across Southwestern Pennsylvania, prompting Allegheny County to seek a disaster declaration from the Federal Emergency Management Agency for emergency funds to help clean up the damage. The county estimated that landslides caused $18 million in damage in 31 municipalities, including Pittsburgh, between February and April.
Climate change is causing more extreme rainfall events across the U.S., resulting in an increase in the frequency and severity of flooding.
"People will say this explosion happened because of unusually heavy rains," Mehalik said, "but if you're building a pipeline that can't withstand five inches of heavy rain over a weekend, something is wrong."
Jalbert emphasized that the Energy Transfer Partners pipeline exploded just a week after being brought online.
"Representatives from oil and gas pipeline companies often say that explosions only happen on old pipelines, and that they're using the most stringent design standards available to build these safe new pipelines," he said. "They can't say that anymore. This pipeline was brand new. Clearly something is wrong with the regulatory review process."