ExxonMobil, LyondellBassel and Chevron among Houston’s top polluters: Report
“We know this is a business, and you want to make a profit, but consider the communities next door.”
HOUSTON – The top industrial polluters in Harris County, which encompasses Houston, are overwhelmingly petrochemical companies, which are responsible for millions of pounds of chemical releases and hundreds of state and federal environmental violations, according to a new report.
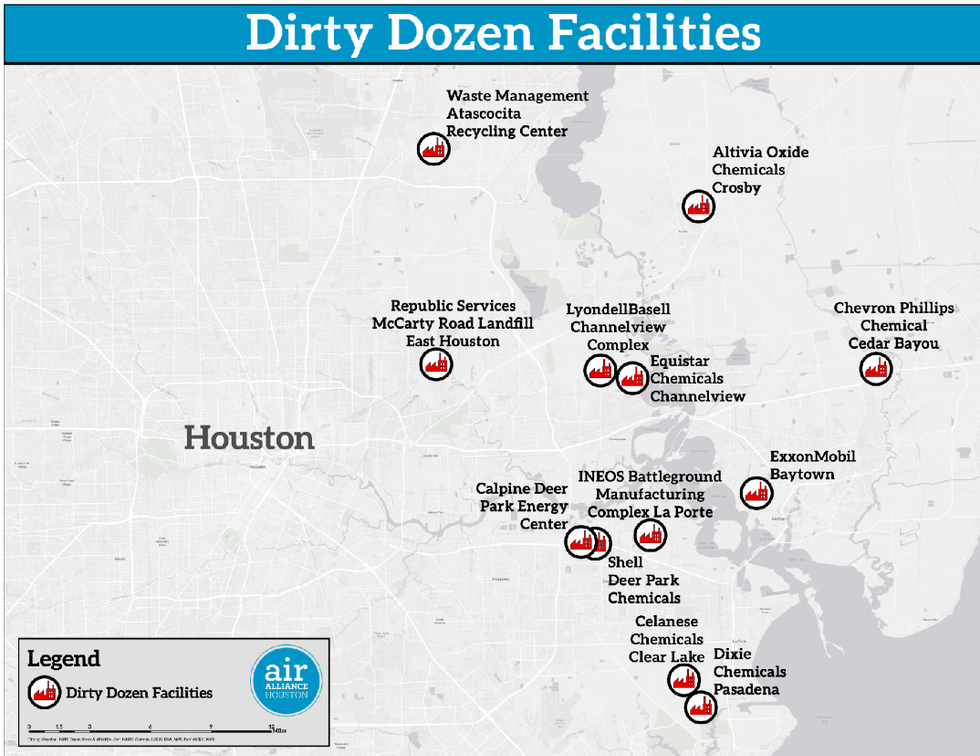
Using data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, Air Alliance, a Houston-based environmental non-profit dedicated to clean air, identified 12 of the Houston area’s top polluters.
The report details millions of pounds of chemical releases, greenhouse gas emissions and environmental regulation violations. Many of the chemicals — including cancer-causing compounds such as ethylene oxide and formaldehyde — are linked to potential health risks to surrounding communities. The greenhouse gas emissions contribute to localized issues like increased ozone and particulate matter pollution, and broader climate warming.
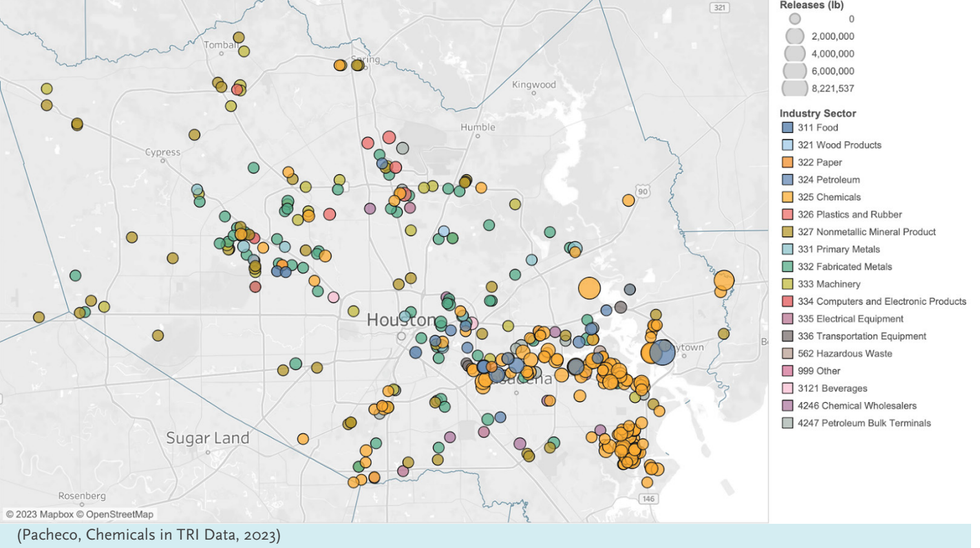
The report examined data for 272 chemicals and 350 facilities from the EPA’s Toxics Release Inventory from the years 2018-2022. The database compiles self-reported chemical releases from industrial sources like spills, leaks or emissions. Of the 350 analyzed facilities, three — ExxonMobil, Chevron Phillips Chemical and LyondellBasell — were responsible for more than 19 million pounds of chemical releases, which represents about 60% of all Harris County pollution releases over that time span.
Here is Air Alliance’s “dirty dozen,” the region’s top 12 industrial polluters, according to the report (listed here in no particular order):
- ExxonMobil Baytown Site
- Chevron Phillips Chemical
- Shell Deer Park Chemical
- LyondellBasell Industry
- Altivia Oxide Chemicals
- Equistar Chemicals Channelview
- Atascocita Recycling Center
- McCarty Road Landfill
- Deer Park Energy Center
- Dixie Holdings Inc
- Ineos Oxide
- Celanese Clear Lake
“We found it necessary to identify the most polluting facilities to call attention to the amount of emissions released by the same facilities and to be cognizant of the cumulative impact of their emissions on the surrounding communities,” the report authors wrote.
EHN reached out to the three companies with the most chemical releases. LyondellBasell has not responded.
Chevron Chemicals’ communications representative Lisa Trow told EHN via email “Chevron Phillips Chemical is committed to responsible operation of our facilities and to continuous improvement of our environmental performance.”
She added Chevron is working to “decrease air emissions through flare gas recovery equipment” and to “reduce greenhouse gas emissions by sourcing greater amounts of renewable energy.”
ExxonMobil's communication representative Lauren Kight told EHN via email, "We’re focused on reducing emissions from our manufacturing sites, improving air quality in our communities and helping protect the environment."
Ten of these facilities are within the petrochemical hub in the southeastern and eastern regions of greater Houston. According to the EPA, the fenceline communities in the surrounding zip codes bear the brunt of the pollution and are dominantly people of color. Individuals in the area also tend to have lower incomes than county averages.
“We know this is a business, and you want to … make a profit, but consider the communities next door,” Inyang Uwak, environmental epidemiologist for Air Alliance, told EHN at a press conference in Baytown on Tuesday.
Petrochemical pollution
The chemicals were ranked in two sets: the top 10 most commonly released and the 10 with the highest hazard scores from an EPA model.
The top 10 most commonly released chemicals, including chemicals like ethylene, methanol and toluene, range in their toxicity to humans but many are linked to health issues like cancer, altered brain development and reproductive harm. The chemical released with the highest frequency was ethylene, which can become carcinogenic when oxygen reacts with it.
Additionally, the top 10 most hazardous chemicals included carcinogenic chemicals like chromium, benzene and ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide, or EtO, ranked as the most hazardous chemical released in Harris County. LyondellBasell was identified by Air Alliance as the largest source of EtO emissions during the report’s timeframe. When inhaled, EtO is toxic and a carcinogen known to cause leukemia and lymphoma.
Climate impacts
The report found that the number one category for greenhouse gas emissions in Harris County is the petrochemical industry, with the power companies second. ExxonMobil’s Baytown complex was the number one greenhouse gas emitter of the dozen, with more than 67 million pounds of climate-warming emissions, most of which was carbon dioxide. Beyond greenhouse contributions, carbon dioxide can cause health issues like rapid breathing, altered heart rhythms and increased blood pressure.
Emissions of methane, an even more potent climate-warming compound, were mainly driven by the waste management industry, which accounted for 78%.
Violations of environmental regulations
Nine out of Air Alliance’s “Dirty Dozen” have violated environmental regulations or permits. At the federal level, some facilities are currently violating or have recently violated the Clean Water Act, Clean Air Act or Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. Some have violated multiple regulations and are repeat offenders. The top three polluters all have complicated histories of violations and resulting fines. The report found that the most penalized companies in Harris County were Altiva Oxide Chemicals and Chevron Phillips Chemical.
Altivia Oxide Chemicals, previously KMCO, was charged more than $10.2 million in fines, $10 million of which was related to Clean Air Act violations settled in December of 2020.The payment of these fines has not been marked as complete by the EPA.
In 2022, Chevron Phillips Chemical was ordered by the Department of Justice to pay $3.4 million in fees and $118 million in compliance action costs for violations at its Cedar Bayou plant and two other Texas plants. However, the EPA still has not marked completion of payment for an additional $236,000 dollars related to Clean Air Act fines. The Cedar Bayou plant currently has 12 consecutive quarters, or three years, of non-compliance with the Clean Air Act.
LyondellBasell Channelview was issued more than $66,000 in fines for violations, with only $2,500 marked as paid. An additional $3.4 million in fees were issued for the Channelview facility and four other LyondellBasell-owned facilities, including Equistar, also on the “dirty dozen” list. The Channelview location has violated the Clean Air Act in the past year.
ExxonMobil’s Baytown Complex was issued nearly $89,000 in fines related to Clean Air Act violations. Currently, the Baytown Complex has been in violation of the Clean Air Act for three years, and has been noncompliant with the Clean Water Act for four quarters. The Baytown Complex is by far the largest facility, at 3,400 acres, producing 10 billion pounds of petrochemicals annually.
ExxonMobil is still in a 13 year litigation process of appeals in the case of Environment Texas Citizen Lobby v. ExxonMobil Corp. The case alleges that Exxon contributed to 1.5 million pounds of illegal pollutants from October 2005 through September of 2013. The most recent ruling upheld the fine of $14 million dollars, the largest ever citizen lawsuit penalty.
“When we sued them it went to trial and ultimately a federal judge reviewed the facts and determined that [Exxon] had violated the law several thousands of times,” Luke Metzger, executive director for the environmental nonprofit Environment Texas, told EHN.
Despite these violations and legal issues, Exxon is in the renewal process for its federal operating permit and community members say it hopes to expand its Baytown operations if its permit is renewed.
In addition to these violations and fines, the report included hundreds of additional violations across the facilities at the state and federal levels.
“Unfortunately what we’ve seen, both with Exxon and many facilities in Texas, is that the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality rarely issues fines when companies have violations and if they do, it’s just a slap on the wrist,” Metzger said.














