Solar power on the rise at US schools
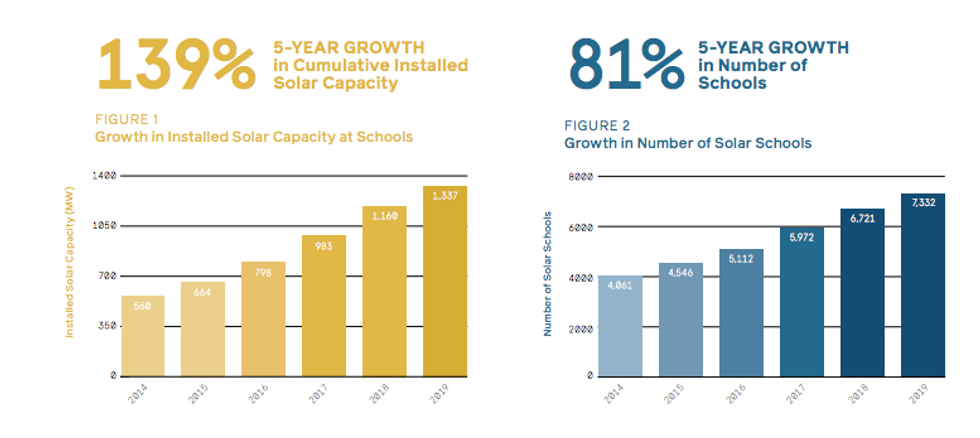
Report finds an 81% increase in K-12 schools using solar power over the last 5 years.
When Mount Desert Island High School in Maine decided to use solar power, they turned to the students.
"We have a [student] club here that helped with the project, helped choose the installer we'd go with," principal Matt Haney told EHN. "They did research on vendors and helped evaluate proposals."
About a year ago the roughly 550-student high school flipped the switch.
"We had no pushback at all on solar panels, especially since this essentially cost us nothing," Haney said. "It was a no brainer."
Mount Desert is not alone: Since 2014, the number of K-12 schools in the U.S. using solar power increased by roughly 81 percent—and now more than 5.3 million kids and teens go to a school using solar energy, according to a new report.
That increased capacity represents a 139 percent surge in the amount of solar installed over the past five years, according to the report released today by the clean energy nonprofits Generation180 and The Solar Foundation, and the Solar Energy Industries Association.
"We know from research, solar is contagious, the best indicator if someone goes solar is if their neighbor has solar," Tish Tablan, a program director at Generation180 and author of the new report, told EHN. "We want to bring solar to the heart of communities—which is schools."
The report, which is the third edition and uses publicly available data from 2014 to 2019 on school solar use, finds that solar trends at schools mirror those more broadly in the country, and that bolstered solar energy at schools is offering not only clean power but cost savings and educational opportunities.
Credit: Brighter Future: A STUDY ON SOLAR IN U.S. SCHOOLS
Low or no cost
The authors say that solar energy is increasing in part at school because there are often no costs to the school—roughly 79 percent of the solar energy installed at schools over the past five years was financed by solar developers or other third parties.
"In 28 states and DC, they can use third party ownership, where a solar developer pays for panels, does the install, does maintenance … and, in exchange, schools purchase electricity produced by that system," Tablan said.
"With the pandemic and economic downturn, and as schools face financial crises, they can do this as a way to save money and they don't necessarily have to have the budget to do it," Tablan added.
Haney said at Mount Desert High School they had looked into solar for years but the "logistics kept not working out," however, then they worked with the local climate action group A Climate to Thrive, which helped the school find local installers and navigate agreements.
"The installers own the array, sell us the energy for about seven years, then there's an option to buy [the array] after that," Haney said. "We're offsetting all of our power usage, so we're producing as much or more than we use."
The report highlighted the Batesville School District in Arkansas, which has 1,483 solar panels that generate roughly half of the district's energy. The district estimates it will save $4 million over the next 20 years in electricity costs, and plans to use some of the savings to bump up teachers' salaries.
"Our goal is to be net zero on utilities, which would mean paying nothing for utilities. Those savings can go to salaries and staff," Michael Hester, superintendent of the school district, said in the report.
Another district highlighted in the report, the Tucson Unified School District, expects to save about $43 million over the next 20 years due to its 73,000 solar panels powering nearly half of the energy for 80 schools in the region.
The Tucson Unified School District's solar energy has reduced annual carbon dioxide emissions by about 38.7 million pounds a year.

Maryland students learn about solar power on Earth Day 2014. (Credit: US Army Combat Capabilities Development Command C5ISR Center)
Job training
Tablan said schools are also using solar energy onsite as teaching opportunities and job training.
"We're seeing schools do a great job of using solar for professional development, integrating it into classrooms using it as a learning opportunity and for job training," Tablan said.
For example, in New York City—which has more than 250 solar installations completed or underway in its school system—more than 2,500 students have participated in the NYC Solar Schools Education Program, which trains teachers and students on solar energy, energy efficiency and energy storage.
Students can go on to intern with solar developers and learn to install solar at schools.
Haney said at Mount Desert the solar array is part of a broader learning environment that emphasizes climate change and science.
"Climate change, science are a big part of our curriculum," he said. "All of the students are engaged in learning about climate science in classes, it's embedded pretty deeply."
State differences
Beyond cost savings and job training, Tablan points out schools using solar energy can serve as anchors of "energy resiliency." The report focuses on solar schools in California serving energy needs for their community during wildfire-driven power outages—something crucial right now as the state experiences its worst wildfires in decades. Over the past week, Pacific Gas and Electric Co., the state's largest utility, has imposed blackouts for hundreds of thousands of people.
The increases weren't balanced across the country: California has by far the most schools using solar. One-third of the schools nationwide using solar are in California and the state accounts for 45 percent of the solar capacity at U.S. schools.
The report found that the three fastest growing states for school solar are Illinois, Indiana, and Virginia.
The bottom eight states—Nebraska, Wyoming, Alaska, Alabama, Mississippi, North Dakota, Oklahoma, and South Dakota—all have fewer than five solar schools. South Dakota was the only state with zero.
Tablan said, while 7,332 schools across the country are using some form of solar power, that accounts for just 5.5 percent of all kindergarten through 12th grade public and private schools, so there are still a lot of opportunities for solar to grow at schools.
"School decision-makers, principals and school board members … they all have a lot on their plate right now. They're not energy experts and they shouldn't be," Tablan said. "We are working to get the word out to bring [solar] to schools to enhance learning, provide vocational opportunities and save money on a constrained budget."
Haney said the solar panels, in part, motivated Mount Desert to further their greening by successfully applying for an electric bus grant, which should arrive in a couple weeks.
He said the school plans to buy the solar array after the seven years are up because it just makes sense.
"We've already budgeted to take that over and purchase that, the array was somewhere around $850,000 to install, and the option to buy is at $370,000 in 2025," Haney said. "It's very low maintenance to take it over."
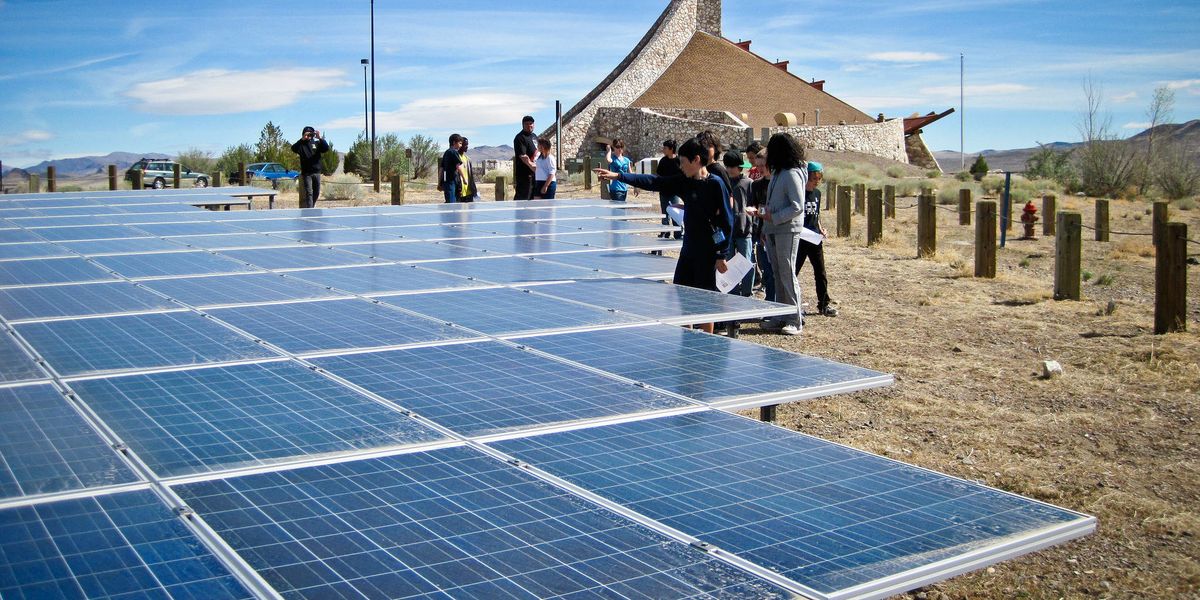
Banner photo: Pyramid Lake High School from Nixon, Nevada, visits a solar installation. Pyramid Lake School is partially powered by a solar array installed by Black Rock Solar. (Credit: BlackRockSolar/flickr)













