Analysis: Has there been a “greening” of Christianity?
Despite some inroads, Christians remain largely unconcerned about the environment
Recent efforts by religious leaders to emphasize environmental stewardship, particularly as it relates to climate change, has led some scholars to argue there has been a "greening of Christianity."
However, my recent research finds that environmentalism among Christians in the United States has not increased—and, if anything, Christians over the past two decades have become less concerned about the environment.
A half century ago, the prominent historian Lynn White argued that Judeo-Christian beliefs have contributed in a significant way to environmental decline. In the decades since his essay was published in Science, there has been debate about the role of religion, and specifically Christianity, on shaping attitudes and behavior toward the environment.
There are two main arguments: First, consistent with White's thesis, is that Christianity emphasizes human dominion over the Earth, which undermines any obligation to protect the environment. A second, competing perspective emphasizes the importance of stewardship, and that the Christian faith instills an ethic of "creation care."
The relationship between religion and the environment has taken on more practical significance in recent years with the increasing importance of climate change. Many faith-based organizations have become vocal advocates at the local and national level for policies to address climate change.
The highest profile example came in 2015 when Pope Francis released his encyclical letter on the environment, which elevated climate change, and stewardship of the environment more generally, as issues central to the Catholic Church's teaching and mission. In the United States, efforts include several initiatives led by Evangelical Protestant groups, such as the Evangelical Environmental Network.
These developments, however, contradict arguments made by Lynn White and extensive social science research—including my most recent work. In a study recently published in the journal Environmental Politics, I analyzed nearly 20 years of public opinion data collected by Gallup to evaluate whether Christians express higher levels of concern about the environment over time.
In short, the answer to this question is decidedly no. The evidence suggests that Christians in the United States have become less concerned about the environment over the past two decades.
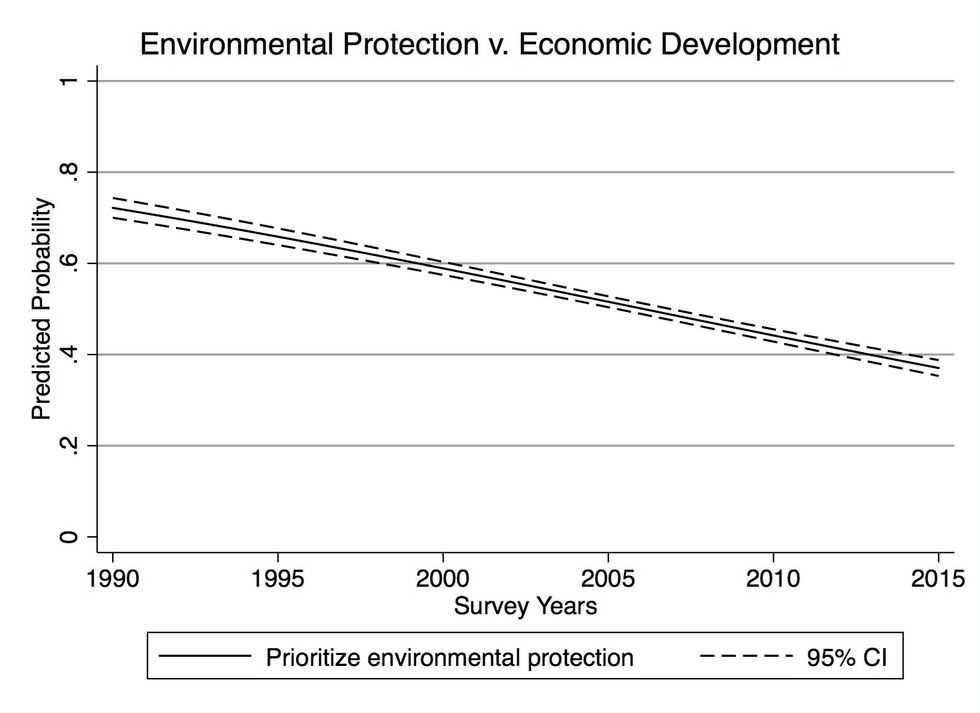
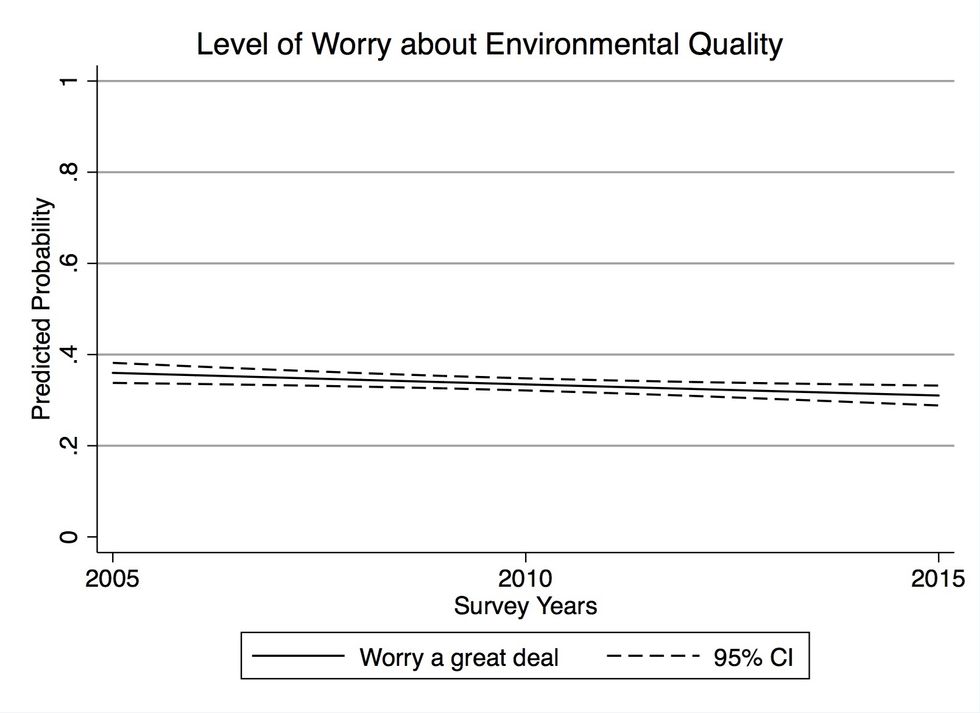
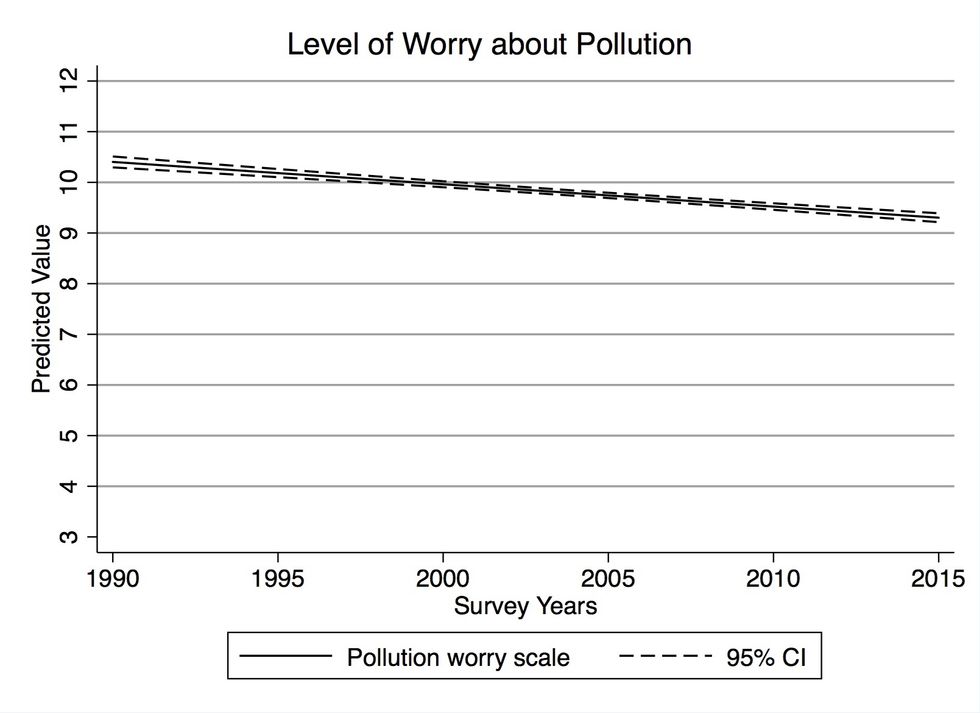
I studied Christians' responses to multiple questions pertaining to the environment that have been regularly asked by Gallup, including how people prioritize between environmental protection and economic development and energy production, levels of concern about environmental quality generally, and levels of worry about pollution (air, water, and toxic waste) and global warming specifically, and attitudes toward the environmental movement.
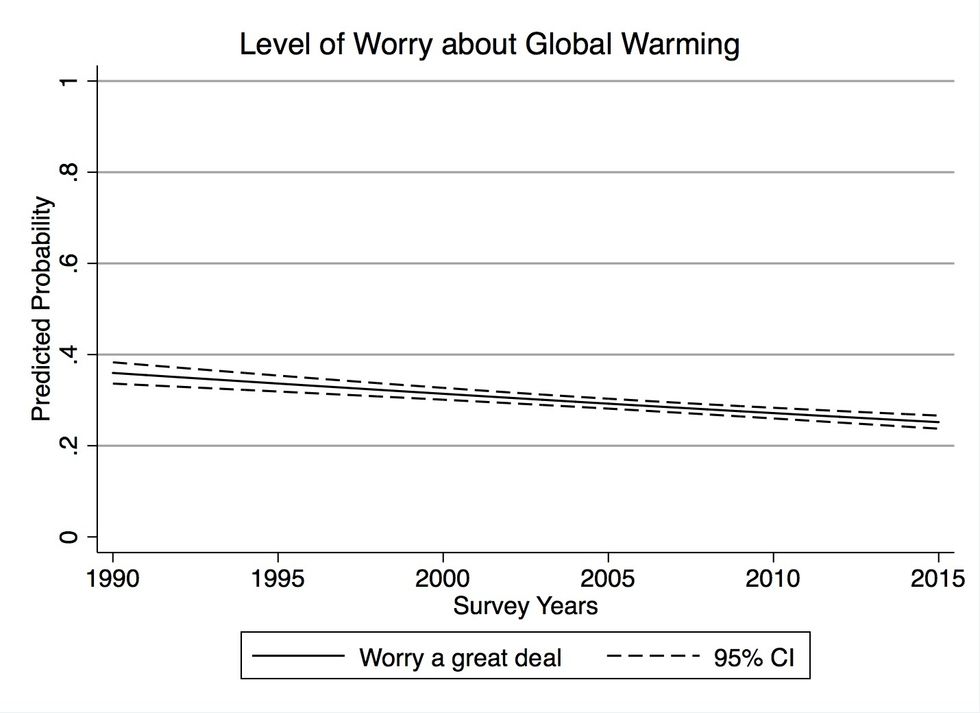
The figures below shows the likelihood that a self-identifying Christian responded to the Gallup survey questions with the most "pro-environmental" answer for four of the measures. (The comparison is between Christians and individuals that identify as atheists, agnostics, or have no religious affiliation, controlling for other factors such as political beliefs and demographic characteristics.)
Protestants, Catholics, and other Christian denominations all exhibit less worry about the environment over the time period studied—and do not differ depending on an individual's level of church attendance.
The analysis does not allow me to infer why this is the case and it's important to emphasize that, even though the evidence of a "greening of Christianity" has yet to emerge on a wide-scale basis, it is undoubtedly true that many religious organizations and faith leaders are actively engaged in promoting stewardship of the environment.
This engagement is important, and should not be dismissed.
Sustained leadership among religious organizations over the long run has the potential to generate more interest in protecting the environment, and stronger demand for actions to take on challenges such as climate change.
The figures show the likelihood that a Christian respondent, compared with individuals that identify as atheists, agnostics, or have no religious affiliation, indicated the most “pro-environmental” response to the Gallup survey question. More details are provided in the paper.
David Konisky is Associate Professor of Public and Environmental Affairs at Indiana University, Bloomington. The full article discussed is "The greening of Christianity? A study of environmental attitudes over time," Environmental Politics."