Together, we make mud
Environmental politics at the start of a new decade
The noted philosopher Rodney Dangerfield described his fictional marriage in a way that provides insight into the widening gulf in U.S. environmental politics: "She's a water sign. I'm an Earth sign. Together, we make mud."
It's a useful exercise to look at today's muddy, swampy political mess through the lens of five decades past.
Since the 1970's, each new decade brought a different perspective.
1970s
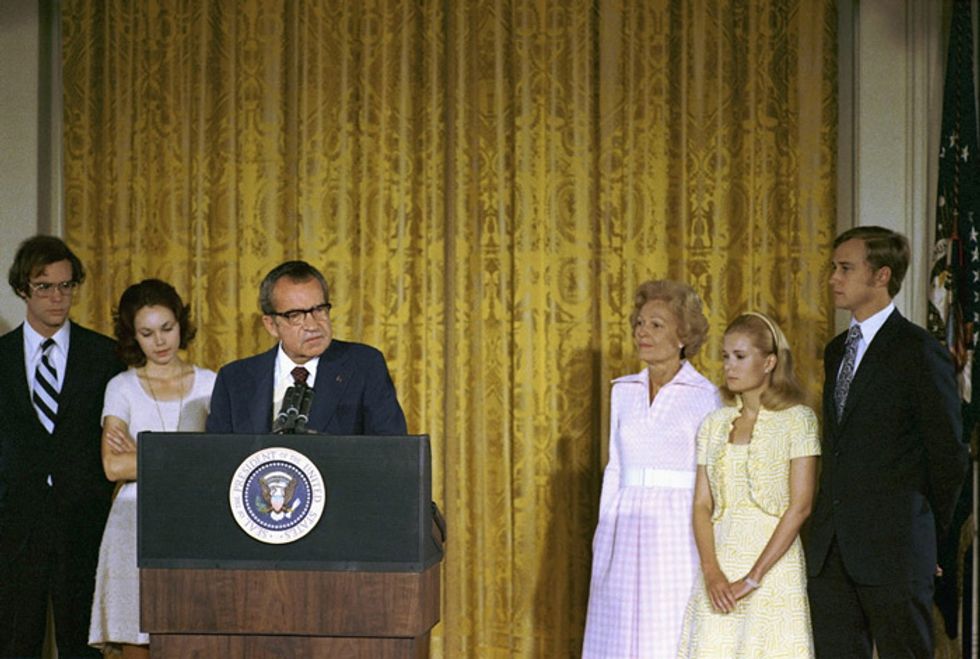

President Nixon in 1974. (Credit: National Archives)
The seventies dawned with a year that saw the founding of Earth Day and two pivotal government agencies—the Environmental Protection Agency and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration—under that quintessential tree-hugger, President Richard M. Nixon.
Three weeks into the decade, Nixon killed a proposal to pave 39 acres of the already-stressed Everglades into a massive jetport. Within two years, he banned DDT, and signed the Clean Air Act, Endangered Species Act, National Environmental Policy Act (the Environmental Impact Statement law).
Even when Nixon vetoed the Clean Water Act as too costly, a unified Congress overrode it. Nixon tipped his hat to bipartisan environmental values in his 1970 State of the Union address: "Restoring nature to its natural state is a cause beyond party and beyond factions".
Existing conservation groups like the Environmental Defense Fund (founded 1967), the World Wildlife Fund (1961) and the Sierra Club (1891) enjoy expanded memberships and political clout, while new groups like Friends of the Earth and the Natural Resources Defense Council (both 1970) and Greenpeace (1971) joined the fray.
1980s
Late seventies resentment over the snail darter undermined support for the Endangered Species Act. The tiny fish with a tiny habitat temporarily blocked completion of Tennessee's Tellico Dam.
Meanwhile, a toxic waste crisis at Love Canal led to the 1980 Superfund law. And 1979's near-calamity at Three Mile Island ended construction of new nuclear power plants.
Jimmy Carter suffered a landslide loss to Ronald Reagan, whose EPA and Interior leaders schemed to hobble their own departments.
And my favorite artifact concerns two young Congressmen and the 1980 voting scorecard from the League of Conservation Voters: Georgia Republican Newt Gingrich got a 50 percent approval rating from LCV, outpacing Tennessee Democrat Al Gore, at 35 percent.
1990s
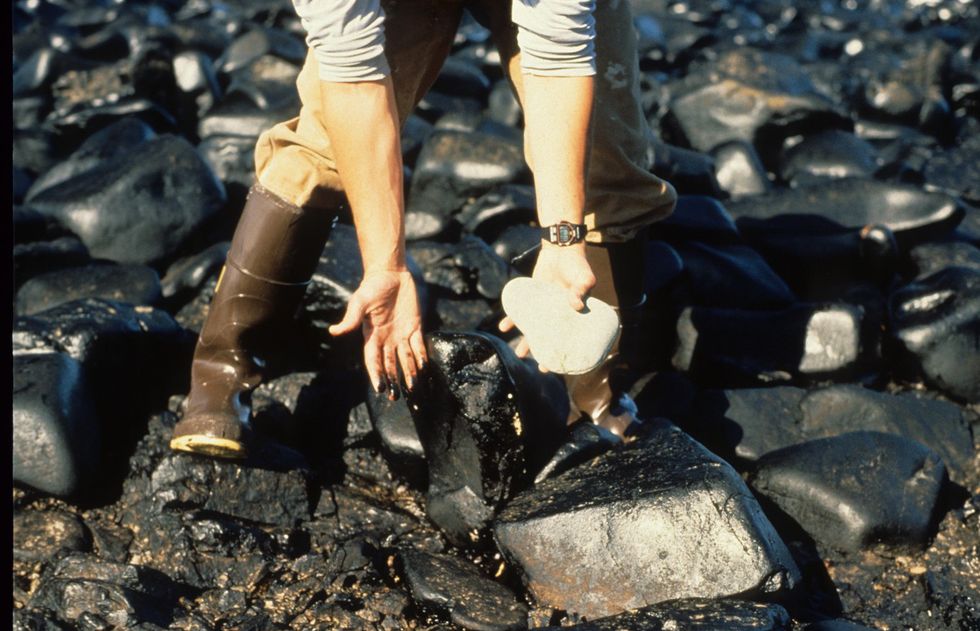

Exxon Valdez oil spill (Credit: ARLIS Reference/flickr)
The nineties arrived on the heels of a decade of high-profile eco-disasters: Bhopal, Chernobyl, medical waste on New Jersey beaches, the first dire reports of a warming planet and a vanishing ozone layer, and, in 1989, the Exxon Valdez spill.
The 20th annual Earth Day saw a huge crowd turn out on the Washington Mall.
George H. W. Bush, who promised to be the "Environmental President," signed strong revisions to the Clean Air Act – unthinkable for subsequent Republican presidents.
Corporate "greenwashing" – dubious marketing-inspired claims of environmental virtue by notoriously dirty companies and industries – hit an all-time high. And ABC turned over two hours of its most valuable property – prime time – for an Earth Day special positively choked with A-list celebrities: Bette Midler as Mother Earth, Dustin Hoffman, Meryl Streep, Magic Johnson, the aforementioned Rodney Dangerfield, and of course, America's Dad, Bill Cosby.
2000s
21st Century environmental politics began with Bush v Gore. Al Gore's million-vote win was an excruciating Electoral College loss. Instead of a president both fluent in and passionate on climate change we got an oil man whose Cardinal Richelieu, Vice President Dick Cheney, took charge of deregulatory efforts and energy policy.
Cheney's Energy Task Force operated largely in secrecy, paving the way for the fracking boom by removing regulatory obstacles. The decade was bracketed by domestic disasters that reduced the environment as a political concern: The 2001 Al Qaeda attacks and the 2008 economic collapse.
2010s
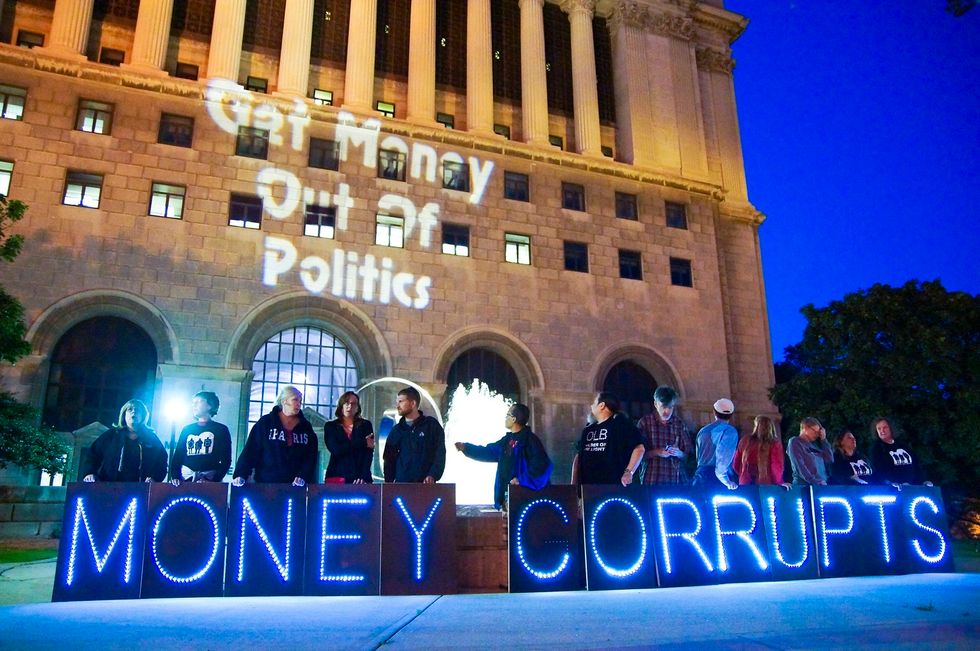

Protests over the Supreme Court Citizen United decision. (Credit: Joe Brusky/flickr)
In the last month of 2009, the Copenhagen climate talks ended in failure. Climate deniers made hay with a few ill-worded emails in a cache of thousands of hacked messages from climate scientists.
Not all Americans have come to grips with the 2010 Supreme Court Citizens United decision. It unleashed huge amounts of anonymous campaign spending for candidates and fake grassroots groups like the Koch-funded Americans for Prosperity.
As the money started pouring in, the Tea Party (b. 2009) brought in the ground troops. Many moderate Republicans, spooked by the prospects of being "primaried" from the far right, either altered their views or fled from politics altogether. Prominent Republicans who backed away from advocating action on climate change included Mitt Romney, John McCain, Newt Gingrich and Lindsey Graham.
The Democrats lost control of the House in the 2010 midterms, stifling much of the "hope" in the two-year-old Obama presidency. And the kind of high profile disasters that jelled public sentiment in 1990 had impact only as lethal tragedies, not catalysts: the Deepwater Horizon spill in 2010, the Fukushima meltdown a year later, and the unprecedented damage of Superstorm Sandy in 2012.
2020s
Clean energy is finally taking hold. But climate-denying leaders hold forth in the U.K., Australia, Brazil, and, of course, the U.S.
This is the decade when we may let one of those comparatively easy-to-save marine mammals, the vaquita porpoise, go extinct in full view. The ice caps liquidating. Venice awash. Australia ablaze. Oceans full of acid, and plastic.
Is America awake? We'll see. We cannot afford to make mud anymore.
Peter Dykstra is our weekend editor and columnist. His views do not represent those of Environmental Health News, The Daily Climate or publisher, Environmental Health Sciences.