Community activists plead to be heard through “closed doors” outside nation’s top energy conference
“It is our communities that are being harmed and hurt.”
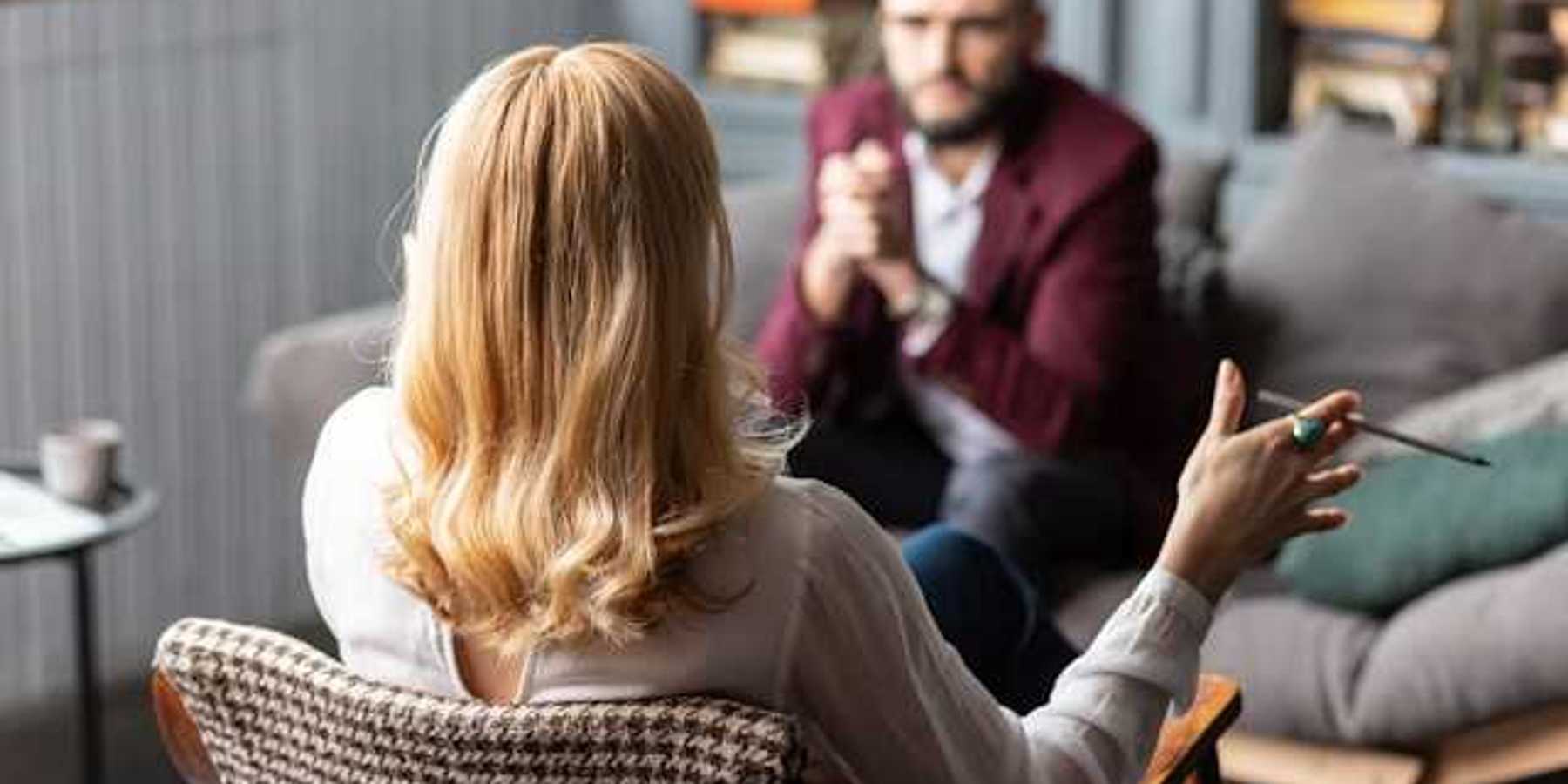
HOUSTON — Climate activists expressed concern that discussions behind closed doors at the nation’s largest energy conference, CERAWeek by S&P Global, will further contribute to environmental health risks.
As energy executives and political leaders across the nation convened for the conference in Houston, Texas this week to discuss the future of energy, representatives from the Gulf Coast, Rio Grande Valley, Ohio River Valley, and Cancer Alley highlighted the fossil fuel industry's impact in their communities.
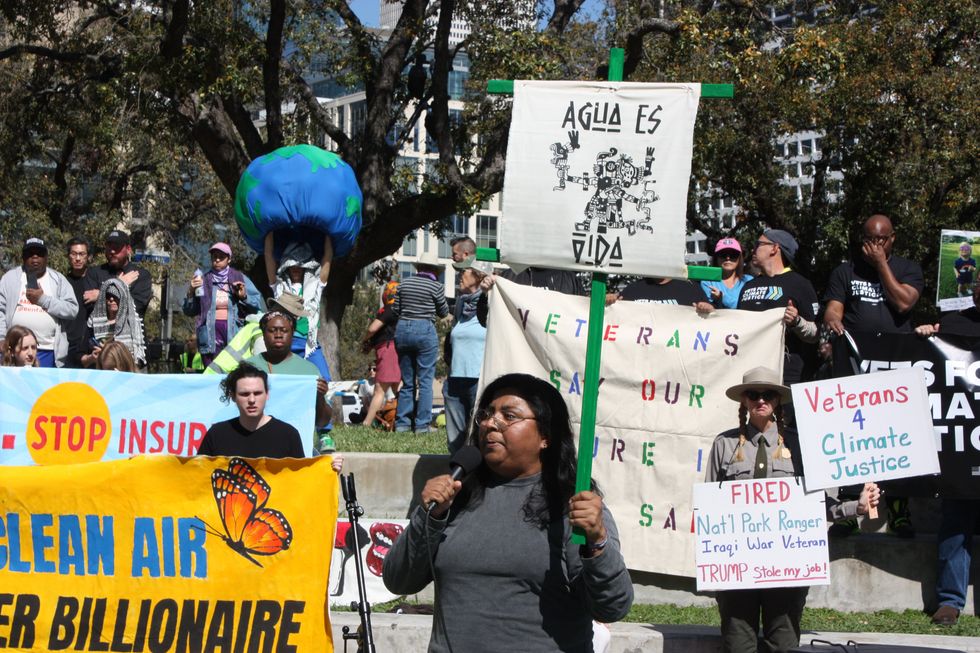
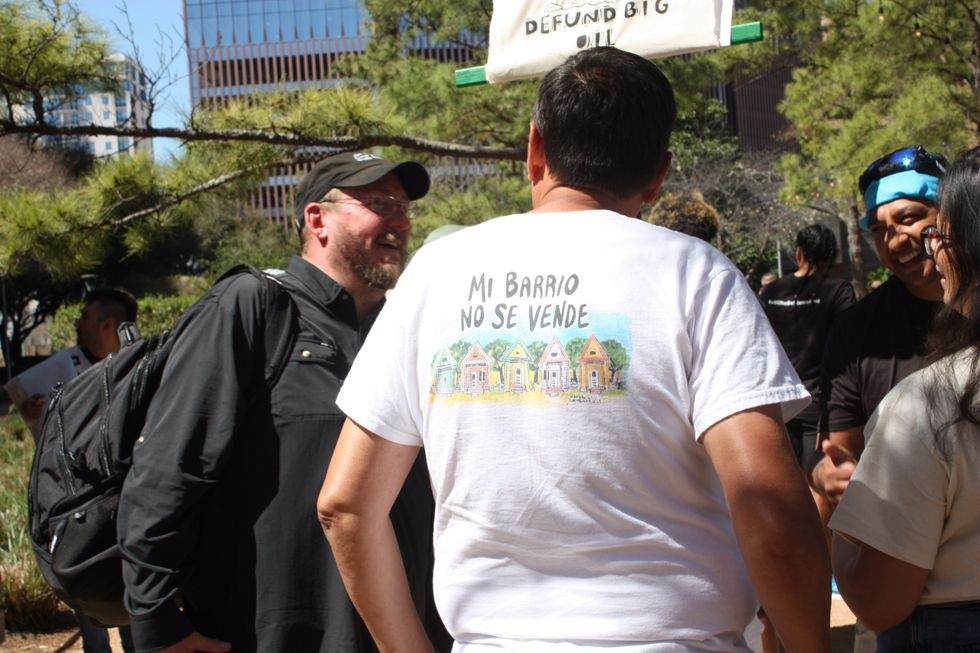
“It is our communities that are being harmed and hurt,” Yvette Arellano of the Houston environmental organization Fenceline Watch said. “It is our children that are having to play in playgrounds across the street from chemical plants and oil refineries.”
Despite attempting to purchase conference tickets at costs of up to $10,500, activists have been barred from the conference in recent years, Arellano said.
“The conference has shut out civil society from entering and understanding the projects that are coming to harm our communities,” Arellano said at a press conference at a park about 10 minutes from the convention center on Monday. “We demand transparency.”
S&P Global has not responded to Environmental Health News’ request for comment.
Health concerns and “energy additions”

Some sessions at CERAWeek were devoted to climate discussions, like Monday’s session about climate change priorities featuring industry voices from S&P Global and the Oil and Gas Climate Initiative (OGCI), alongside environmental advocacy groups like the Environmental Defense Fund and the Energy Futures Initiative Foundation.
The panel tackled questions about whether climate change will remain a priority for the industry and how the energy transition will continue under the Trump administration. Bob Dudley, chairman of the OGCI, repeatedly rephrased his own statements about the energy transition to “energy additions,” emphasizing the continued use of fossil fuels.
“Oil and gas operators in the U.S. alone waste $3.5 billion worth of methane a year through leaks, flaring, and other releases, enough to supply the energy needs of 19 million American homes,” Fred Krupp, president of the Environmental Defense Fund, said in the same conference session.
Less than a mile away from the CERAWeek convention, the Buffalo Bayou flows through downtown and into the Houston Ship Channel, which facilitates global access to the “energy capital of the world” for many of the companies in attendance at the conference. According to the Greater Houston Partnership, 44 of 128 publicly traded oil and gas companies and nearly one-third of the nation’s oil and gas jobs are located in Houston. With more than 600 petrochemical facilities, this single area produces about 42% of the nation's petrochemicals.
Last year an Amnesty International report dubbed the area a “sacrifice zone,” where fenceline communities, predominantly populated by people of color, are exposed to disproportionately high levels of pollution. In these areas, chemical disasters, climate-warming emissions, and higher cancer risks are common. Several high-profile companies, including ExxonMobil, LyondellBasell, and Chevron Phillips Chemical, receive substantial tax breaks despite having poor environmental track records.
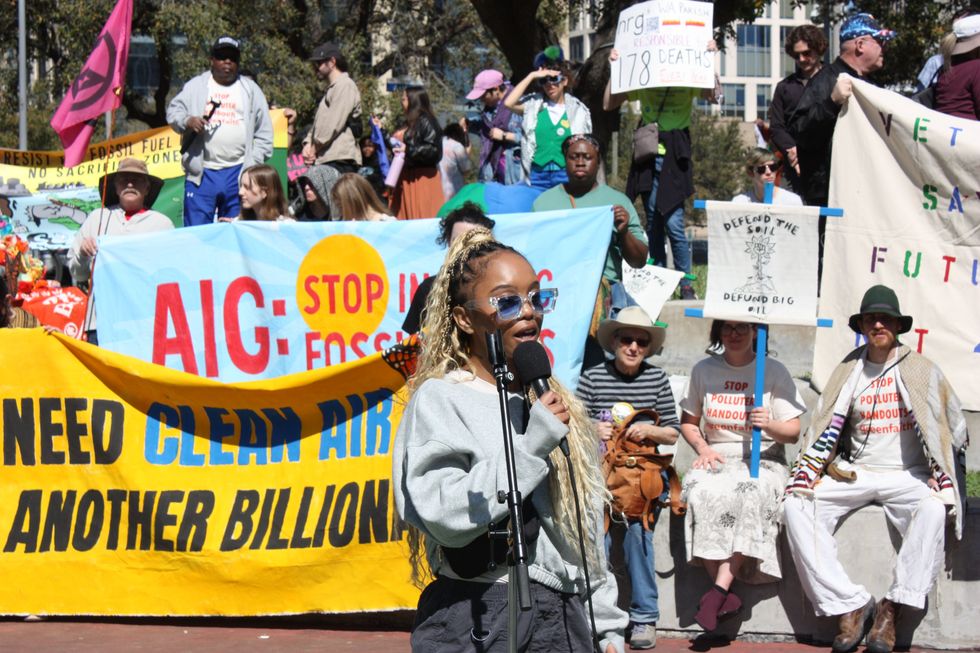
“We have people who are over there who are making these decisions for our community,” said Breon Robinson, organizer for Southwest Louisiana and Southeast Texas at the environmental group Healthy Gulf, motioning toward the conference center. “They see us as scraps, they see us as a sacrifice zone … but we tell them hell no.”
Protesters arrested
After the press conference, hundreds of protestors made their way toward a second public park just steps away from the CERAWeek convention center. Some held banners with messages like “No faith in fossil fuels” and “We need clean air, not another billionaire.” Others held cardboard cutouts or piñatas made in the likeness of oil and gas executives. Alexis Ramírez, Corpus Christi resident and elementary music teacher, played music during the march.
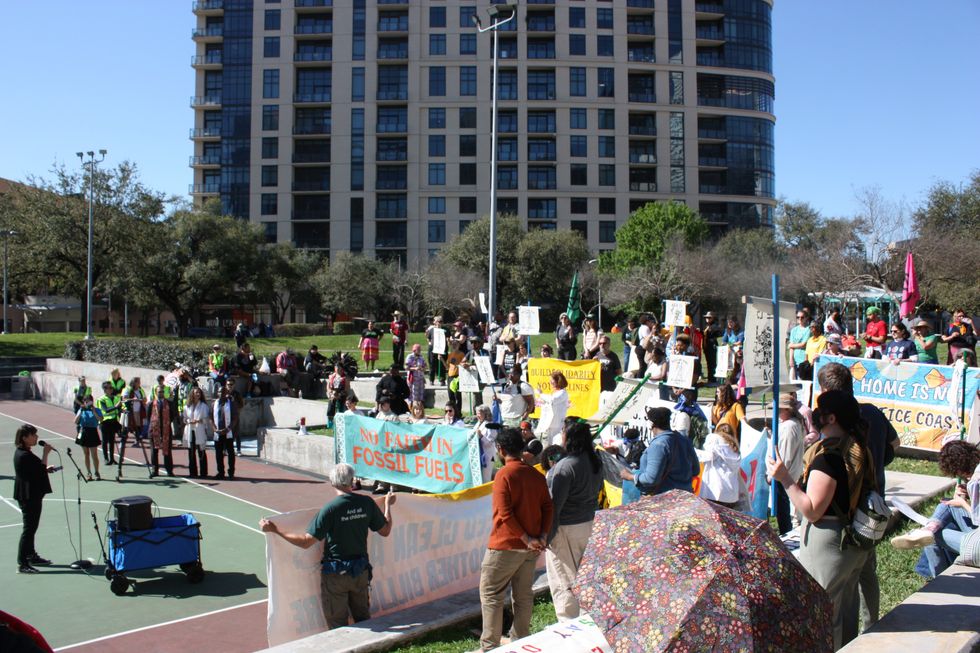
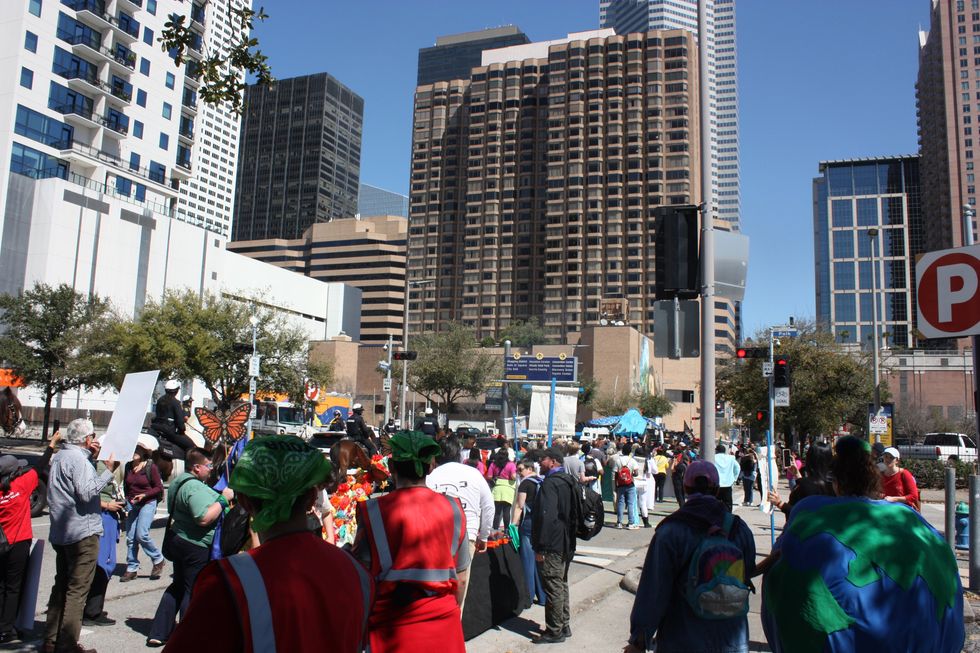


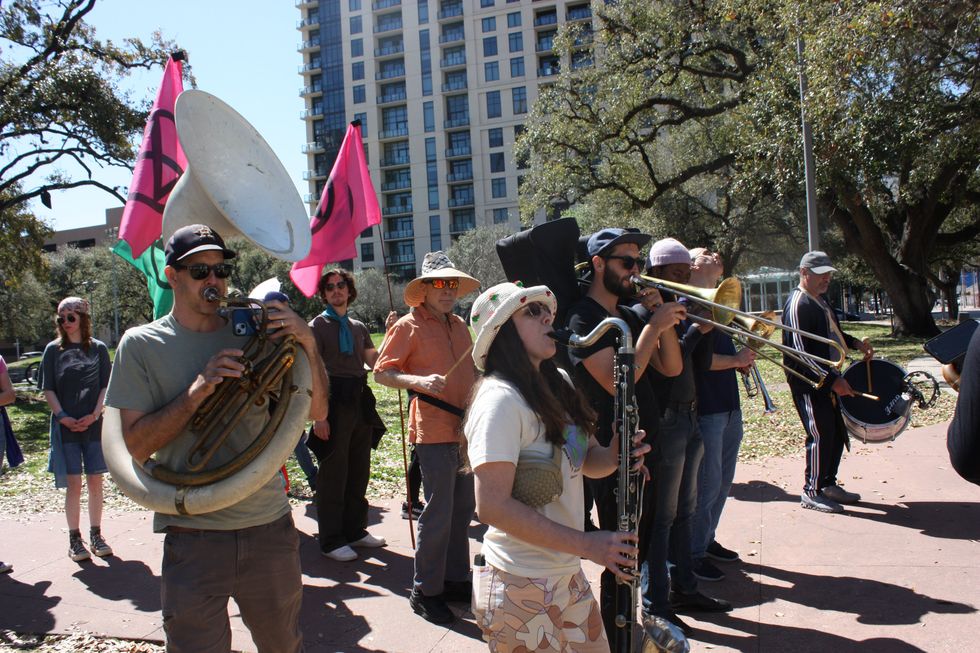
“I want to spread the joy of music and the power of music through this protest for my students,” Ramírez said. “They’re going to be our doctors, our teachers, whatever they are, they are going to take care of me and you when we are old. And that’s why I’m here, to take care of them.”
The protest was escorted by dozens of police officers in vehicles and on horseback. As the protesters neared the convention center the group split in two as eight individuals interlocked arms briefly in front of traffic. After asking them to move and pressing forward with their horses, police officers arrested eight protesters, including Arellano of Fenceline Watch.
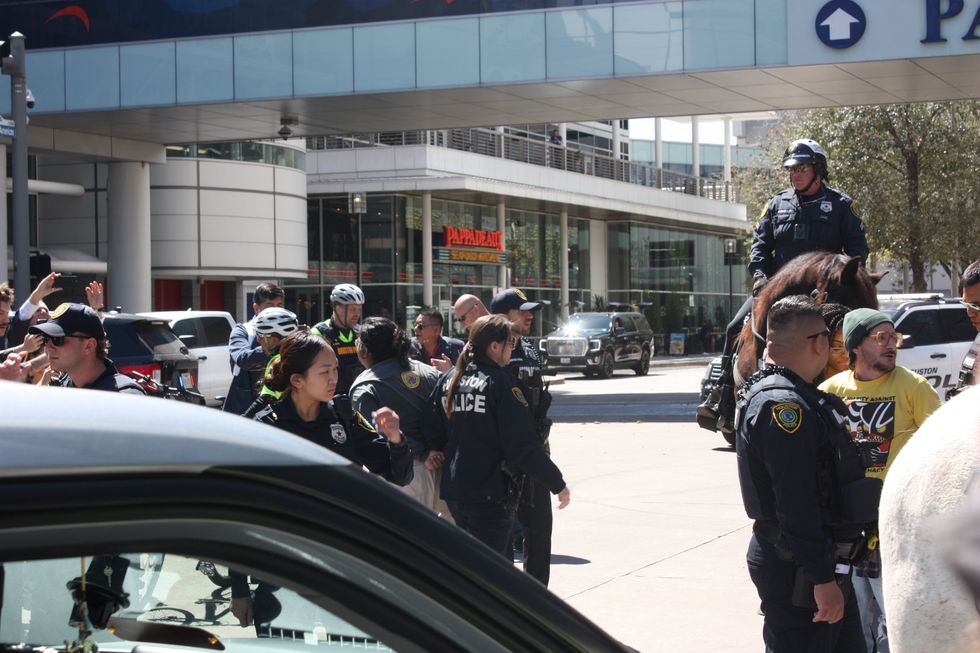

While many groups said their concerns existed before the presidential administration change, some expressed worry that Trump’s policy shift toward “energy dominance” will further exacerbate environmental risks with promises of fast-tracked permitting processes and the repeal of pollution and climate rules.
Despite these shifts, local activists are still calling for a just energy transition.
“We get there together, or we never get there at all,” the protestors sang. “No one is getting left behind this time.”















