Fracking may alter fat cells: Study
A look at chemicals commonly found in fracking wastewater finds sign that they are influencing cell growth.
Chemicals released by fracking may increase the size and amount of fat cells, even at low concentrations often released into the environment, according to a new study released today.
Low concentrations of frack waste triggered robust activity in fat cells
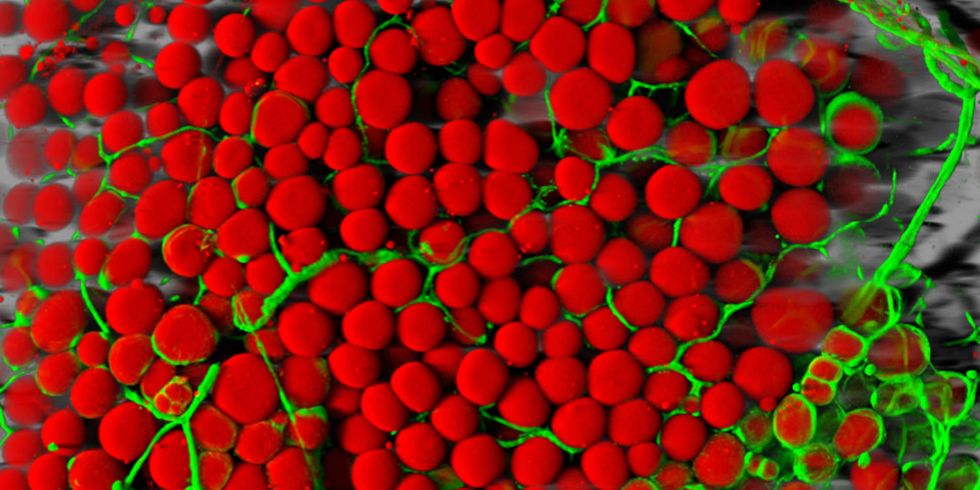
Researchers at Duke University and University of Missouri exposed cells to 23 chemicals associated with fracking, wastewater and surface water contaminated with wastewater from fracking sites. They found that exposure at both low and high concentrations of the chemicals and water samples led to changes in the fat cells, according to results published today in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
"One of the perhaps surprising things about this is that we actually saw effects diluting the water," said lead author Chris Kassotis, a postdoctoral researcher at Duke's Nicholas School of the Environment.
The effects at low concentrations were unexpected, but they suggest that at environmentally-relevant levels, fracking chemicals may interfere with how fat cells are regulated.
The changes were comparable to effects of a pharmaceutical known to increase fat cells, Kassotis said.
The experiment produced "pretty high levels of activity," he said, "at low concentrations."
Examining fracking's interplay with endocrine disruption

The study also looked into underlying mechanisms triggering the cell growth. Approximately half the cells were found with an activated receptor called "PPAR-gamma."
The PPAR-gamma receptor promotes fat cell development. When switched on, dormant fat precursors cells awaken. But given that this only happened in about half the cells, researchers suspect other undetermined underlying causes are at play.
The study was a follow-up to earlier work by Kassotis and others looking at links between fracking and endocrine disruption. In one study, Kassotis exposed pregnant mice to fracking chemicals and found that the offspring had higher weights for the first few weeks of life, prompting a deeper look into fat cell development.
The study published today was a cell study, so there is not a direct link to humans, yet. But the effects on fat cells may be an underlying cause of the increased weights, Kassotis said, and he and others hope to see future research to determine how exposure to chemicals from fracking affect human fat cells.
"We know that the chemicals have negative health impacts," said Susan Nagel, one of the co-authors and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology and women's health at University of Missouri. And researchers regularly find those chemicals in fracking wastewater.
"So it is imperative to examine the health impacts in people near fracking operations," she added.
Fat cell activity from fracking shows need to link studies to human health
Kassotis said he sees some relevance to human health, noting that he has conducted both animal and cell studies, looking at fracking chemicals and endocrine disruptors. Many hormone regulators are comparable between rodents and humans, he said.
Still, it is unclear at what concentrations these chemicals could be harmful to humans, he said.
Hence the need for further studies, Nagel said, pointing to the fact that the most "dramatic effects" came from low concentrations, which are in the range that humans could be exposed to. The published study helps researchers look for effects in humans and can help researchers design precise epidemiological studies, she said.
"This is a completely unresearched area of potential impacts on human health, and if we are contributing in any way to metabolic syndrome in the country with this process then that is of utmost importance," she said.













