Reader response: Opponents of geoengineering misunderstand humanity’s choices
"Without some kind of prompt geoengineering action, climate change will accelerate the damage we are already seeing."
Editor's note: This letter to the editor is in response to EHN's June 10 story Solar geoengineering: Scientists decry a 'foolish' idea.
In recent months, the popular and "soft" scientific media have carried numerous articles opposing research on climate-related geoengineering designed to ameliorate climate disruption. These articles build on a mistaken premise, sometimes explicit and often implicit, that geoengineering strategies are an unnecessary alternative and an excuse to avoid ending fossil fuel use.
Most informed advocates for geoengineering research agree that ending fossil fuel use and associated emissions before 2050 is an urgent necessity to prevent the desolation of Earth as a habitable planet for all life. There is no doubt that a "business as usual" fossil-fuel-based economy will destroy us all.
Geoengineering research opponents ignore the fact that even ending all fossil fuel use tomorrow would still leave the carbon already in the atmosphere, which will continue to cause enormous climate-related harm during at least the next several decades.
The most under-appreciated aspect of the IPCC's January 2019 Report on Global Warming of 1.5C is that even if all emissions decline according to the IPCC's optimistic timeline, global warming will not be limited to 1.5 degrees C. On the contrary, the report projects that Earth's temperature will likely rise well above 1.5 degrees C and remain there for several decades as it slowly declines to 1.5 degrees C by 2100.
Here is the IPCC's key summary figure below. Look closely at the period between 2030 and 2080. Likely temperature levels are above the 2100 target throughout most of this period – our entire lifetimes.
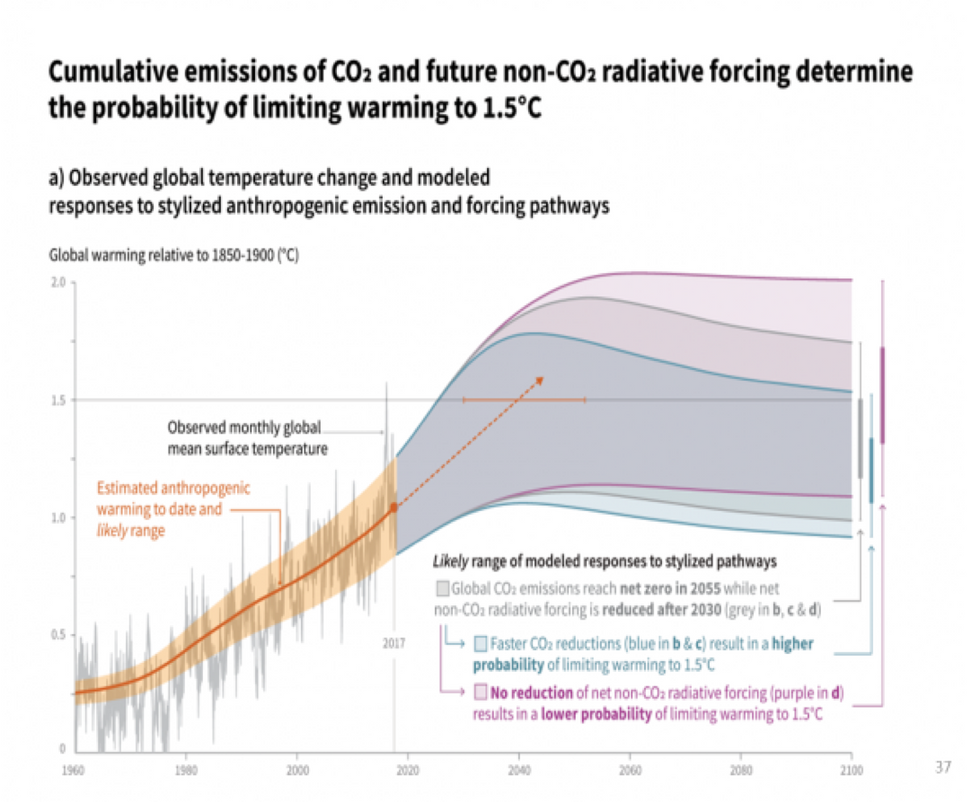
Moreover, we now know that crucial emissions of methane and other non-CO2 gasses have far exceeded the IPCC's target levels for them in the years since the 2017 baseline. And we have every reason to believe these emissions will continue to exceed the IPCC suppositions long past 2030.
Bloomberg Green, like the IPCC, sugar-coats its commentary:
In principle, the goal is simple: Roll this number [carbon emissions] downward by phasing-out emissions until reaching zero. In practice, however, this number continues to rise. Global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels stopped growing from 2014-2016, . . . Increases resumed since then, despite a temporary drop-off during 2020 pandemic quarantines. These emissions need to fall to half their 2010 level by 2030 to keep alive the Paris Agreement goal of limiting warming to below 1.5°C.
There's some help on the way. Dozens of countries, including nine of the 10 largest economies have pledged to zero-out emissions by mid-century. . . . No collective task has ever been more difficult.
Geoengineering needed to stop climate change destruction
The hard reality is that without some kind of prompt geoengineering action, climate change will accelerate the damage we are already seeing: disappearing glaciers and polar icecaps, droughts, extreme flooding, hurricanes, massive forest fires, and destruction of coral reefs and fisheries, food insecurity, and species extinction.
Together these events will cause more mass migrations, ethnic genocides, and frequent civil and international wars, which in turn could cause irreversible damage to human civilization and most life on the planet. U.S. government agencies, including reports by the U.S. Global Change Research Program and testimony by the former Director of National Intelligence, already foresee multiple, serious threats that shape their view of the future.
Geoengineering research might demonstrate that proposed geoengineering projects cannot achieve their aims without unacceptable risks and damage. But only more scientific and engineering research can answer those questions. Humanity must pursue every possible means of minimizing the foreseeable climate disruption of the coming half-century. The alternative is passivity in the face of an incredible amount of human and animal suffering during the coming decades.
Pursuing geoengineering research might also weaken some world leaders' sense of urgency about decarbonization, but that is a questionable hypothesis. Climate-related damage will increase visibly during the coming decades, and the public clamor for action will inevitably increase along with it.
Even if the IPCC's timeline for ending fossil fuel emissions is achievable, by 2100 the disintegration of what we think of as modern civilization could be so great that it won't matter exactly when we succeed in ending fossil fuel use. Much of what we hope to preserve will have been swept away by then.
Sam Bleicher is an Adjunct Professor Georgetown University Law School and author of two "climate future" novels: THE PLOT TO COOL THE PLANET, A Novel, and GUARDIANS OF THE SOLAR SHIELD: EARTH'S CLIMATE MIRRORS UNDER ATTACK 2029-37.
Banner photo credit: redcharlie/Unsplash













