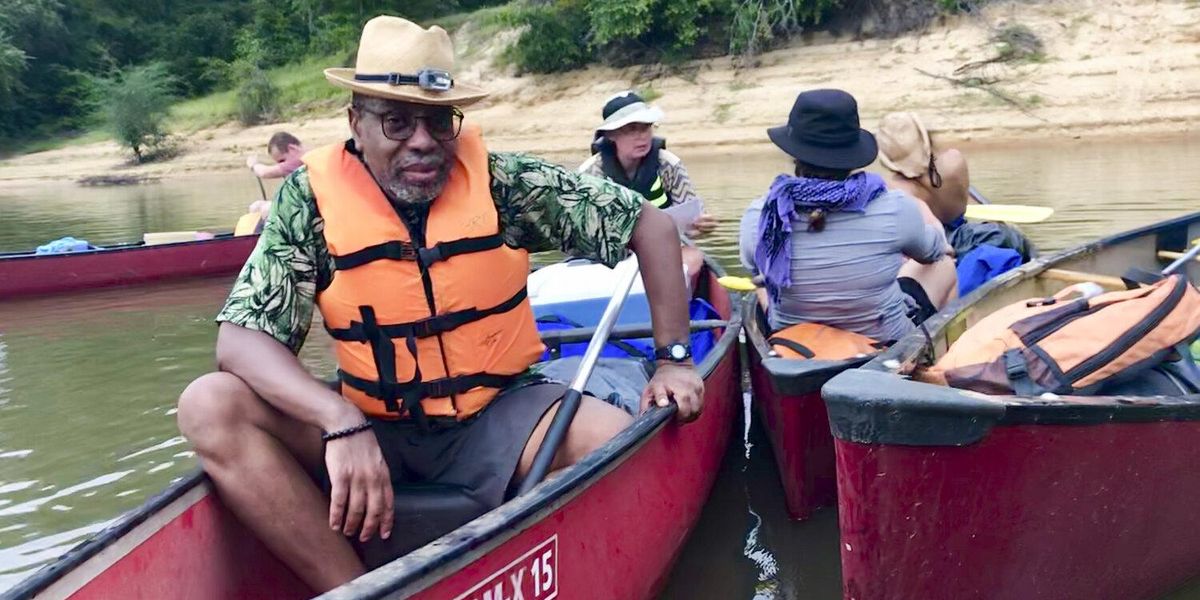
In Georgia, a bold comeback for a dirty river
The South River, my old haunting & hiking ground, is officially endangered but battling back
Last month, I saw an old friend show up in a surprising place.
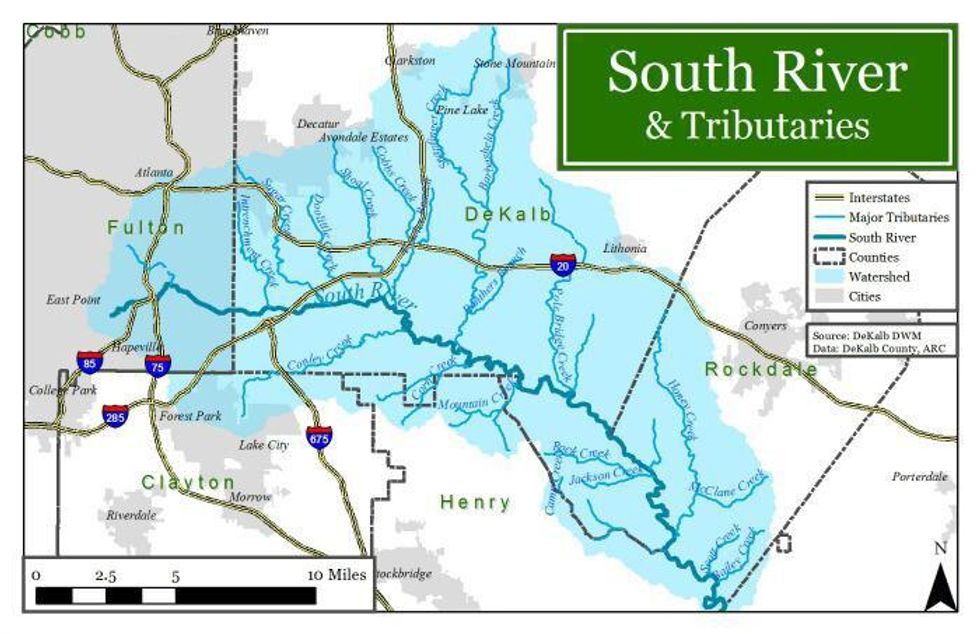
I used to escape the home office each day with a walk along the South River near my former home in Conyers, Ga. To my shock, the group American Rivers added the South River to its annual list of the ten Most Endangered Rivers.
The designation is both good and bad news for the South River and its defenders, bringing stigma but also leverage to improve the river's condition.
South River's toxic load
South River Watershed Alliance
The river itself is a mix of good and bad, so we'll get the bad out of the way first: The South has its origins in small streams just south and east of downtown Atlanta. There, aging industrial parks, truck terminals, most of metro Atlanta's biggest landfills, crowded freeways, and one of the world's busiest airports all do their worst to give the river a troubled upbringing.
Just east of the city in DeKalb County, heavy rains frequently overwhelm the sanitary sewage system, giving the river arguably its worst problem. The American Rivers designation highlights DeKalb's battle against state and federal regulators and against a tenacious nonprofit, the South River Watershed Alliance. Citing the high costs of cleaning up its own mess, the county is in defiance of a Federal consent decree to do so.
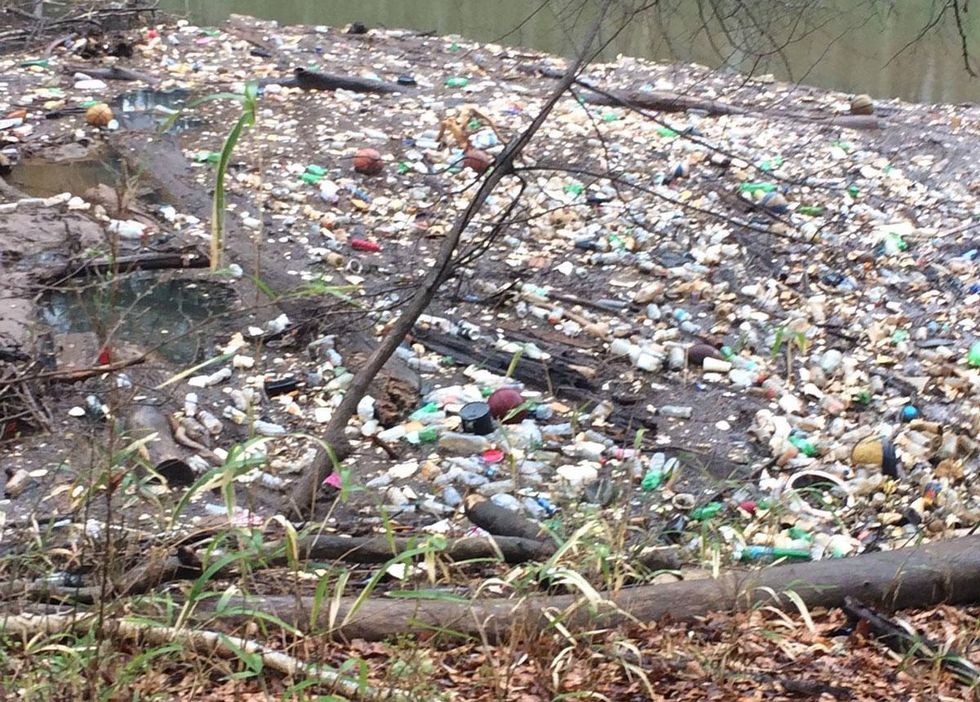
Plastic pollution

South River Watershed Alliance
Then, there's the plastic. After those heavy rains, the river becomes a highway not just for tree limbs and other natural detritus but for fugitive lawnchairs, picnic coolers and two-liter soda bottles. They come to rest on riverbanks, coves or in boatslips at the 60-mile-long river's outlet at Jackson Lake.
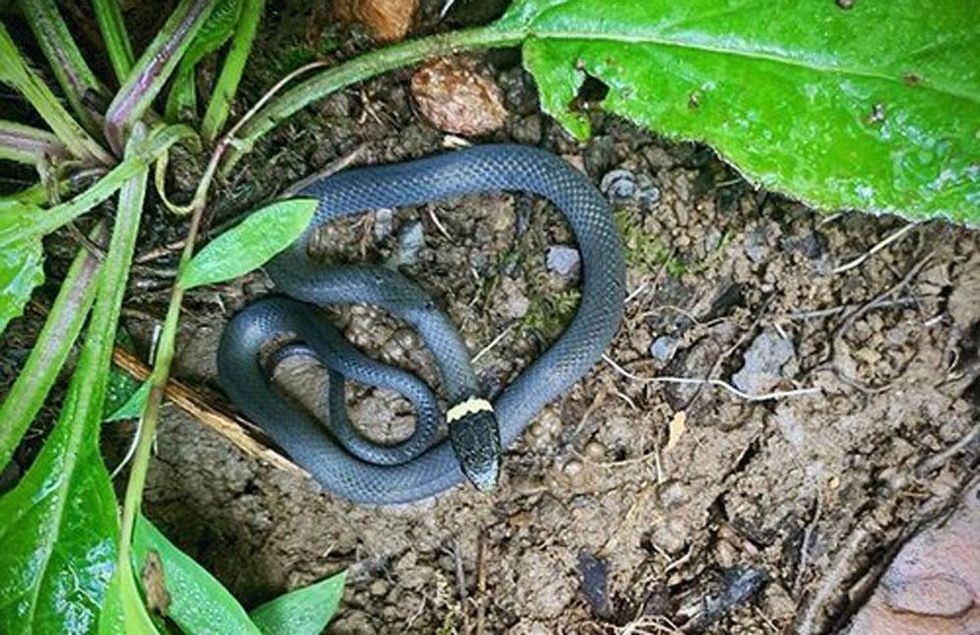
A wild river, full of life

South River Watershed Alliance
But even through the harmful human impacts, nature rules the day, and more people are beginning to notice. Memorial Day means pink-and-white rhododendrons are ending their riverside rule and, in sunny spots, wild blackberries are there for the picking.
Kingfishers patrol their riverine habitat, sign the river is well-supplied with fish. Blue herons offer another sign of a comeback, but they're still not too keen on sharing the river with more and more humans.
At dusk and beyond, when the soothing sound of the barred owl turns frantic, it's a signal that they're eager to either mate or kill something.
Hiking haven
Hikers and cyclers are out to enjoy it all on a network of paved and dirt trails that will, if you've got the time and proper footwear, carry you literally to the next time zone, 75 miles west in Alabama. The PATH Foundation has built a network of government, corporate, and citizen supporters to bring North Georgia to nature, and vice versa.
Riparian comeback

So how does the tiny South River measure up against the other Most Endangered Streams?
This year's list includes a couple of hardy perennials at the top: No. 1 is the Lower Snake River, stuck in a decades-long effort by Native tribes and environmentalists to force the takedown of four aging hydroelectric dams that have devastated salmon runs.
In second place is the Lower Missouri. Upstream dams and an extensive levee system make the Missouri one of the most altered major waterways in the U.S.
Others include the Ipswich River in Massachusetts, a threatened drinking water source; and Minnesota's legendary Boundary Waters canoeing area, jeopardized by a nearby copper mining proposal.
But who doesn't love a riparian comeback? I'm no longer able to visit the South River, but I can still hear the rushing water, and the love-or-death owls.
Peter Dykstra is our weekend editor and columnist and can be reached at pdykstra@ehn.org or @pdykstra.
His views do not necessarily represent those of Environmental Health News, The Daily Climate, or publisher, Environmental Health Sciences.
Top photo of the South River canoeists courtesy South River Watershed Alliance













