Peter Dykstra: The greatest retired US government hero
For almost 42 years, he’s never exactly retired.
But in addition to his exemplary post-White House life, Carter’s Oval Office stint was an extremely busy one for environmental politics.
- The nation’s first acknowledged toxic waste disaster was discovered on his watch in the Love Canal neighborhood of Niagara Falls, New York. Carter responded by visiting, and by championing, the well-intended Superfund cleanup program. Superfund languished for years, however, with legal stonewalling thwarting virtually every one of the program’s 1,000+ sites.
- The Alaska Lands Bill was an instant success, setting aside 222 million pristine acres — the largest chunk of protected land in American history.
- In 1979, a reactor at Pennsylvania’s Three Mile Island complex nearly melted down. Carter’s Naval Academy training was in nuclear physics,* which served him well in addressing the near-disaster. But Three Mile Island stopped the nuclear power industry in its tracks.
And Carter became a moderately successful evangelist for energy efficiency, preaching basic common sense on gasoline after an OPEC embargo caused long gas lines and outlandish price hikes to $.90 (!!) a gallon. In July 1979, Carter scolded the nation in what became known as the “malaise” speech, even though the word “malaise” was never used in the speech.
So, on energy and environment, let’s give Carter an “A” for effort and a “C+” for accomplishment.
"Passive" solar symbol
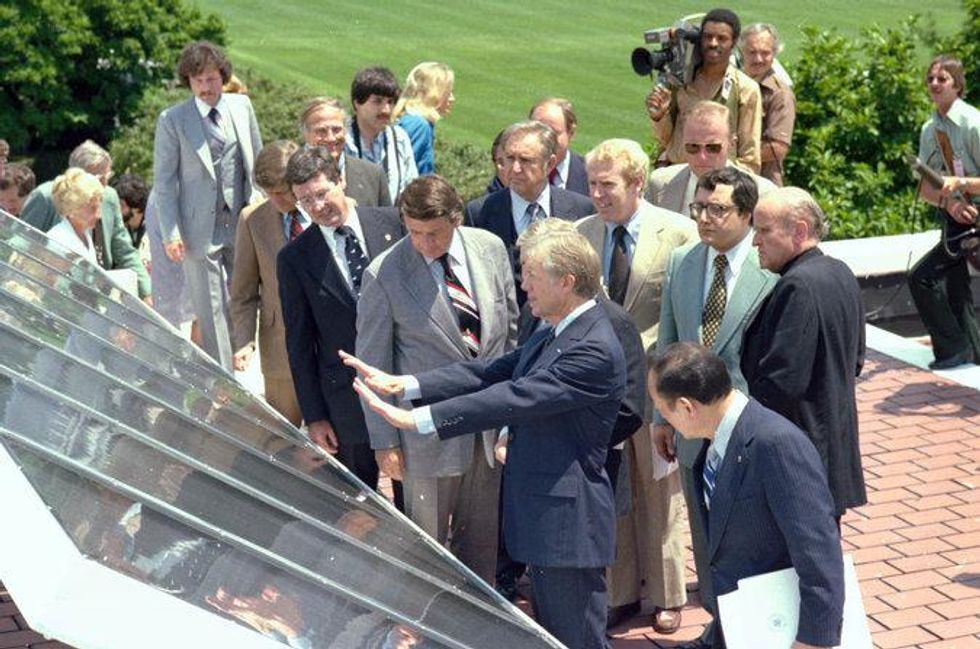

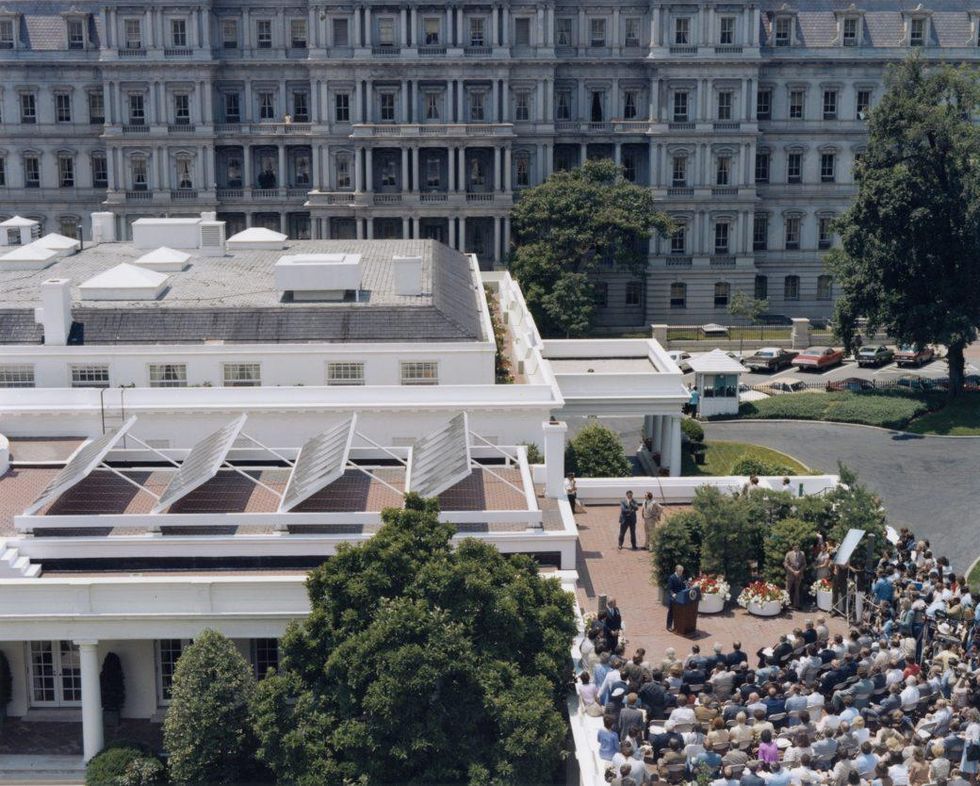
He was ahead of his time in some ways. In 1979, a year before his rout by Ronald Reagan, he held a news conference on the White House roof.
Carter unveiled 32 passive solar panels prepared by the new Department of Energy. They would circulate sun-heated water into the White House to augment its hot water heaters.
In other words, “passive” meant minimally useful as anything but a symbol. But as a symbol, Carter had a powerful one.
“In the year 2000 this solar water heater behind me will still be here supplying cheap, efficient energy,” he said. “A generation from now, this solar heater can either be a curiosity, a museum piece, an example of a road not taken, or it can be just a small part of one of the greatest and most exciting adventures ever undertaken by the American people; harnessing the power of the sun to enrich our lives as we move away from our crippling dependence on foreign oil.”
How did that work out?
Well, President Reagan quietly had the panels removed shortly after taking office.
And as for that “move away from our crippling dependence on foreign oil”— President Biden in Saudi Arabia this very week making nice over oil prices and supplies.

Pardon the lack of humility, but here’s where I come in. In 1990, I was wrapping up my hellraising days at Greenpeace.
As President George H.W. Bush waged a strategic oil war against Iraq following its takeover of oil neighbor Kuwait, I wondered about the mysterious disappearance of those 32 solar panels and filed a Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request to locate them. I got the kind of quick response that doesn’t often happen anymore under FOIA. The panels were in storage in a vast General Services Administration warehouse outside Washington, DC.
If you’re thinking of the last scene of “Raiders of the Lost Ark,” you’d be right. One of the panels was destroyed by a surplus federal desk that had been tossed on top of – and through – it.
Many of the panels ended up at Unity College, a small environmental studies school in Maine. Unity used a rule that allowed educational institutions to claim unused federal property.
Since Jimmy Carter left the White House in 1981, Ronald Reagan’s been the best horse riding ex-Prez; Bush the First, the best skyjumper; Bill Clinton the best near-First Gentleman; Bush II the best brush-clearer; Obama has the best jump shot. And let’s give credit where credit is due: Trump is the best golfing, anti-democracy blowhard.
But as he nears his 98th birthday on October 1, Jimmy Carter is simply the best in so many ways.
*Nuclear Physics training aside, Carter was a member of that eclectic group, along with President G. W. Bush and Homer Simpson, that can’t pronounce “nucular.”
Peter Dykstra is our weekend editor and columnist and can be reached at pdykstra@ehn.org or @pdykstra.
His views do not necessarily represent those of Environmental Health News, The Daily Climate, or publisher Environmental Health Sciences.