How coastal communities can prepare for the challenges of storms and rising seas
What can a small or medium sized community do to be better prepared for risks of storms and rising seas?
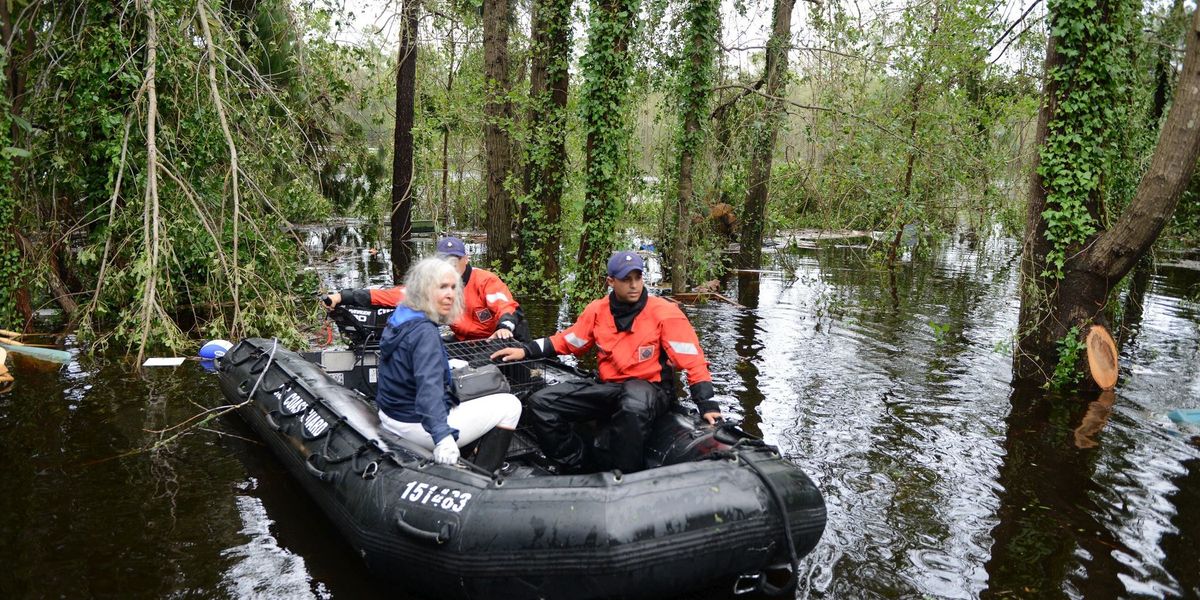
Major coastal storms commonly kill hundreds of people and wreck homes, businesses and communities.
The three major storms in 2017 – Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria – generated some $265 billion in damages and over 3,000 deaths. In 2018, Hurricanes Michael and Florence caused $50 billion in damages and over 100 deaths. Scientists predict that, as the climate warms, coastal storms will become more intense.
A warmer climate also is melting glaciers and ice sheets and accelerating the rate of sea level rise. Global sea level is likely to rise between 2 and 4 feet by 2100 and continue rising for centuries after that. Unfortunately, along the American coast, the rise in sea level could be 15-25 percent higher due to land subsidence and ocean dynamics.
These higher sea levels will drive future storms farther inland, expanding risks to life and property.
Novel challenges posed by coastal flooding
Storms and rising seas pose some novel challenges for coastal communities. For example, most past coastal flooding has been temporary in that storm surges recede and random in terms of where a storm hits the coast. Factoring in sea level rise requires thinking about permanent flooding that occurs along the entire coast.
Rethinking local planning to add sea level rise requires extending the time horizon for planning from the common 5-20 years to more like 50-100 years. This is especially important for decisions related to infrastructure and public facilities. Novel legal issues involving ownership of land at risk of rising seas, including potential "takings" claims, need to be considered.
Communities also face novel financial risks from the one-two punch of coastal storms and rising seas. Damages to coastal property, and eventual permanent inundation, will reduce property tax revenue and the resources available to recover from a major storm. Removing buildings abandoned to the sea can be another unexpected cost.
Steps small communities can take to manage flood risks
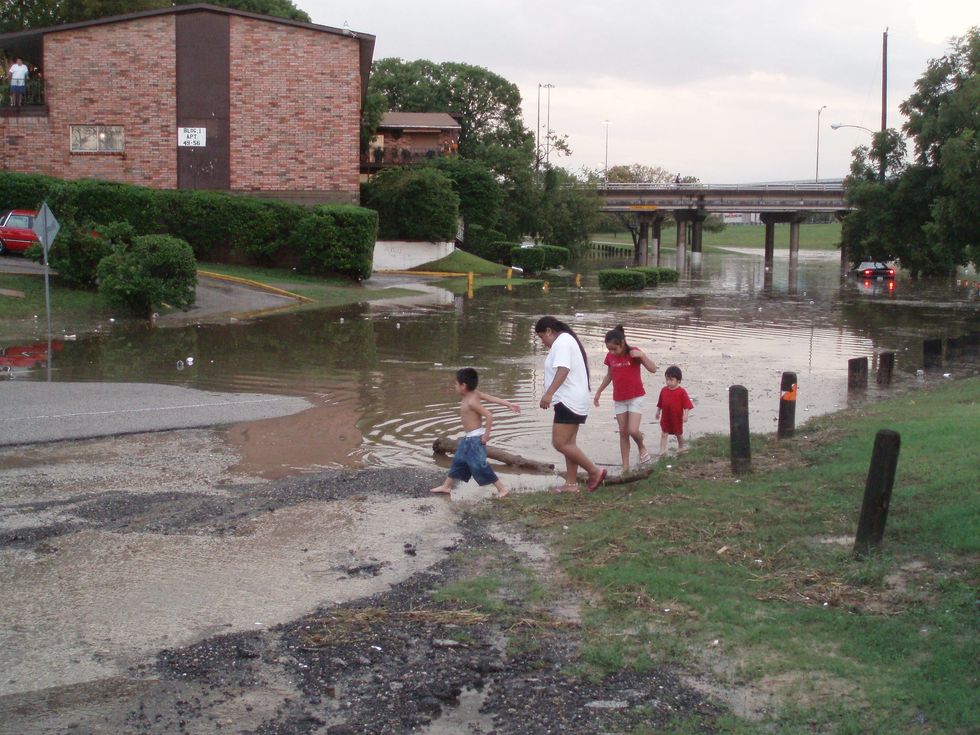

Flooding in Houston's White Oak Park. (Credit: mmmH/flickr)
What can a small or medium sized community do to be better prepared for risks of storms and rising seas?
Once a community decides to engage coastal flood issues a key first step is to assess risk and educate the public. States, Federal agencies, and local universities are all good sources of information about the storm and sea level rise risk that a community faces. Education can include teaching kids about these flood risks in school, engaging the business community, and disclosing flood risks to coastal property.
Communities can also develop or revise plans for managing storms and sea level risks. Key ideas here are to plan for both storms and rising seas and to adopt a planning horizon in the range of 50–100 years. In addition, local plans need to be coordinated with neighboring jurisdictions and give special attention to the needs of low income and minority communities.
One of the most challenging aspects of planning for storms and rising seas is evaluating tradeoffs between structural protection (e.g., seawalls) and phased relocation of homes, businesses, and infrastructure to higher ground as seas rise. Communities need to consider short and long-term costs of these options, impacts on the ecological and recreational values of the coastline, and the social and psychological consequences for people in the community.
Communities have a range of regulatory and financial tools to implement coastal flood plans. For example, communities can use regulatory tools to limit new development in areas identified as at risk of permanent inundation by rising seas.
Communities can also use tax incentives to encourage owners of property at risk of rising seas to gradually step back from risky areas.
Support national investment in safer coasts
Although communities can make progress in preparing for future coastal flood risks acting alone, in many places the scale of the problem and the complexity of solutions will require new and substantially expanded national programs.
What might a new national program look like?
As a first step, the Federal government needs to reform existing programs for flood insurance and disaster relief. The flood insurance program encourages people to stay in risky coastal places that will eventually be inundated by rising seas. Disaster programs do a good job of providing relief after a storm but need to refocus on smarter investments to prepare for and avoid disasters in the first place.
Significant new federal funding is needed for grants for state and local governments to plan for coastal storms and rising seas and for implementation of the plans. Plans need to reflect local needs and conditions but be guided by national frameworks to allocate funding to areas with the greatest needs and to protect the interests of low income and minority populations.
Storms and rising seas are a threat to more than just communities. The federal government needs to work with state and local governments to protect or relocate critical infrastructure, such as military bases, transportation assets, and water facilities. In addition, ecosystems, such as beaches and coastal wetlands, need space to migrate landward as seas rise. The federal government needs to work with states and communities to fit together the puzzle of how best to manage critical infrastructure and ecological resources as coastal communities plan for future flood risks.
Finally, coastal homeowners need help to avoid devastating financial losses as growing flood risks drive down property values and the federal government is best equipped to provide this financial assistance. For example, the federal government could buy risky property well ahead of rising sea levels. Current owners could stay until the property becomes unsafe paying rent but not flood insurance premiums. The federal government would pay local property taxes.
Given the likely increase in coastal storm intensity and steadily rising sea levels, a new federal investment in safer coasts seems sure to happen in time.
A harder question is whether national support will arrive in time to reduce the costs, and toll in lives, that will come with more extensive and permanent flooding.
Communities along the coast can advance their own interests, and those of the country as a whole, by calling on federal agencies and Congress to step up to this important challenge.

Jeff Peterson worked at the Environmental Protection Agency, US Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works, and White House Council on Environmental Quality. His book "A New Coast: Strategies for Responding to Devastating Storms and Rising Seas" will be published in November.