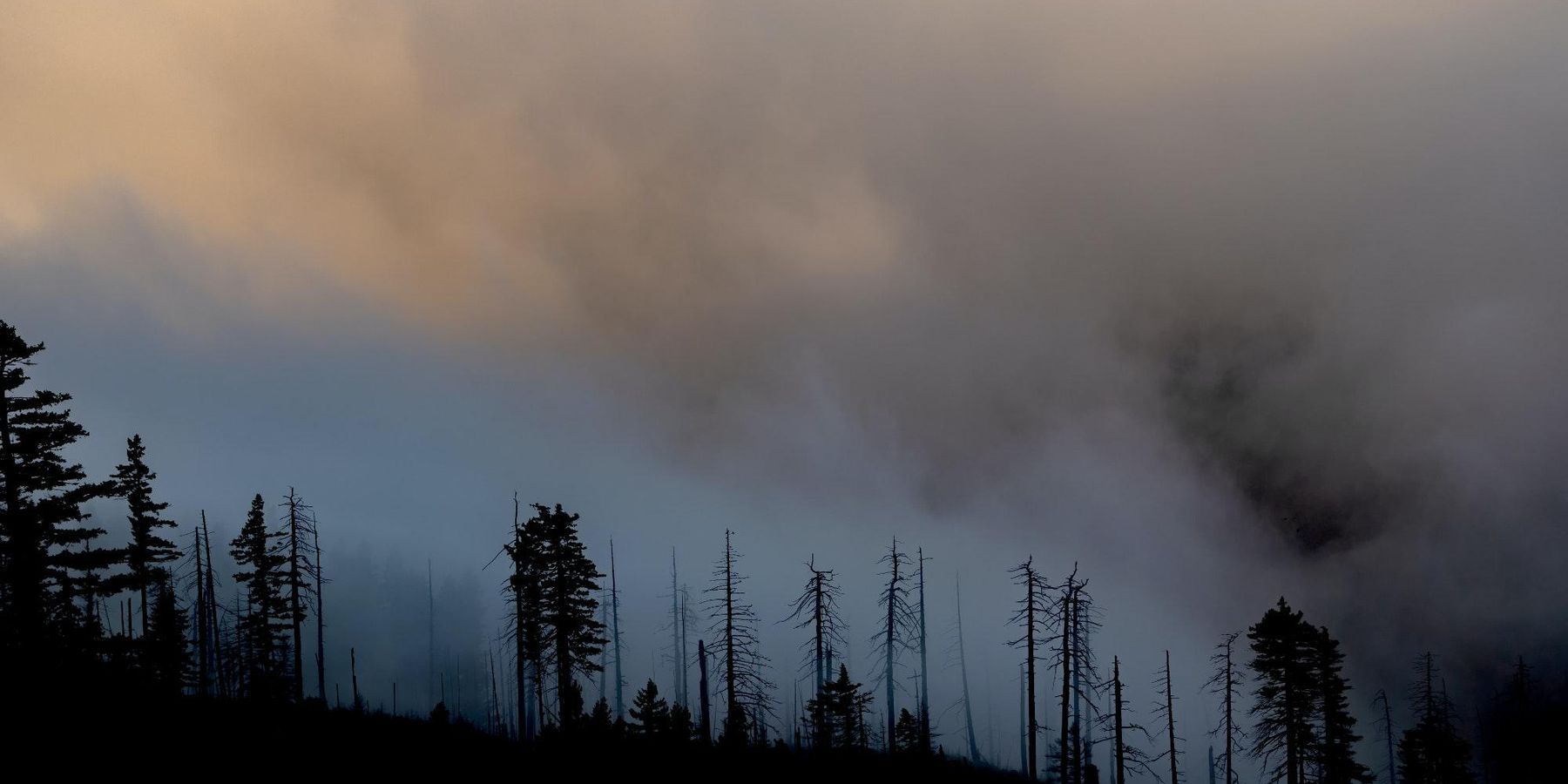
Global study: Wildfire smoke kills people in cities far from fires
Guatemala, Thailand, and Paraguay had the highest proportion of estimated annual deaths from wildfire smoke.
Wildfire smoke causes more than 33,000 deaths a year across 43 countries, according to a new global study.
While previous studies estimated premature deaths from wildfires in a specific country or region, authors of a study published Wednesday in Lancet Planetary Health say this is the most comprehensive assessment to-date of global wildfire mortality. The findings come as the smoke from yet another season of record-breaking wildfires in the Northern Hemisphere impacts air quality hundreds of miles away from burn areas.
"Policy makers and public health professionals should raise awareness of wildfire pollution to guide prompt public responses and take actions to reduce exposure," write the study authors.
The study authors first estimated daily fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) concentration using a combination of machine learning, ground measurements, weather conditions, and chemical transport models. They then cross-referenced those pollution levels with data on more than 65 million deaths from 2000-2016 across 749 cities in 43 countries to get city-specific death estimates from wildfires.
They found that short-term exposure to wildfire PM 2.5 pollution caused, on average, 33,150 deaths a year in the countries looked at in the study, with an estimated 6,993 cardiovascular deaths and 3,503 respiratory-related deaths a year.
Of the countries studied, Guatemala had the highest proportion of estimated deaths from wildfire smoke, followed by Thailand and Paraguay. The authors note that all the mortality data used in the study comes from cities, and that the study is not a comprehensive look at global mortality; for example, although wildfires have burned more than 40 million acres in Siberia this summer, no Russian cities were included in the study.
Far-reaching impacts of wildfires

Wildfire approaching South Lake Tahoe, September 1, 2021. (Credit: The National Guard/flickr)
Lead author Yuming Guo, professor of global environmental health and biostatistics at Monash University, told EHN that he was surprised to see that citizens from certain countries that don't have frequent wildfires, like France and Germany, were still harmed from wildfire smoke.
PM 2.5 refers to particles that are 2.5 microns or smaller in diameter—for reference, a human hair is about 70 microns wide. Because of their small size, these fine particles can travel deep into the lungs, where they can damage airways and enter the bloodstream. Children, infants, older adults and people who already have heart and lung conditions are especially at-risk from PM 2.5 pollution.
While wildfires are far from the only source of PM 2.5 pollution in cities, the study authors found that PM 2.5 exposure from wildfires was more deadly, and longer-lasting, than fine particle pollution from other urban sources. They suspect that's in part because of the chemical makeup and smaller size of the particles in wildfire smoke.
Wildfire smoke also contributes to suicide, diabetes, renal diseases, and other conditions, said Guo. The study authors suggest that future research should look at the mortality data by age, sex, and other factors to better understand who is most vulnerable.
Climate change is worsening wildfires by making wildfire-prone parts of the world, like California and Australia, hotter and drier.
Banner photo credit: Chris LeBoutillier/Unsplash