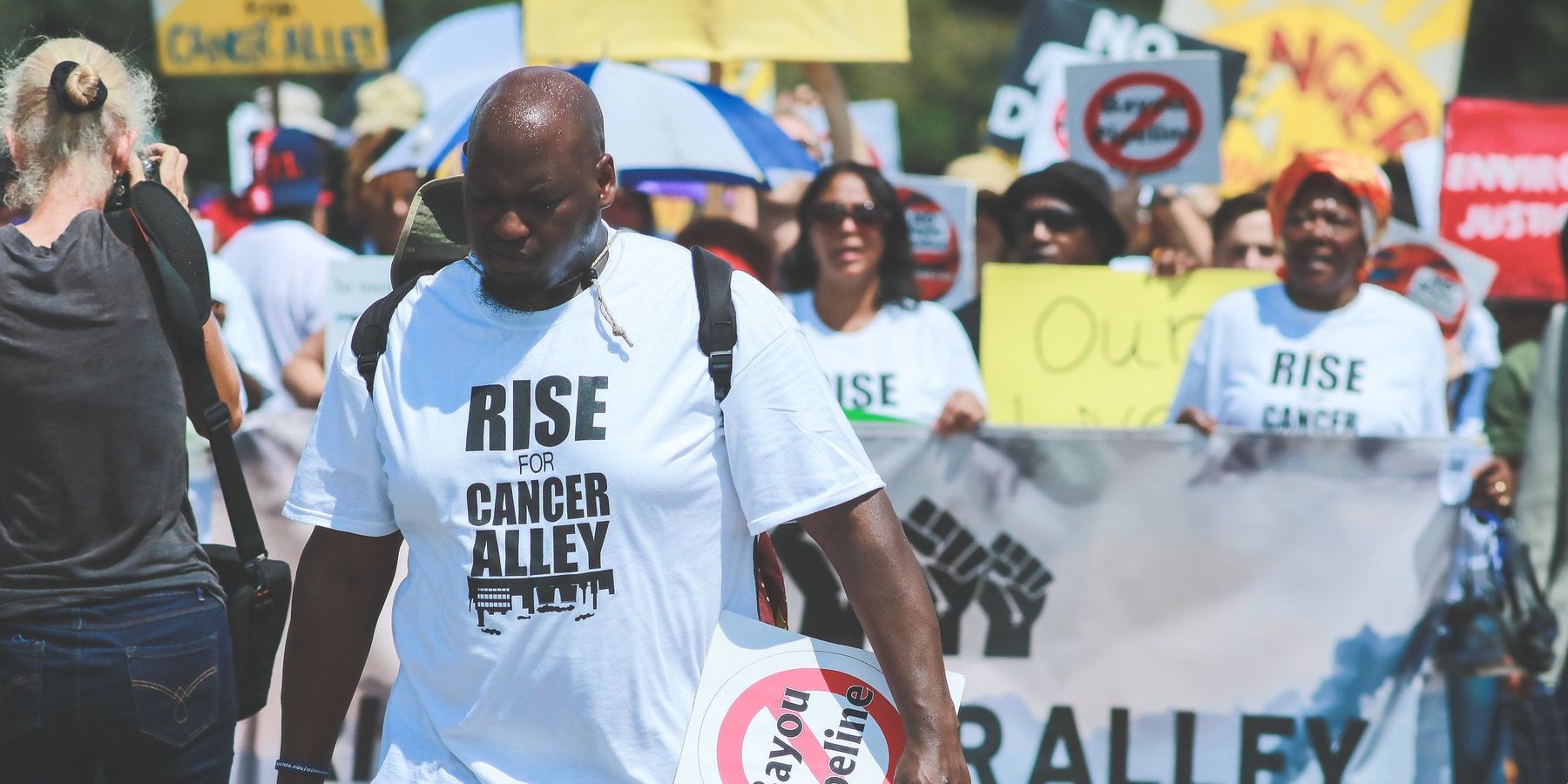
“Cancer Alley” residents exposed to more than the lifetime exposure limit for cancer-causing compound: Report
"We are sick and tired of being sick and tired."
HOUSTON – Louisiana communities are experiencing up to 1,000 times the lifetime exposure limit for the cancer-causing compound ethylene oxide, according to a new study published in Environmental Science and Technology.
In February 2023 Johns Hopkins University researchers measured ambient ethylene oxide in one of the most polluted portions of Louisiana, often called the “Cancer Alley” of the United States. The 85-mile stretch of land along the Mississippi River from Baton Rouge to New Orleans is lined with more than 150 petrochemical facilities, and previous studies have found most residents along the 85-mile stretch are in the top 10% of exposure to air toxics related to cancer and are more likely than people that live elsewhere to develop prostate, lung and breast cancers. The burden of cancer-risk compounds is higher for communities of color.
The new report found ethylene oxide measurements were nine times higher than previously estimated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The EPA notes that life-time cancer risk should not exceed 10.9 parts per trillion, yet the study measured an average of 31.4 parts per trillion. In some parts closest to facility fencelines, the number grew to 140 parts per trillion.
“Accurate measurements of ethylene oxide are needed to understand exposure and cancer risks for communities near to petrochemical facilities,” said lead researcher Peter DeCarlo of Johns Hopkins University. “We encourage state, local and federal agencies to prioritize accurate emissions data to properly estimate risks to communities and protect public health and the climate—in Cancer Alley and beyond."
Ethylene oxide is a colorless gas used in petrochemical facilities to make other chemicals and resins. Considered a known carcinogen by the EPA, ethylene oxide poses substantial health risks when inhaled, and it has been linked to blood, lymph and breast cancers to those exposed.
"We are sick and tired of being sick and tired," said Sharon Lavigne, founder and director of RISE St. James, an environmental justice organization dedicated to opposing petrochemical development in the St. James Parish. “We're flat-footed, exhausted from enduring these health risks and demand immediate action to ensure the safety of our neighborhoods."
Along the same coast as “Cancer Alley” is Houston. Self-titled the petrochemical capital of the nation, it is estimated to have more than 600 petrochemical facilities. The city has struggled with air monitoring in the past, and was awarded $500,000 to increase air monitoring of ethylene oxide and other chemicals last year.
Concentrations of ethylene oxide are expected to drop in the future according to the EPA. In April of this year the EPA updated its regulations related to hazardous air pollutants that aim to reduce cancer risk and air pollution at 200 chemical facilities. The agency is targeting six cancer-causing compounds, including ethylene oxide. Nearly 24% of the impacted facilities are in Louisiana and 40% are in Texas.
*Editor’s note: Bloomberg Philanthropies Beyond Petrochemicals campaign did provide funding for this report. EHN does receive some funding from Bloomberg Philanthropies.













