Dykstra: A corpse in a barrel in a drying reservoir
And other climate change tales for our age
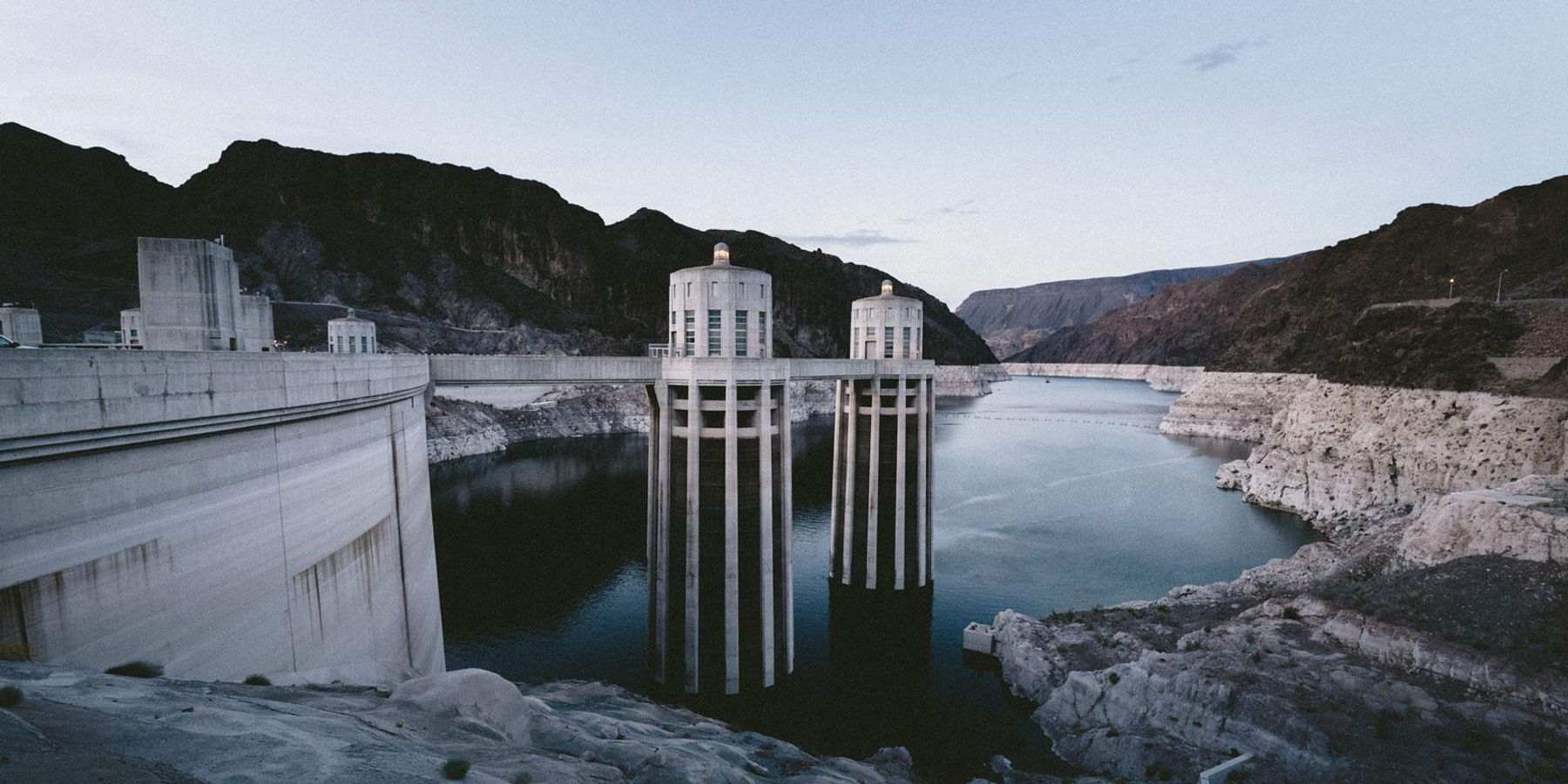
A grim story about human remains found in a barrel exposed by the receding shoreline of Nevada's Lake Mead caught my eye this past week.
For me, it had all the elements: I grew up in a North Jersey town known for housing a few Mafia celebs, like Willie Moretti, the real-life inspiration for The Godfather’s legbreaker, Luca Brasi.
A few miles away were the heavily-polluted Meadowlands, a once-gorgeous wetland that had become, among other things, the alleged final resting place of countless Mafia debtors, rivals, and no-account Goodfellas.
So when drought-parched Lake Mead gave up the skeletal remains of a potential Western wiseguy, I was fascinated.
Lake Mead drought
Lake Mead is in desperate shape. Along with Lake Powell, upstream on the Colorado River, Mead is the key to prosperity for the booming cities, suburbs and farms of the desert Southwest – Arizona, Southern California, and, of course, Las Vegas. In addition to the unfortunate guy in the barrel, decades of overuse capped off by several years of brutal, climate-driven drought has exposed an intake pipe for Southern Nevada’s 2.2 million people.
They’re running out of water. Putting megacities like Phoenix and Vegas in a desert was never a good idea. They were always destined to run out of water, some day. But the rampant growth and a years-long, killer drought have made the crisis immediate.
And with the corpse-in-a-barrel story, we have one more link between climate and popular culture: The Sopranos meets fossil fuels.
It hardly made a wave, thereby joining the long rap sheet for climate change’s impact on our culture. Mostly, it’s things we’re losing.
Climate change and wine

A California vineyard
Winecountry Media, via flickr
From Bordeaux to the Napa Valley, vineyards are in trouble. Bordeaux’s quarter million acres of vines face “a slow but simmering” climate crisis, according to Wine Enthusiast magazine. Increased temperatures, more frequent damaging storms and more can have a big impact on the sensitive grape, increasing the alcohol content in some varieties by 10% or more.
In California’s Napa Valley, frequent wildfires have scalded multi-million-dollar vintages. Other vintners who thought they were spared by the flames were felled by the smoke, which either ruined the taste of America’s priciest wines, or blackened the grapes to make the costliest raisins in history.
Insurers have also turned the screws on California wineries, either jacking up premiums, limiting coverage, or cancelling policies outright.
Changing seasons
Phenology is the science of measuring plants’ and animals’ responses to long-term changes in weather and climate. (Note: phenologists get really upset when their work gets mixed up with that of phrenologists, the sideshow quacks who tell your fortune by reading the bumps on your head.)
As spring replaces winter each year, the time- honored work of the tree tappers yields the sweet sap of sugar maples from the northeast U.S. and Quebec. But researchers tell us two things about rising temperatures and sugar maples: The maple syrup is less sweet, and the trees’ range is slowly moving north. Someday, phenologists tell us you won’t be able to find Vermont maple syrup in Vermont.
Lobsters, fluke and whales
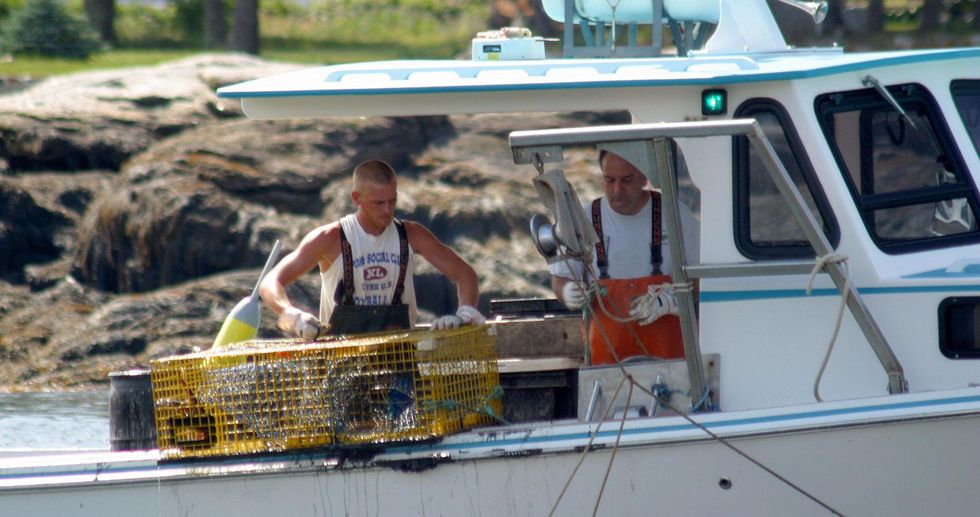

Lobstermen hauling traps on the Maine coast
Offshore, New England lobsters could meet the same fate. Warming waters are chasing much of the food chain northward. Connecticut and Long Island lobstermen are struggling with a dwindling catch; within decades, Maine lobsters may only exist on the state’s license plates.
Summer flounder, or fluke, are a popular target for both sport and commercial fishermen. North Carolina commercial boats hold most of the permits for fluke in the $22 million industry, but they have to motor north to New Jersey to find the fish.
Northern right whales winter and calve off the Georgia and Florida coasts. They feed in summer in the Gulf of Maine. For now. The 300 or so remaining whales are what’s left after centuries of whaling. Ship strikes and entanglement in fishing gear risk taking more But three recent studies indicate that climate change may be a final blow. The zooplankton that are right whales’ primary food source are increasingly scarce in the whales’ northern range.
So many climate stories
I could go on. Ocean wildlife everywhere is under threat from acidification and from the everyday torrent of microplastics. Shorter term, the energy dynamics of the Ukraine crisis have become the newest rationales for keeping the oil & gas infrastructure afloat.
But I guess that’s plenty for now.
Peter Dykstra is our weekend editor and columnist and can be reached at pdykstra@ehn.org or @pdykstra.
His views do not necessarily represent those of Environmental Health News, The Daily Climate, or publisher Environmental Health Sciences.
Banner photo credit of Lake Mead: Jakob Owens/Unsplash