Proposed bill seeks to ban single-use plastic foam products in US
Expanded polystyrene foams are convenient packaging products, but they harm human and ecological health. Two US congresspeople proposed a national ban to address this issue.
Takeout containers from restaurants on the side of the road. Discarded coffee cups floating in rivers. Packing peanuts shipped off to landfills.
Plastic foam products are ubiquitous. Now, a proposed congressional bill seeks to reduce this waste.
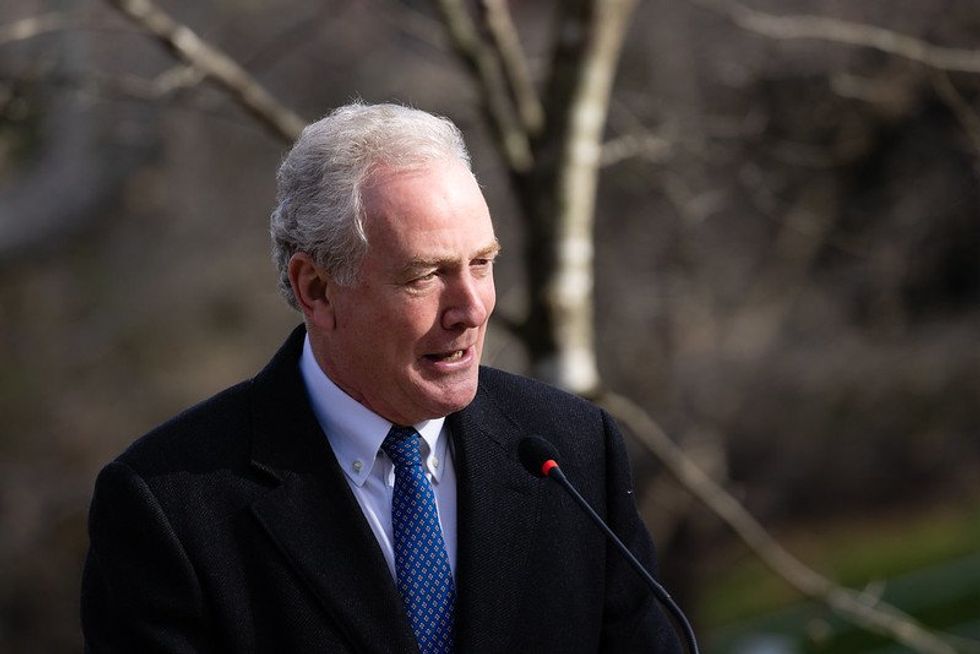
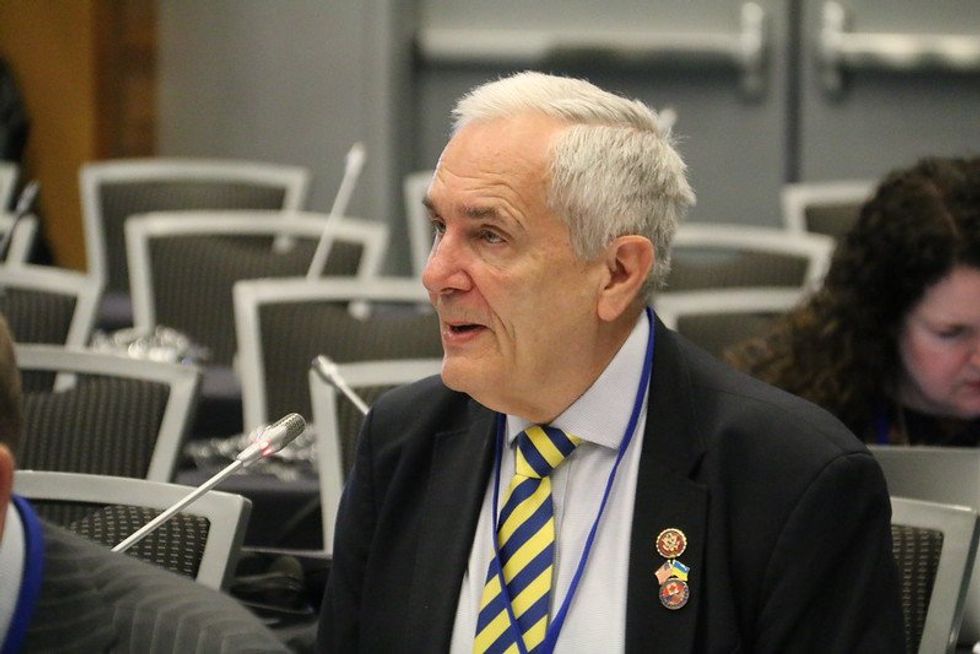
In December 2023, Democratic Sen. Chris Van Hollen and Democratic Rep. Lloyd Doggett jointly introduced the Farewell to Foam Act in both the Senate and House of Representatives. The bill would ban single-use expanded polystyrene food packaging products, coolers and loose-fill packaging products like packing peanuts by January 2026. The legislators cited plastic foam’s environmental and health harms as driving the bill. Though it’s uncertain whether it will move forward, experts and advocates say its introduction is a significant step toward establishing national single-use plastic bans, none of which currently exist in the U.S.


Expanded polystyrene, or EPS—erroneously referred to as Styrofoam, a trademarked material used in construction—is a fossil-fuel-derived plastic comprised of approximately 98% air and 2% plastic beads. This airiness makes EPS desirable for packaging: it insulates food, cushions products and costs little.
However, Van Hollen and Doggett claim the consequences of plastic foam pollution outweigh its convenience. “As trash clutters our waterways, roadsides, and greenspaces, foam doesn’t fully disintegrate. Instead, it ever so slowly degrades into microplastics that pollute our bodies and our planet,” the Texas Rep. said in a statement.
Plastic foam takes hundreds of years to break down. Within that lifespan, it can make a mess.
“Foam is particularly challenging because it’s lightweight and easily breaks up into tiny, tiny pieces, like micro- and nanoplastics,” Christy Leavitt, the plastics director at the ocean advocacy group Oceana, told EHN. These pieces spread across terrestrial and aquatic habitats, leading to massive deposits that animals can mistake for food.
Currently, 11 states, Washington D.C. and hundreds of cities across the U.S. have passed similar plastic foam bans. The Farewell to Foam Act, though, is the first national motion to prohibit EPS foams across the country.
“It is a great time to build off of what the cities and states have been doing and to have federal action on reducing foams,” Leavitt said.
Recycling challenges
Some of the bill’s critics argue that bans are not the best way to keep plastic foams out of the environment. In a statement to EHN, Matt Seaholm, the president and CEO of the Plastics Industry Association, acknowledged plastic pollution as an issue but said the proposed bill was “misguided” and that time would be better spent on policies that prioritize “improving our recycling infrastructure, increasing the market for post-consumer recycled content and creating well-constructed extended producer responsibility programs.”
However, while more than 10 million tons of plastic foam are produced globally each year, in the U.S., less than 10% is recycled. Most recycling stations do not accept it because it breaks into beads and cannot be processed using standard machinery. Since the material is mostly air, it’s also more expensive to recycle than to produce new materials.
“I really hunger for an effective way to recycle polystyrene and upcycle polystyrene,” Guoliang “Greg” Liu, a polymer chemist and chemical engineer at Virginia Tech, told EHN. Scientists like Liu have found ways to recycle plastic foam into products with applications in manufacturing and medicine. However, the economic incentives aren’t yet widespread enough to make these processes commonplace. “We can’t just consider very cool chemistry and science. We must consider if we can do this in a realistic and scalable manner,” he said.
Though recycling could help divert EPS from the polluting water and land, it wouldn’t solve the problem of its potential health risks.
Microplastics, styrene exposure concerns
In a press release, the legislators referenced expanded polystyrene’s tendency to leach microplastics into their contents as a human health concern. There’s also concern over the presence of styrene in it. Styrene, its resinous building block, is categorized as possibly carcinogenic by the International Research Agency on Cancer. People typically come into close contact with styrene in manufacturing workplaces, where exposure can irritate their eyes, lungs, skin and nervous systems.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has upheld plastic foam as a safe packaging material because the trace amounts of styrene leached into food tend to stay under the recommended daily limit and don’t necessarily exceed the amounts of styrene found naturally in foods like strawberries and nuts. However, some researchers and advocates worry about the effects of repeated exposure to styrene in EPS-packaged food. Processing styrene into expanded polystyrene tends to minimize exposure, but the amount of leached styrene can increase if the material is damaged or improperly manufactured or if the edible contents are very hot and oily.
It’s unclear whether styrene leached into foods impacts human health, since most research focuses on workplace exposure. Regarding microplastics, current research suggests potential links between microplastics and increased inflammation.
An important step on plastic waste
Michelle Nowlin, co-director of Duke’s Environmental Law and Policy Clinic, told EHN she believes a national plastic foam ban is sound. “You think about all the other risks and threats that it poses and the difficulties with recycling it, and it just doesn't make sense to continue using the product, particularly for food ware,” she said.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) would have the power to enforce this ban and would give warnings and fines to violators. The ban would apply to food distributors who use plastic foam packaging, while manufacturers, retailers and distributors would be held responsible for loose fill and coolers. Single-use medical supplies would not be affected.
As of March 2023, the bill has been referred to the Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation in the Senate and the Subcommittee on Innovation, Data, and Commerce in the House. The committees have yet to review the bill, but 86 congresspeople (all Democrats except for 2 independents) across both chambers have signed on as co-sponsors.
However, it appears unlikely that the bill will pass by January 2025, when the current Congress ends, as it has been one of the least productive legislative bodies in American history. Nowlin added that the political polarization of the 118th Congress has stymied many bills from passing.
However, Nowlin still believes that this bill’s proposal is an important step. “Introducing these types of provisions is really important to elevate the national consciousness, to get these conversations started,” she said. “We’ll get there eventually.”