Pittsburgh's air was unhealthy to breathe for 57 days in 2020
"Even a single day of unhealthy air is unacceptable. When we're seeing nearly two months of unhealthy air, that's a huge problem."
PITTSBURGH—Air pollution in Pittsburgh reached unhealthy levels for 57 days—or nearly two months—in 2020, according to a new report.
The report, published today by environmental and public interest advocacy groups Environment America, U.S. Public Interest Research Group (PIRG), and Frontier Group, tallied days that exceeded federal guidelines for ozone or particulate matter pollution in urban and rural areas across the U.S.
Ozone and particulate matter pollution can trigger a host of respiratory and heart issues including heart attacks, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Particulate matter pollution is also linked to cancer, premature births, and autism. The Pittsburgh region has higher than average rates of asthma and certain types of cancer linked to air pollution.
Most of the region's air pollution comes from traffic and a handful of industrial polluters.
"We found that unhealthy air pollution continues to be a problem for millions of Pennsylvanians across the Commonwealth," Zachary Barber, a clean air advocate with PennEnvironment, the Pennsylvania chapter of Environment America, told EHN. "Here in southwest Pennsylvania, many people are experiencing one or more days of unhealthy air quality every week."
"For parents of kids with asthma, these were all days they had to be concerned about their kids being able to walk to school and play on the playground without having an asthma attack," he added.
Not just an urban problem
The report found widespread exposure to unhealthy levels of air pollution across the country. It estimates that 237.6 million Americans—more than 70% of the population—were exposed to more than a month of unhealthy air days in 2020.
While it's somewhat expected for large urban areas to have air pollution problems, the report also highlighted poor air quality in smaller cities and rural areas across the country and in Pennsylvania.
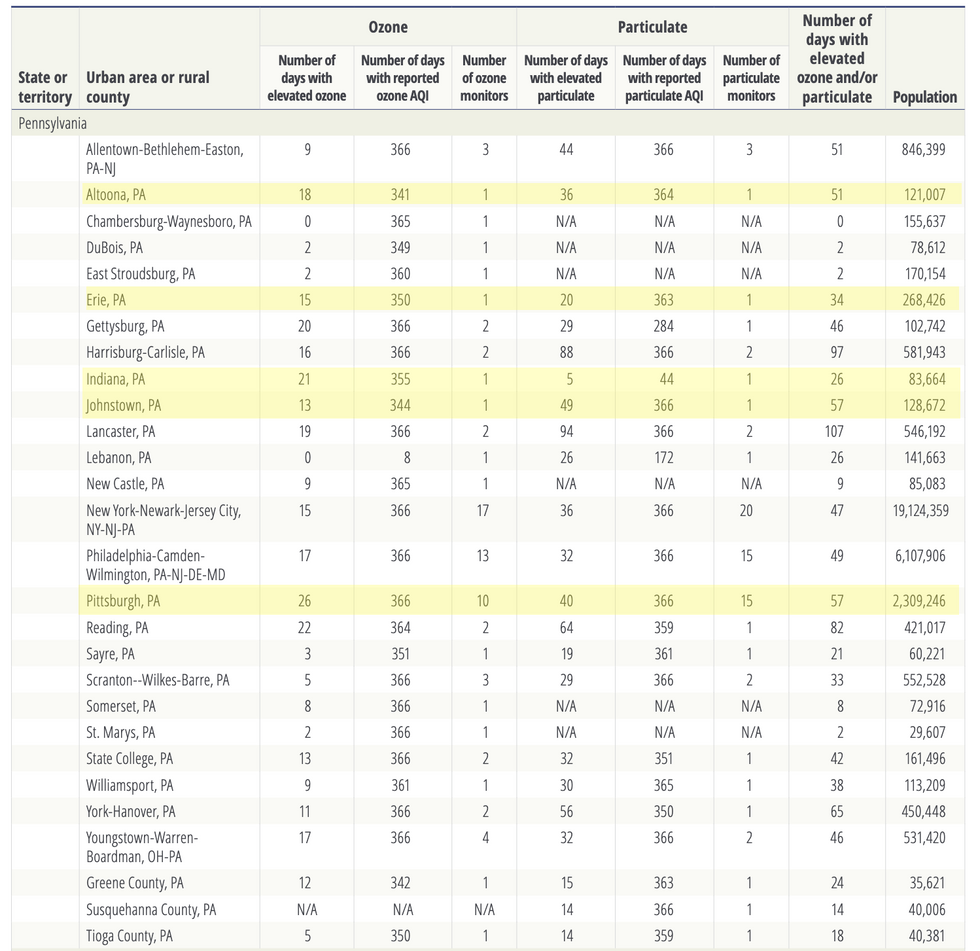
In western Pennsylvania, Altoona, Johnstown, Erie, and Indiana were among the small towns and cities with more than 25 unhealthy air days in 2020. Johnstown, a former steel town with a population of around 120,000, saw 57 unhealthy air quality days in 2020—the same number as Pittsburgh, which has a population of around 302,000.
Some smaller cities and rural areas in the eastern part of the state had trouble with unhealthy air, too: Lancaster, Pennsylvania saw 107 unhealthy air days in 2020—the highest number seen in any region in the state.
"Our report shows that air pollution continues to be a problem across urban, suburban, and rural communities in Pennsylvania, which speaks to the importance of acting now to tackle this problem," Barber said.
Air pollution solutions

Credit: Thijs Stoop/Unsplash
The report is published annually, but does not draw comparisons between air quality in 2020 versus previous years due to changes in the way the data is reported and analyzed, Barber said.
Other studies have indicated that after several decades of improvement, air quality in many parts of the U.S. is declining. Some regions saw small improvements in air quality during the shutdowns caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, but those improvements didn't last.
Meanwhile, emerging scientific research increasingly suggests that even when air pollution levels stay below current legal thresholds, long term exposure still leads to increased rates of disease and premature death.
Pittsburgh's air quality has shown some improvements in recent years, but it still recently received an "F" grade from the American Lung Association.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is currently considering strengthening national standards for particulate matter. In 2019, the agency published a scientific report estimating that current air standards for the pollutant are associated with 45,000 deaths per year, and that tightening them even slightly could reduce that number by 27%, saving around 12,150 American lives each year.
The EPA expected to propose the new air pollution rules by the summer of 2022 and finalize them by the spring of 2023. If that happens, Barber said, the Pittsburgh region will likely see significant improvements to its air quality.
"Here in Pittsburgh we're often hovering right on the edge of those standards, so this could have a big impact," Barber said. "Instead of making incremental changes like we've been doing, it would require us to take big steps to significantly reduce long-term emissions from vehicles and the region's big industrial polluters."
At the state level, clean air advocates are urging lawmakers to join the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, supporting a transition away from fossil fuels toward renewable energy and supporting low-emission transportation initiatives.
"There are lots of options for solutions," Barber said. "But we need to act quickly. We know that climate change will bring hotter summers and more wildfires. These problems will continue to get worse unless we act to tackle them now."
Banner photo: Mladen Borisov/Unsplash













