Op-ed: Ending toxic threats to Alaska from plastics and petrochemicals
An ambitious Plastics Treaty that controls plastic production and eliminates the use of toxic chemicals would begin to rectify the environmental injustices experienced by Indigenous Peoples.
As a community health aide in Nuiqsut, Alaska, when nearby oil and gas operations were flaring, I would see a stream of people with respiratory issues. Before I was done with one patient, I had another coming in. It got to the point where we were up all night to help people breathe.
Within a single lifetime, Indigenous communities in the Arctic have seen the rates of illness skyrocket due to toxic pollution caused by the interlinking of chemicals, plastics and the climate crises. Respiratory disease, cancer, reproductive disorders and many other health disparities are threatening our very existence.
This April 23-29, the world’s nations will gather for the Plastics Treaty negotiations in Ottawa, Canada. An ambitious Plastics Treaty that controls plastic production and eliminates the use of toxic chemicals throughout the plastics life cycle is critical to protect human health and the environment. This would begin to rectify the environmental injustices experienced by Indigenous Peoples and benefit fence-line communities and all of us who are exposed to toxic chemicals from plastics.
Respiratory disease, cancer, reproductive disorders and many other health disparities are threatening our very existence.
The Plastics Treaty talks aim to finalize negotiations by the end of the year. Alaska and its inhabitants can’t wait. The Arctic is warming nearly four times faster than the rest of the world, and In 2019, over 70 of 200Alaska Native villages were facing environmental threats from flooding, thawing permafrost, and erosions. Alaska is home to 229 federally recognized tribes, and their cultures and livelihoods are critically under threat from the linked threats of climate change, plastics, fossil fuels, and petrochemicals.
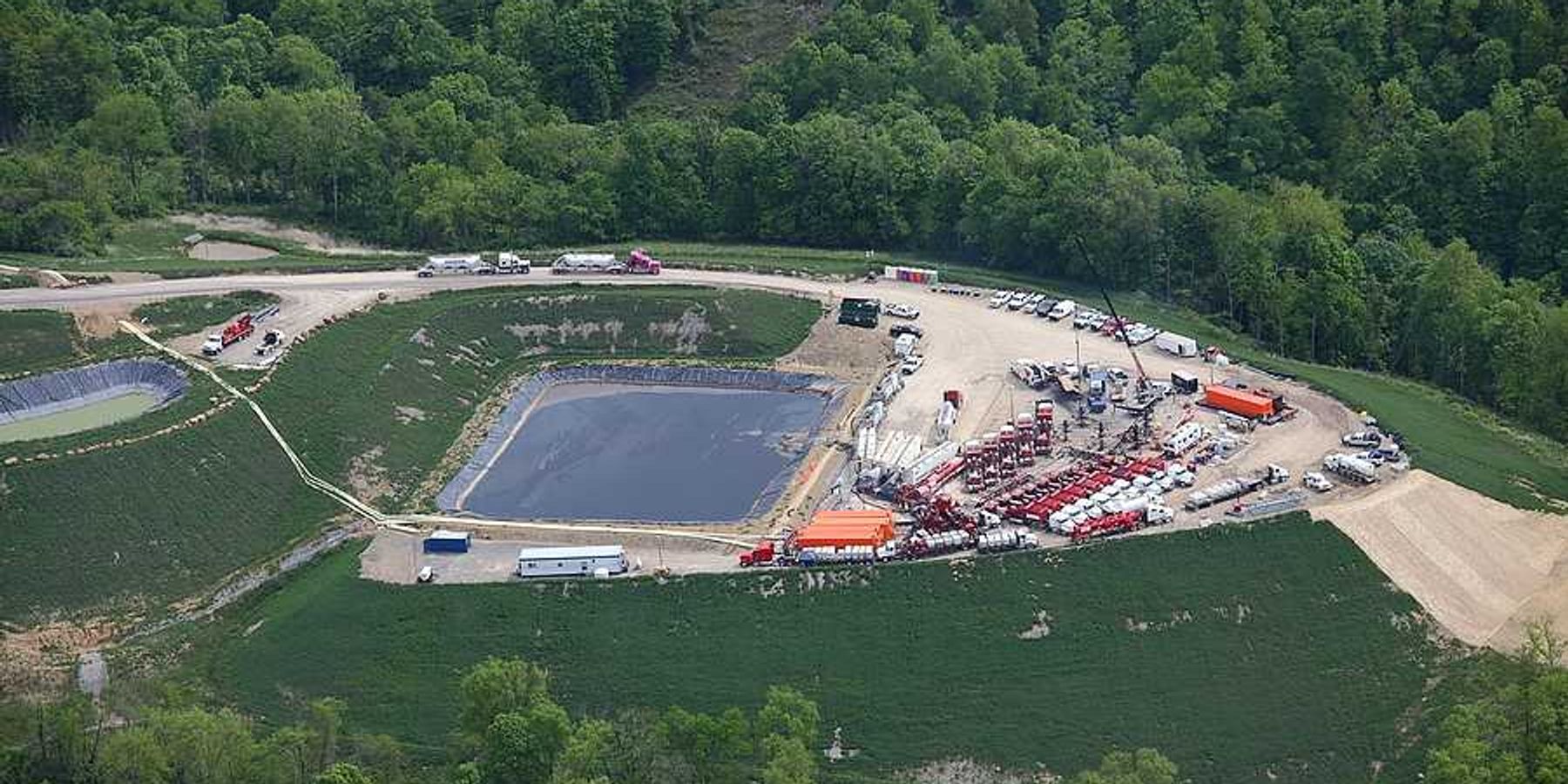
Plastics are made from fossil fuels and chemicals, and the oil and gas industries are betting on plastics to grow their markets. Left unchecked, the petrochemical industry is projected to account for 50% of oil consumption by 2050. More plastics means more oil and gas and more health disparities for Indigenous Peoples.
Fossil fuels extracted from Alaska, often near Indigenous lands, expose Indigenous Peoples to toxic chemicals. When plastic waste is disposed around the world, the waste and its toxic chemicals are carried by atmospheric and oceanic currents to the Arctic, which acts as a “hemispheric sink” concentrating the toxic pollutants. This source-and-sink cycle results in increased health problems and food insecurity for Indigenous Peoples, as traditional food sources become scarce or contaminated. Earlier this year, microplastics were detected for the first time in the tissues of the Pacific walrus of the Bering and Chukchi Seas, an animal critical to the traditional diet of Indigenous Peoples of this region.
More plastics means more oil and gas and more health disparities for Indigenous Peoples.
As the First Peoples of Alaska, we have been stewards of our lands, airs, and waters. Now our People are being exposed to toxic chemicals without our consent. These are burdens we did not create but we face some of the most drastic changes here in the Arctic.
A Plastics Treaty aimed at protecting our health and healthy environments will be a vital step in the drive to advance human rights and healthy communities. We must put an end to toxic plastic production and stop producing toxic petrochemicals while the planet is already overwhelmed by plastic and chemical pollution. Now, the world has an opportunity to move toward toxics-free solutions for a healthy planet.