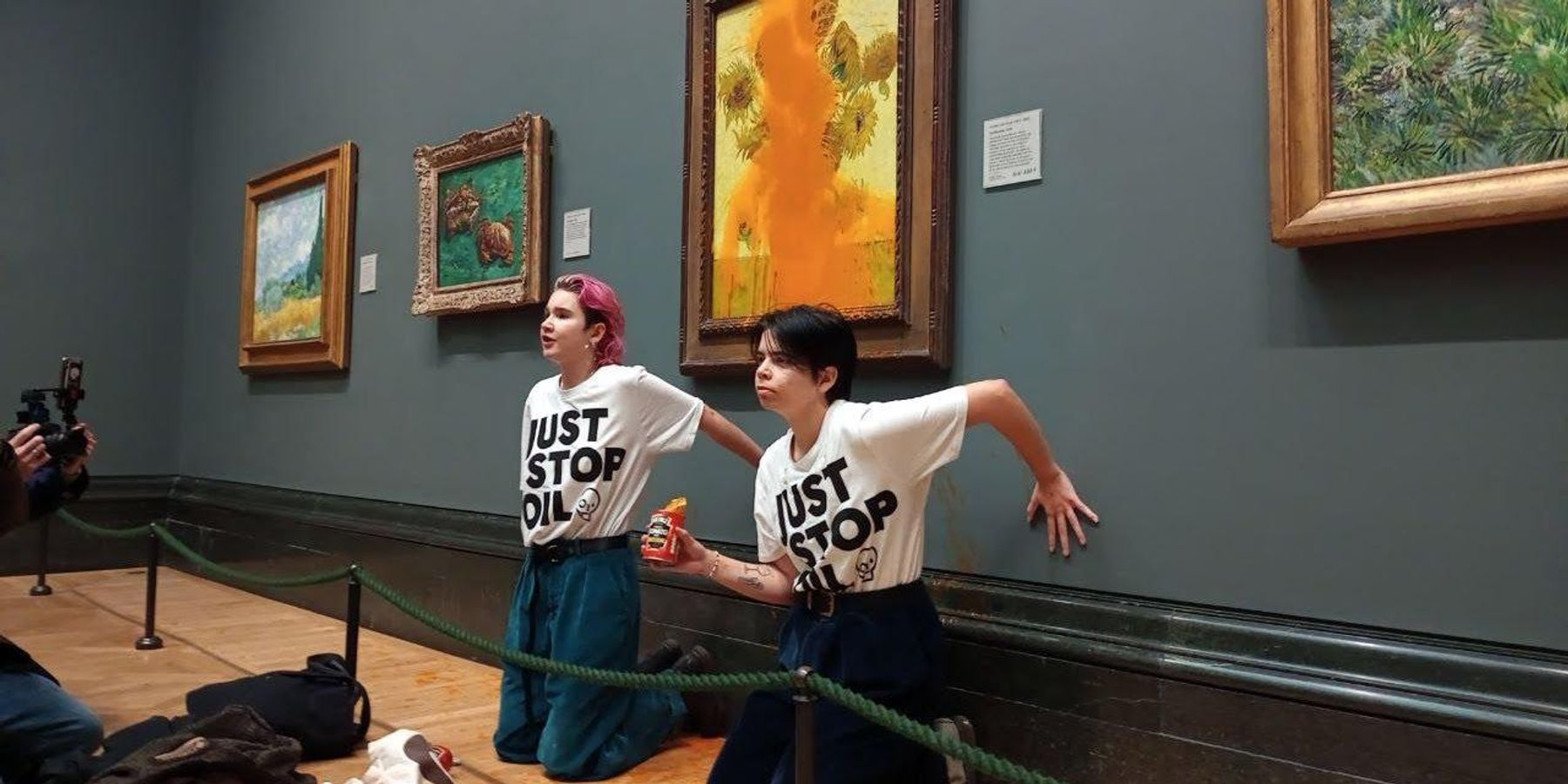Op-ed: On climate protests, the media misses the point
What does van Gogh matter to billions of victims of climate inaction?
In the face of global inaction, climate change — inextricably linked to health inequities — is leading us toward planetary collapse with a ‘fast track to climate disaster’ and ‘civilization collapse,’ as has been highlighted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
Yet, much of the narrative — perpetrated by the corporate media, of which, in the U.S., 90% of is controlled by six conglomerates — remains focused on pseudo-optimism akin to the cult of toxic positivity with the logic that if optimism works in other situations, it must work in this too. This approach insists that we must create cognitive dissonance around what needs to be done versus what is being done.
This is not a case against the tremendous amount of evidence that highlights the need to balance effective climate communications with empowering actions that people can take, rather climate optimism is inconsequential, and basically selling snake oil, without transformative changes and actions.
One of the key ways these media narratives keep consumers content around their climate inaction, beyond individual-level action such as expensive organic foods and recycling, is by setting the public’s social reality about the enoughness of these actions and decentering the urgency of transformative societal changes, political action, and sacrifices — primarily by the rich — that are needed to tackle the existential threat of climate change.
The other important way the media supports these narratives is by delegitimizing the dread and desperate pleas and protests calling attention to the existential crisis of climate change. Case in point: the latest protest by youth activists involving an unharmed van Gogh painting.
Media, climate coverage and van Gogh
Much of the U.S. media attention has decentered the reasons for the protest (hint: the planet is on a pathway to collapse on itself due to climate change), instead pontificating about what “the spectrum of acceptable” climate protests ought to be and how these tactics are unproductive, irresponsible and strange, as captured by the article Throwing tomato soup on Van Gogh: Why climate protests are getting weirder, published in the Washington Post. Another example, The Contradictions of Climate Activism, was written by the New York Times’ Ross Douthat, a fellow of the American Enterprise Institute, a right-wing think-tank well known for climate denial and conspiracy theories. This article, perpetuating disinformation, states “...the world has made great progress on alternative energy, which is one reason climate change’s existential risks have dropped meaningfully in recent years, with worst-case scenarios becoming much less likely than before,” while citing a single Substack article by a scientist known for “delivering talking points and conspiracy theories.”
Related: Colonialism, the climate crisis, and the need to center Indigenous voices
These articles, among many others, insist we direct attention to the soup and the painting and not the intended outcome: drawing our attention to our colossal failure to act on climate change. It also highlights that no matter the extreme nature of climate protests, the media has consistently ignored the urgency of the threat.
Polite politics and climate protests
What gets lost in much of this debate and pithy one-liners is the important and insidious function of this coverage, which is to limit the debate on the issue and distract us. Akin to the mindless maxim of ‘violence is never the answer’ and ‘marketplace of ideas’ as the solution, whenever those subjugated and oppressed react, the polite politics of the liberal elites insist just how unproductive it is to engage in the type of protests that might be against their sensibilities and comfort. This narrative forgets that art on a planet headed toward civilizational collapse is the domain of the rich, not in perpetuity but on borrowed time. What does van Gogh matter to billions of victims of climate inaction — that these protesters are drawing our attention to — from Pakistan to Puerto Rico?
Anti-protest legislation
These narratives also conflate legality and morality, which are not synonymous. This pearl-clutching of what is and isn’t an acceptable form of protest in the face of a collapsing planet also, however inadvertently, give moral legitimacy to fascist measures such as the rise in anti-protest legislation as a response to racial justice protests, which coincides with the militarization of the police and climate inaction.
Anti-protest legislation legitimizes state violence against people protesting for their right to enjoy a life on a habitable planet, while drawing their support from media coverage and the public sentiment that portrays climate activists as ‘radicals.’
Art or life?
When we buy into these anti-protest narratives we do a disservice to those at the margins of society. While we may not agree with some of their tactics, it is critical that we defend the pursuit of a habitable planet, while reflecting on the question, “what is worth more — art or life?”
Dr. Ans Irfan, MD, EdD, DrPH, MPH, MRPL, is an Associate Professor at the University of Southern California, Keck School of Medicine, and a senior Agents of Change in Environmental Justice Fellow. He also serves as a Religion and Public Health Fellow at Harvard Divinity School, Harvard University.