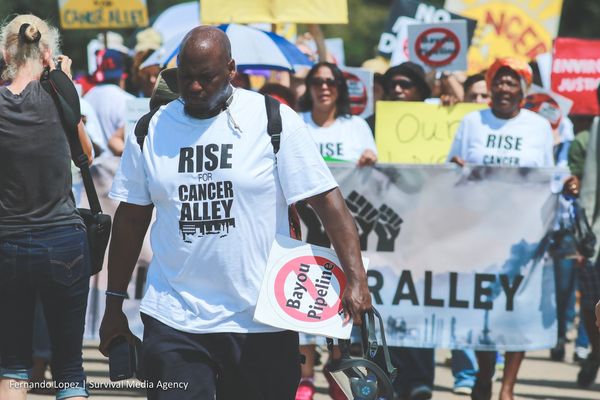petrochemical industry
The world is drowning in plastic, with 57 million tons of pollution annually
The world generates an astonishing 57 million tons of plastic pollution every year, spreading from the depths of the oceans to inside human bodies, with two-thirds coming from the Global South, according to a recent study.
In short:
- Researchers found that the Global South produces more than two-thirds of the world’s plastic waste, much of it due to lack of infrastructure and government waste management.
- The study received criticism, however, for not examining the toll of plastic production, which generates planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants harmful to human health.
- Microplastics, from improperly discarded waste, are increasingly found in human bodies, with uncertain health consequences.
- Final negotiations on a global plastics treaty are scheduled for November, aiming to address this growing problem.
Key quote:
“They [microplastics] are in the most remote places ... the peaks of Everest, in the Mariana Trench in the ocean, in what we breathe and what we eat and what we drink.”
— Costas Velis, University of Leeds environmental engineering professor
Why this matters:
All eyes are on the global plastics treaty negotiations in November, as world leaders try to rein in this crisis before it spirals further. If they succeed, we could finally see a coordinated effort to curb this plastic tidal wave.
Read more: Scientists say health should be the core of global plastic treaty.
Op-ed: “I’m sorry, I can’t hear you” — disabling environments in Cancer Alley and the Ohio River Valley
For communities plagued by energy extraction and petrochemical buildout, struggles of environmental justice often fall on deaf ears.
The low hum of a tour bus engine underpins the constant buzzing of insects. Air conditioning on full blast circulates the bus interior, shielding us from the muggy Louisiana summer.
Sharon Lavigne stands at its center, microphone in hand. She crouches slightly, one hand gripping the headrest of a black leather seat, and peeks out the tinted windows. White petroleum storage tanks stand in stark contrast to the green grass and red bricked homes. A man mows his lawn, his toddler rolling down the sidewalk in a Cozy Coupe.
To read a version of this story in Spanish click here. Haz clic aquí para leer este reportaje en español.
Ms. Lavigne shares tidbits of the health-related ailments of the residents of St. James Parish, a fragmented conglomerate of homes, elongated fields and petrochemical infrastructure. She points to a house, “he died of a rare cancer last year.” She points to another, “her daughter decided to leave after she became gravely ill.”
Whispers fill the cabin, muffled by disposable masks. I struggle not only to hear, but to truly comprehend the myriad ways in which the predominantly African-American community has been disabled, robbed of its full potential by the petrochemical industry.
Hearing, seeing and being in the world has always been different for me. At a young age, it was found that I had Single Sided Deafness (SSD) – or unilateral hearing loss – meaning that I could not hear out of my right ear at all. Living with SSD has brought me a heightened spatial awareness, allowing for a more introspective understanding into the complexities of the environment. My experience has led me to believe that analyzing environmental injustices through a disability lens can help us to better understand communities – how humans and the environment are inextricably linked and how my own feelings of isolation in contexts that ignore my disability mirror how the struggles of environmental justice often fall on deaf ears. Understanding disabilities forces us to look at who is excluded, what barriers perpetuate that exclusion and what assumptions are made about the interactions between people and the places they live in. I believe the same questions can be asked to better capture the lives of environmental justice communities burdened by the oil and gas industry.
While geographically distant, Cancer Alley, where St. James Parish is located, and the Ohio River Valley, where I’ve spent most of my time as a geographer, share common challenges. Both have been utilized as sacrifice zones for energy extraction, and, in many ways, have been disabled. They have also been socially barred by the broader U.S., cast off as rural, backwards and seemingly unoccupied spaces that are not worth “saving.” This reality reminds me of the many ways in which meeting the needs of people with disabilities is considered a "burden" that is not worth attending to as a society.
And yet, both people with disabilities and these two regions have continued to exist, to persevere and to fight back against injustice. Like my hearing disability, just because someone – or an entire community or region – is disabled (or assumed to be), does not mean that they are not able.
A disabling context
Growing up with a physical disability was no small feat. I had trouble locating sounds, constantly felt a dull, ringing sensation and was unable to wear traditional hearing aids. I received ridicule from classmates, poking fun at my inability to hear adequately on my right-side. At times I felt defeated, unable to cope with the mentally debilitating prospect of being labeled “different.” And yet, over time and into adulthood, I have grown to accept and understand my hearing disability, as it has shaped me into the person that I am today.
Living with Single Sided Deafness, I occupy an in-between space. In some contexts, I am considered disabled, while in others I might appear able to the naked eye. This perception of disability – both my own and others’ – shifts over time and in different contexts. The environments we occupy can also be an in-between space where factors outside of our immediate control can shift the way we act and exist in the world. I often think about communities in Cancer Alley as also occupying an in-between space, as they’ve been cast away as a “sacrifice zone” but at the same time they’re creating real progress. People like Ms. Lavigne embody the community’s struggle between the harm inflicted and the progress being made toward justice. In March, her organization Rise St. James, among other environmental advocacy groups, filed an application to ask the Louisiana Supreme Court to grant review and overturn the issuance of Formosa Plastics’ air permits. Further, Rise St. James has urgently called on President Biden to stop Formosa from building their a mega petrochemical facility in St. James Parish, which has gained traction toward the White House.
Living with Single Sided Deafness, I occupy an in-between space.
On that bus ride, I positioned myself close to Ms. Lavigne to fully understand her words. Ms. Lavigne is the leader of Rise St. James, a faith-based community organization that works to stop the proliferation of petrochemical industries in St. James Parish, Louisiana. Adorned in her Rise St. James tee, Ms. Lavigne spoke at-length of the Parish’s history. Starting in the 1980s, fossil fuel, oil-refining and plastic-production operations have proliferated along an 85-mile stretch on the Mississippi River between New Orleans and Baton Rouge, running directly through the Parish. Such facilities emit high levels of harmful air pollutants and other environmental toxics, which have caused a high incidence of rare cancers, respiratory diseases, asthma and other severe health conditions. Today, the area is known as Cancer Alley.
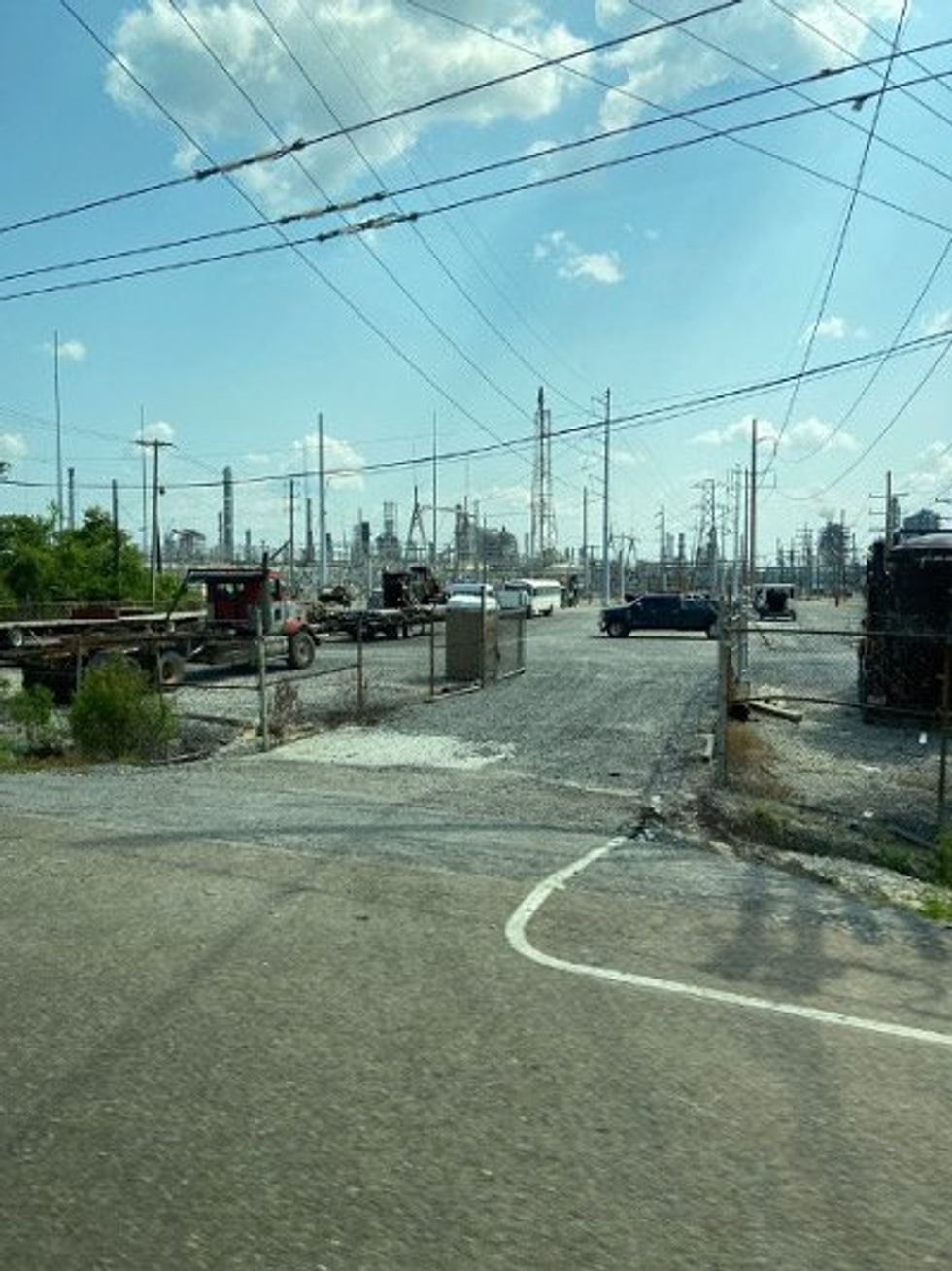

Shell Norco Manufacturing Complex outside of New Orleans, Louisiana.
Credit: Brandon Rothrock
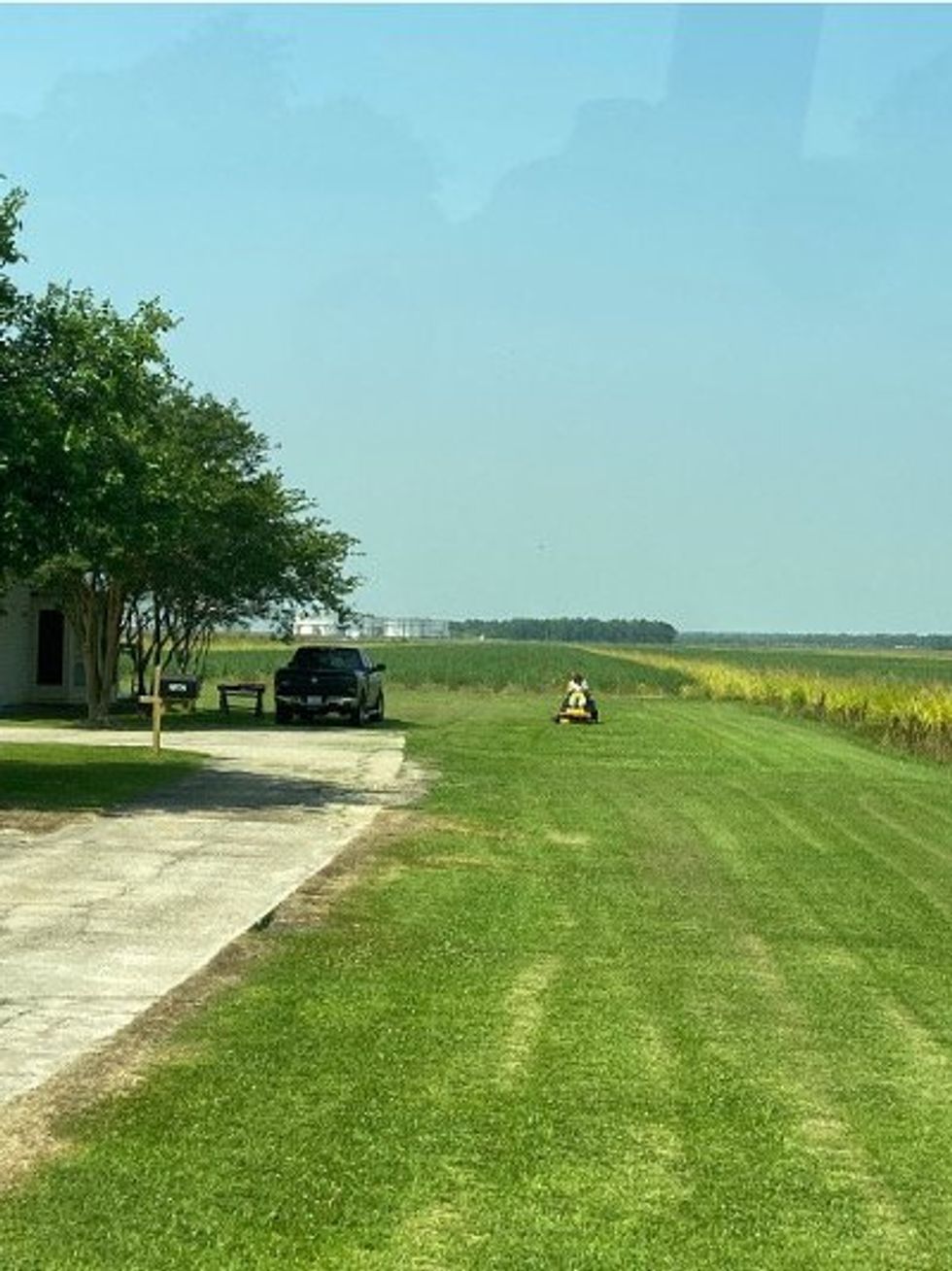

A man mowing the lawn outside his house in St. James Parish, Louisiana.
Credit: Brandon Rothrock
Despite the obvious injustices these communities already face, Louisiana state officials continue to downplay environmental and health concerns raised by Rise St. James. The most recent example is their support for a proposed $9.4 billion petrochemical complex called the Sunshine Project, heralded by Formosa Petrochemical Corporation. The proposed complex would include 14 facilities that will process ethane from fracked natural gas to produce various chemicals used in everyday materials such as single-use plastics and antifreeze. In the “name of progress,” the majority African American community is forced to exist in a disabling environment: a context that makes them incapable of breathing clean air and living long and healthy lives. This situation in Louisiana reflects a broader national issue.
Despite the obvious injustices these communities already face, Louisiana state officials continue to downplay environmental and health concerns raised by Rise St. James.
Fracked natural gas – the kind of gas the Sunshine Project would process– is in itself another example of how this industry disables communities, and there’s no better example than the Ohio River Valley. For centuries, communities in Pennsylvania, Ohio and West Virginia, first through coal and now through natural gas, have been dominated by fossil fuels production. In the last two decades, the region, which sits on top of the largest shale gas formation in the U.S., has become the epicenter of the country’s fracking industry. Injecting chemicals deep underground to fracture shale deposits and release the gas stored within them releases climate warming gasses like methane, and airborne toxics like particulate matter, which are linked to respiratory problems and other health conditions like skin issues and cancer. It also pollutes underground water supplies with cancer-causing chemicals like PFAS, also known as “forever chemicals.”
Fracking continuously fractures communities. The physical landscape is altered forever while people grapple with a shattered sense of community, damaged property and high rates of depression. Here again, we see communities being robbed of their ability and barred from their agency. Such extractive acts can be considered disabling, in the sense that once communities lose their ability to exist and make decisions freely, the industry will be able to extract further. In a similar vein to Rise St. James, Appalachian-based groups such as the Ohio River Valley Institute work directly with community partners to fight back against injustice.Fighting back against injustice
I often find myself struggling in large lecture halls where the acoustics are poor, and the professor’s voice is drowned out. I also miss critical pieces of the lectures due to a lack of closed captions or visual aids, such as lecture slide printouts. Similarly, friends who may be visually impaired frequently encounter poorly designed websites that can make accessing course materials impossible. All of this creates a hostile environment for people with disabilities to thrive – just like communities are faced with a harsh environment that disables them from reaching their full potential.
I fear this disabling context will only become more entrenched in both regions. As fracking continues to balloon across the Appalachian region, so do petrochemical facilities: at least 61 are in construction or in operation across the Ohio River Valley. The outlook for Cancer Alley communities is no better: in 2015, the Environmental Integrity Project documented 44 petrochemical construction and expansion projects proposed or permitted, with a majority cited for Louisiana. On top of this, the U.S. Department of Energy selected the Ohio River Valley and the Gulf Coast as two of the seven proposed Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs, which are a national network of “clean” hydrogen producers. Touted by politicians as an advancement toward energy independence, these regional hydrogen hubs will fill the landscape with pipelines, fueling stations and carbon storage facilities, locking-in the regions to further plastic production and energy infrastructure buildout for decades to come.
I worry that this build out will further entrench disadvantaged communities in a cycle of destruction. Rhetoric such as “sacrifice zone,” “backwards” and other related terms used to describe Appalachia and Cancer Alley are deeply entrenched in the national psyche, further perpetuating assumptions about the people who live there. But having been there, I think reframing communities facing environmental injustices is needed.
My visit to St. James Parish revealed something profound: the beauty, uniqueness and resilience of these communities. On that bus ride with Sharon Lavigne, I saw children playing joyfully against the backdrop of towering industrial complexes. As we stopped and ate lunch at a community center, I saw community members laughing and chatting about their days, organizing for a better future. Ms. Lavigne’s words – and those of the community – resonated deeply as they spoke of their battle against injustice and the determination to fight for what is right. Her dedication and the community’s solidarity in the face of adversity illustrated remarkable strength.
Environmental justice communities deserve a future where their resilience is not tested by pollution but celebrated and supported by just and equitable practices. As future leaders and educators, it is our responsibility to better understand how extractive practices can disable and to work towards fostering environments that enable and uplift.
This essay was produced through the Agents of Change in Environmental Justice fellowship, a partnership between Environmental Health News and Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health. Agents of Change empowers emerging leaders from historically excluded backgrounds in science and academia to reimagine solutions for a just and healthy planet.
“Lo siento, no puedo escucharte”: los entornos incapacitantes del Corredor del Cáncer y el valle del río Ohio
Las reivindicaciones de justicia medioambiental de las comunidades asoladas por la extracción de petróleo y la industria petroquímica suelen caer en oídos sordos.
El suave murmullo del motor de un autobús turístico acompaña el constante zumbido de los insectos.
El aire acondicionado, encendido en su máxima potencia, circula al interior del vehículo, protegiéndonos del verano fangoso de Luisiana. Sharon Lavigne está parada en el centro, micrófono en mano. Se agacha un poco y se agarra del reposacabezas de un asiento de cuero negro, mientras se asoma por las ventanas tintadas. Los tanques blancos de almacenamiento de petróleo contrastan con el césped verde y las casas de ladrillos rojos. Un hombre poda su jardín, su bebé rueda por la acera en uno de esos carritos para niños llamados Cozy Coupe.
Haz clic aquí para leer este reportaje en inglés. To read and watch a version of this story in English click here.
Doña Lavigne comparte fragmentos de las dolencias que padecen los habitantes de la parroquia de St. James, un cúmulo fragmentado de hogares, campos alargados e infraestructura petroquímica. Señala a una casa, “él murió por culpa de un cáncer rarísimo el año pasado”; señala otra, “su hija decidió irse después de enfermar gravemente”.
Los susurros llenan la cabina del bus, amortiguados por máscaras desechables. No sólo me cuesta oír, sino comprender las innumerables formas en que esta comunidad predominantemente afroamericana ha quedado discapacitada, despojada de todo su potencial por la industria petroquímica.
Oír, ver y estar en el mundo siempre ha sido algo diferente para mí. Muy pequeño, los médicos me diagnosticaron con hipoacusia unilateral (SSD por su sigla en inglés), o pérdida auditiva unilateral, lo que significa que no puedo escuchar nada con mi oído derecho. Vivir con una discapacidad auditiva me ha dotado de una mayor conciencia espacial, lo que me permite una comprensión más introspectiva de las complejidades del entorno.
Creo que analizar las injusticias medioambientales a través del lente de la discapacidad puede ayudarnos a comprender mejor a las comunidades que las sufren– a entender cómo los seres humanos somos inseparables de nuestro entorno, y cómo la sensación de aislamiento en contextos que ignoran mi discapacidad reflejan la forma en la que los reclamos de estas comunidades caen en oídos sordos. Entender las discapacidades nos fuerzan a volcar la mirada sobre quienes son excluidos, las barreras que perpetúan esa exclusión y las ideas preconcebidas que tenemos sobre las interacciones entre la gente y los lugares que habitan. Creo que las mismas preguntas pueden hacerse para entender mejor las vidas de las comunidades afectadas por la injusticia medioambiental creada por la industria del gas y el petróleo.
Si bien son distantes geográficamente, el Corredor del Cáncer, donde está ubicada la parroquia de St. James, y el valle del río Ohio, donde he pasado la mayor parte de mi carrera como geógrafo, comparten retos. Ambos han sido vistos como “zonas de sacrificio” para la extracción de petróleo, y, en muchos sentidos, han terminado incapacitados. También han sido marginados socialmente por el conjunto de Estados Unidos, tachados de espacios rurales, atrasados y aparentemente desocupados que no vale la pena “salvar”. Esta realidad me recuerda las formas en las que atender las necesidades de las personas con discapacidades es considerado una “carga” que no vale la pena atender como sociedad.
Y, aun así, tanto las personas con discapacidades como estas dos regiones siguen existiendo, perseverando y luchando en contra de la injusticia. Al igual que sucede con mi deficiencia auditiva, el hecho de que alguien – o toda una comunidad o región – tenga una discapacidad (o se suponga que la tiene) no significa que no tenga capacidades.
Un contexto que incapacita
Crecer con una discapacidad no es poca cosa. Tenía problemas para localizar los sonidos, constantemente sentía un pitido sordo y no podía llevar prótesis auditivas tradicionales. Mis compañeros me ridiculizaban, burlándose de mi incapacidad de oír adecuadamente en mi lado derecho. A veces me sentía derrotado, incapaz de afrontar la posibilidad debilitante de ser etiquetado como “diferente”. Aun así, con el tiempo y a medida que me hice adulto, he aprendido a aceptar y entender mi discapacidad auditiva, pues me ha convertido en la persona que soy.
Al vivir con hipoacusia unilateral, ocupo un espacio intermedio. En algunas ocasiones soy considerado discapacitado, mientras que en otras puedo no parecerlo a simple vista. Esta percepción de la discapacidad – tanto de la mía como la de otros– cambia en el tiempo y el espacio. Los entornos que ocupamos también pueden ser un espacio intermedio en el que factores que no controlamos modifican la forma en la que actuamos y existimos en el mundo. Suelo pensar en las comunidades del Corredor del Cáncer como ocupantes de un espacio intermedio, pues son vistos como una “zona de sacrificio” pero al mismo tiempo son capaces de luchar por el progreso real. Personas como Sharon Lavigne encarnan la lucha de la comunidad entre el daño infligido y los avances hacia la justicia.
En marzo, su organización, Rise St. James, junto a otros grupos activistas ambientales, hicieron una petición ante la Corte Suprema de Luisiana para que revise y revoque los permisos de emisiones aéreos que permiten la construcción de la planta de producción de plásticos de Formosa. Además, Rise St. James ha pedido urgentemente al Presidente Biden que impida que Formosa construya su mega instalación petroquímica en St. James, iniciativa que ha ganado adeptos en la Casa Blanca.
En esa visita en bus, me acerqué a doña Lavigne para poder entender bien sus palabras. Ella es la líder de Rise St. James, una congregación religiosa comunitaria que trabaja para detener la proliferación de las industrias petroquímicas en la parroquia. Vistiendo su camiseta con el logo de Rise St. James, Ms. Lavigne habló largo y tendido sobre la historia del poblado. Empezando en la década de los ochentas, las operaciones de combustibles fósiles, refinerías y producción de plásticos han proliferado a lo largo del tramo de 85 millas (unos 137 kilómetros) del río Mississippi, entre Nueva Orleans y Baton Rouge, atravesando la parroquia. Estas instalaciones emiten grandes cantidades de contaminantes del aire y otros tóxicos, lo que ha causado una gran incidencia de cánceres raros, enfermedades respiratorias, asma y otras condiciones de salud graves. Hoy, la zona es conocida como el Corredor del Cáncer.


A pesar de las evidentes injusticias que esta comunidad sufre, los gobernantes de Luisiana siguen minimizando las preocupaciones medioambientales y de salud que Rise St. James ha señalado. El ejemplo más reciente es su apoyo a la propuesta de un complejo petroquímico de $9.4 mil millones de dólares llamado el Proyecto Sunshine, anunciado por Formosa Petrochemical Corporation. La planta propuesta incluiría 14 instalaciones en las que se procesaría etanol proveniente del gas natural producto de la fracturación hidráulica (más conocida como fracking) para producir varios químicos usados en materiales como los plásticos de un solo uso y sustancias anticongelantes. En el nombre del progreso, la comunidad afroamericana está siendo forzada a existir en un ambiente discapacitante: un contexto que la vuelve incapaz de respirar aire limpio y vivir una vida larga y sana. Esta situación en Luisiana refleja un problema más amplio.
El gas natural producto de fracking –el tipo de gas que el Proyecto Sunshine procesaría– es en sí mismo un ejemplo de cómo esta industria incapacita a las comunidades. El valle del río Ohio es paradigmático. Durante siglos, las comunidades de Pennsylvania, Ohio y Virginia del Este, primero con el carbón y ahora con el gas natural, han sido dominadas por la producción de combustibles fósiles. En las últimas dos décadas, la región, que se sitúa sobre la formación de gas más grande de los Estados Unidos, se ha convertido en el epicentro de la industria nacional del fracking. La inyección de sustancias químicas en el subsuelo para fracturar los yacimientos de lutita y liberar el gas almacenado en ellos emite gases que contribuyen al cambio climático, como el metano, y sustancias tóxicas al aire, como el material particulado, que están relacionadas con problemas respiratorios y otras afecciones como problemas cutáneos y cáncer. El fracking también contamina las reservas subterráneas de agua con sustancias químicas cancerígenas como los PFAS, también conocidos como “sustancias químicas eternas”.
El fracking fractura a las comunidades. El paisaje físico queda alterado para siempre, mientras la gente se enfrenta a un sentimiento de comunidad destrozado, propiedades dañadas y altos índices de depresión. Aquí también podemos ver cómo se roba a la comunidad de sus habilidades y su agencia. Tales actos extractivos pueden considerarse incapacitantes, en el sentido de que una vez que las comunidades pierden su capacidad de existir y de tomar decisiones libremente, la industria podrá extraer cada vez más. Parecido a lo que Rise St. James hace en Luisiana, grupos como el Ohio River Valley Institute trabajan con las comunidades para luchar contra la injusticia.
Luchar contra la injusticia
En la universidad a menudo me encuentro en aprietos en grandes aulas donde la acústica es deficiente y la voz del profesor se ahoga en el espacio. También se me escapan partes importantes de las clases por falta de subtítulos o de ayudas visuales como diapositivas impresas. A mis amigos con discapacidades visuales les pasa algo similar al encontrarse con páginas web mal diseñadas que pueden hacer que acceder a los materiales de la clase sea una tarea imposible. Todo esto crea un entorno hostil para que las personas con discapacidades prosperemos, al igual que las comunidades se enfrentan a un entorno inclemente que les impide desarrollar todo su potencial.
Me temo que este contexto incapacitante no hará sino arraigarse en ambas regiones. A medida que el fracking crece en la región de los Apalaches, así lo hace la industria petroquímica: al menos 61 instalaciones están en construcción o ya entraron a operar en el valle del río Ohio. El panorama para las comunidades del Corredor del Cáncer no es mucho mejor: en 2015, el Environmental Integrity Project documentó que ya han sido propuestos o aprobados 44 proyectos de expansión y construcción petroquímica, la mayoría de ellos ubicados en Luisiana. Por si fuera poco, el Departamento de Energía de los Estados Unidos seleccionó a ambas regiones como dos de los siete Centros Regionales de Hidrógeno Limpio que constituirán una red nacional de productores de hidrógeno “limpio”. Promovidos por los políticos como un avance hacia la independencia energética, estos centros regionales de hidrógeno llenarán el paisaje de oleoductos, estaciones de servicio e instalaciones de almacenamiento de carbono, comprometiendo a las regiones a una mayor producción de plástico y a la construcción de infraestructuras energéticas durante las próximas décadas.
Me preocupa que estas construcciones hundan aún más a las comunidades desfavorecidas en un ciclo de destrucción. La retórica de las “zonas de sacrificio” o el “atraso” y otros términos similares utilizados para describir los Apalaches y el Corredor del Cáncer están profundamente arraigados en la psique nacional, perpetuando los estereotipos sobre las personas que viven en ellos. Pero tras haber estado allí, creo que es necesario re-encuadrar a estas comunidades.
Mi visita a la parroquia St. James me reveló algo profundo: la belleza, singularidad y resiliencia de estas comunidades. En ese recorrido en bus con Sharon Lavigne, vi a niños y niñas jugar alegremente con el telón de fondo de imponentes complejos industriales. Al parar y comer el almuerzo en un centro comunitario, vi a los miembros de la comunidad reír y conversar sobre su día, organizándose por un futuro mejor. Las palabras de doña Lavigne –y todos los demás– resonaron profundamente, pues hablan de su batalla contra la injusticia y su determinación de pelear por lo correcto. Su dedicación y la solidaridad de la comunidad a pesar de las adversidades ilustran su fuerza extraordinaria.
Las comunidades que sufren injusticias ambientales merecen un futuro en el que su resiliencia no sea puesta a prueba por la contaminación, sino celebrada y apoyada por prácticas justas y equitativas. Como futuros líderes y educadores, es nuestra responsabilidad comprender mejor cómo las prácticas extractivas pueden incapacitar a las comunidades y, en cambio, fomentar entornos que las hagan sentir capaces y fuertes.
Este ensayo ha sido elaborado gracias a la beca Agents of Change in Environmental Justice. Agents of Change capacita a líderes emergentes de entornos históricamente excluidos de la ciencia y el mundo académico que reimaginan soluciones para un planeta justo y saludable.
Plastic industry pushes for recycling as a solution to pollution crisis
The petrochemical industry claims to support a global treaty to curb plastic pollution but emphasizes recycling over production caps.
In short:
- Industry groups are promoting recycling targets and waste collection improvements as alternatives to capping plastic production.
- These proposals could cut global plastic pollution by 36% by 2050, but without a production cap, it's harder to achieve significant reductions.
- Industry influence over treaty negotiations is increasing, with substantial lobbying at recent sessions.
Key quote:
“Whether the treaty includes plastic production cuts is not just a policy debate. It’s a matter of survival.”
— Jorge Emmanuel, adjunct professor at Silliman University in the Philippines.
Why this matters:Recycling initiatives proposed by the petrochemicals industry while beneficial, are insufficient to tackle plastic pollution. A comprehensive approach, including production caps, is a more effective approach to achieve meaningful health and environmental benefits. For more read the op-ed by Pete Myers: We must determine which uses of plastic remain essential; eliminate those that aren’t; and design new materials to replace still essential plastics.
Plastic Free July needs systemic change, not just consumer action
A recent analysis argues that while Plastic Free July aims to reduce plastic use, significant impact requires action from governments and companies, not just consumers.
In short:
- Individual efforts during Plastic Free July are insufficient to address plastic pollution without systemic changes.
- Governments and corporations must implement regulations and redesign production and distribution systems to reduce plastic waste.
- Effective solutions need to consider the essential roles plastics play in everyday life and avoid disadvantaging vulnerable communities.
Key quote:
"Consumers shouldn’t have to bear full responsibility for plastic pollution. Individual sacrifices – particularly temporary ones – won’t make a significant difference."
— Bhavna Middha, senior research fellow at the Centre for Urban Research, RMIT University and Ralph Horne, associate deputy vice chancellor of research & innovation at the College of Design & Social Context, RMIT University.
Why this matters:
Focusing solely on consumer action overlooks the need for comprehensive policies and industry accountability to create lasting environmental change. Addressing plastic pollution effectively requires broad, systemic reforms that protect both the environment and vulnerable populations. Read more: A plastic recipe for societal suicide.
WATCH: Enduring the “endless” expansion of the nation’s petrochemical corridor
As mounds of dredged material from the Houston Ship Channel dot their neighborhoods, residents are left without answers as to what dangers could be lurking.
In the course of a century, Houston, once known for its magnolia flowers, turned into the “energy capital of the world.” To many, at 52 miles long and deepening under its 11th expansion, the Houston Ship Channel represents its epicenter.
To read and watch a version of this story in Spanish click here. Haz clic aquí para leer este reportaje en español.
The channel hosts hundreds of chemical facilities, some of which have years of documented Clean Air Act violations. Amnesty International called the channel a “sacrifice zone” where fenceline communities, made up predominantly with people of color, are disproportionately exposed to pollution. This is seen as the “cost of doing business,” according to the report.
But to people like Juan Flores and his family, the area is also home.
Flores, who you’ll meet in the video report above, has lived in Galena Park his entire life, and has been surrounded by the Houston Ship Channel’s dredge material deposit sites for as long as he can remember. He even recalls playing in them as a child.
The current 11th expansion of the port will create new dredge deposit sites and will stack new dredge material on old sites. In response to communities’ concerns of potential risks, Port Houston, the local entity that manages the public ports of the channel and is in charge of the expansion alongside the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, has said there is no cause for concern. According to the Corps, the material is tested before being placed on the mounds — yet the Corps has stated in the past that they do not test the deposit sites.
Watch the video above to learn more about the stories of these communities and their industrial neighbors.
Editor’s note: This story is part of a two- part series that will highlight the expansion of industry along the Houston Ship Channel – and the channel itself – amidst the landscape of an ever growing industrial footprint and the pollution that comes with it.
Reimagining plastic usage to combat pollution
In an interview with CBC, environmental scientist Pete Myers advocates for a significant reduction in plastic production and emphasizes the urgent need to address plastic pollution's health impacts.
In short:
- Pete Myers, chief scientist at Environmental Health Sciences, highlights the toxic health impacts of plastics and stresses the need for urgent reductions in their production.
- Myers criticizes the notion of recycling as a solution, suggesting it distracts from more effective measures like limiting virgin plastic production while Nestlé and other corporations call for collaborative global rules with less emphasis on production caps.
- Canadian Environment Minister Steven Guilbeault acknowledges the need to eliminate the most harmful plastics but expresses hesitation about imposing a cap on all plastic production.
Key quote:
“We have the ability to use the science we have today, which we didn't have when plastic was invented. We know why some plastics are safe and some aren't. And let's use that information, that chemical information, to design safer materials.”
— Pete Myers, chief scientist at Environmental Health Sciences
Why this matters:
Plastic pollution has penetrated every corner of our planet, threatening ecosystems and human health. Read more: Exposure to chemicals in plastics linked to cancer diagnoses.