This is what indigenous resistance to fracking looks like in Pennsylvania
Tribal leaders and Pittsburgh's mayor addressed the crowd protesting a fracking convention in Pittsburgh today—while acting EPA administrator Andrew Wheeler addressed the crowd of industry leaders inside.
Editor's note: This is a follow-up to yesterday's story, Fracking conference and opposing tribal rally highlight competing visions for Western Pennsylvania's future, which offers an in-depth explanation of the issues discussed below.
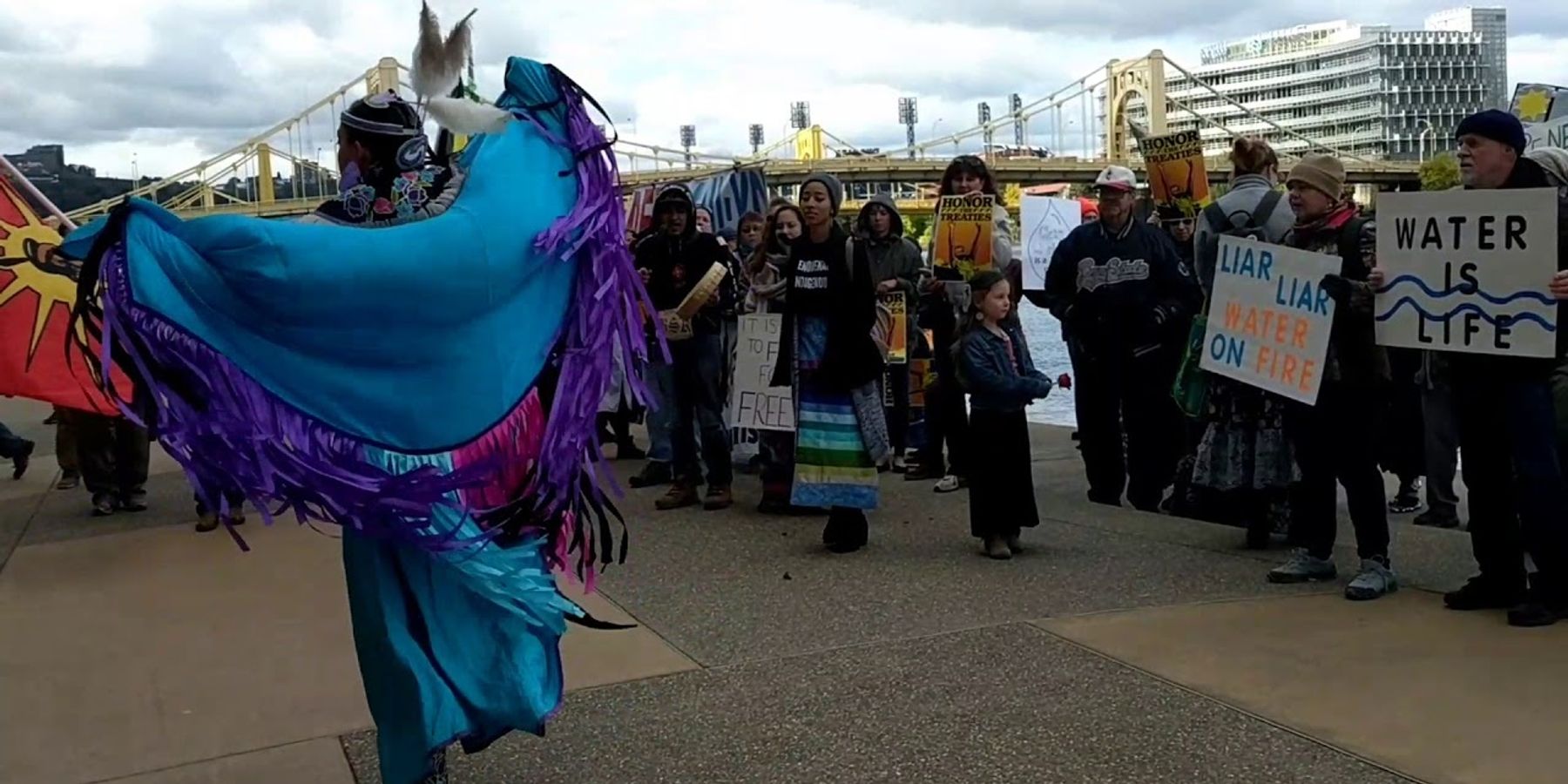
PITTSBURGH—Just after 10 a.m. today, a faithkeeper of the Wolf Clan of the Seneca Nation stood facing the water where the Ohio, Monongahela, and Allegheny rivers converge, and let out three sharp cries as a coal barge drifted beneath one of the city's iconic bridges.
The October sky was a clear, bright blue, and a cold wind blew fluffy clouds by overhead. A crowd of about 70, bundled up in coats and hats, gathered behind the faithkeeper, surrounding the fountain in downtown Pittsburgh's Point State Park. Despite its size, the crowd remained silent—aside from from the faithkeeper's cries, the only other sounds were the rushing of the waters and the shriek of distant train whistles.
Degawenodas, was one of two indigenous tribal faith leaders who traveled to Pittsburgh to lead a water ceremony aimed at protecting the three rivers. The event, which was followed by a rally, was planned to coincide with a massive fracking convention taking place in downtown Pittsburgh at the same time. Both the ceremony and the rally, which were coordinated in collaboration with at least 15 local and national environmental groups, were in opposition to the profusion of new fracking wells, pipelines, and petrochemical industry infrastructure currently under development in Southwestern Pennsylvania, and the threats they pose to waterways in the region and beyond.
The opposing events epitomize an ongoing national struggle between indigenous groups, environmentalists, and the oil and gas industry.
"The extractive relationship we have with this water and this land is like that of an addict to a drug," Sharon Day, an Ojibwe "Water Walker" from Minnesota who co-lead the ritual, told the crowd. "That boom and bust—we always tell ourselves that this time it will be different, but deep down we know that it won't."
During the hour-long water ceremony (which the leaders requested not to be photographed or recorded), incense was burned and sacred herbs were strewn on the ground and into the rivers. Day led the crowd in the singing of an Ojibwe water song with lyrics that translate to, "Water, we love you, we thank you, we respect you."
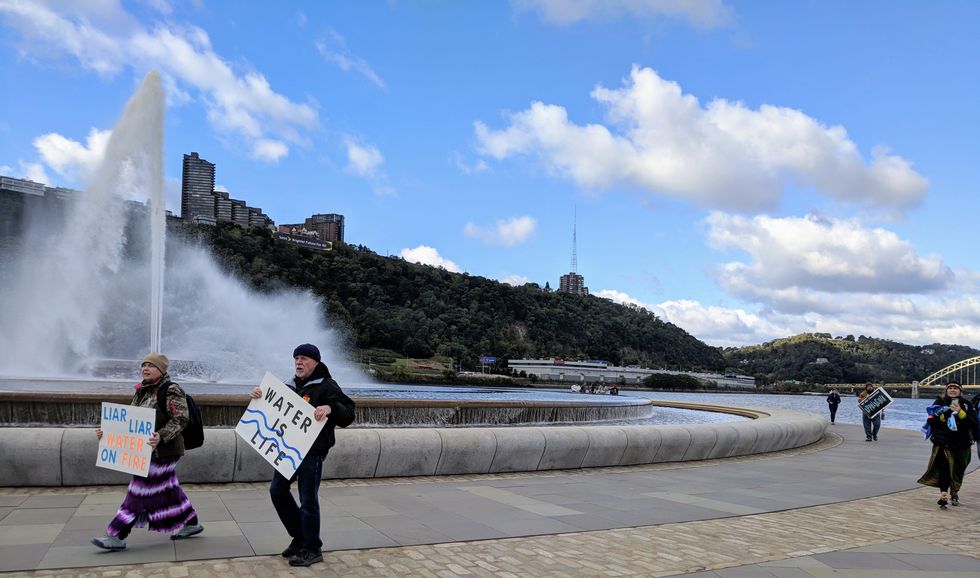
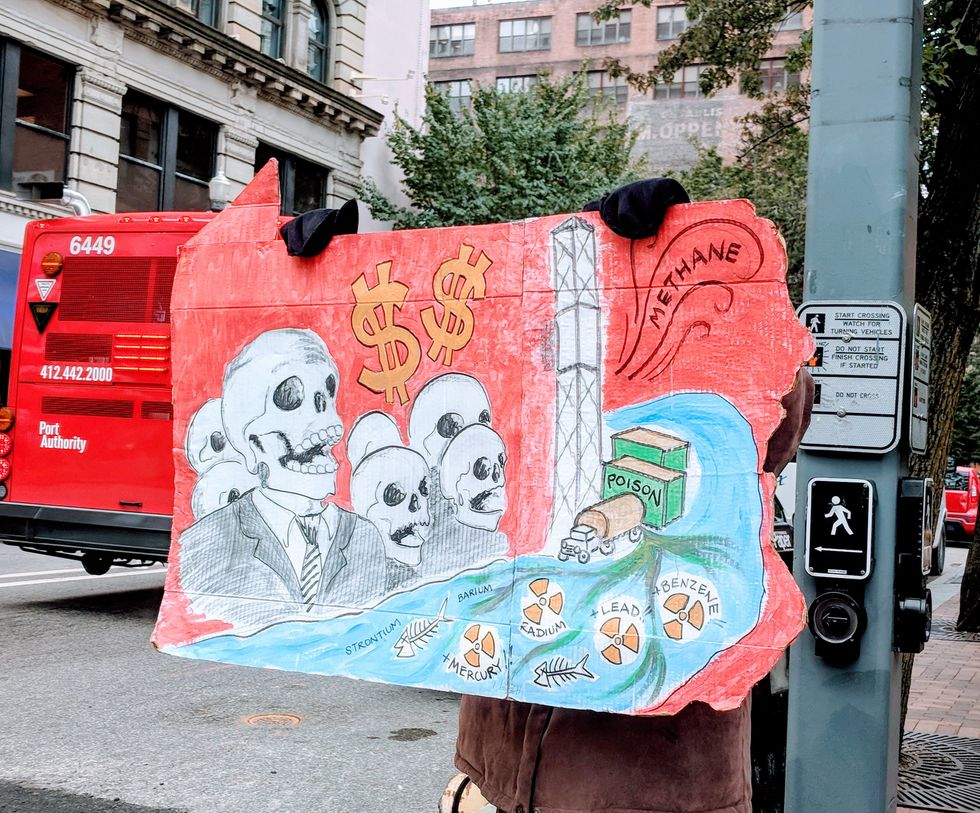



Members of the crowd who'd brought small containers of water from the rivers, streams and tributaries near their homes throughout Pennsylvania, Ohio, Virginia, West Virginia, and New York that eventually feed into the Ohio, the Monongahela, or the Allegheny Rivers, commingled the water they'd carried from home in a small tin bucket so that Day could bless them before pouring them into the rivers, "sending them home."
Following the ceremony, the crowd took up signs and banners then walked through downtown Pittsburgh to the David L. Convention Center, where the 2018 Shale Insight Convention is currently underway, featuring acting US EPA Administrator Andrew Wheeler as one of the keynote speakers.
Tribal leaders are protesting the #SHALEINSIGHT2018 convention in #Pittsburgh right now. Here's why:… https://t.co/b1EHJyoFde— Kristina Marusic (@Kristina Marusic) 1540394793.0
Marching from the Pointyoutu.be

The march ended at the convention center, which sits directly alongside the Allegheny River. The crowd chanted, sang, and danced to protest the continued expansion of the natural oil and gas industry in the region and the associated threats to the region's water and human health.
YouTubeyoutu.be
Lydia Green interviewwww.youtube.com
At one point, a man wearing a Donald Trump mask and a Shale Insight Convention name badge appeared on a balcony of the convention center above, and appeared to chant alongside the demonstrators.
Trump maskyoutu.be
Around 15 speakers addressed the crowd, including Degawenodas, Day, and other indigenous tribal leaders; representatives from environmental groups; residents of nearby Washington County, which is among the most heavily-fracked counties in the nation; and Pittsburgh Mayor Bill Peduto.
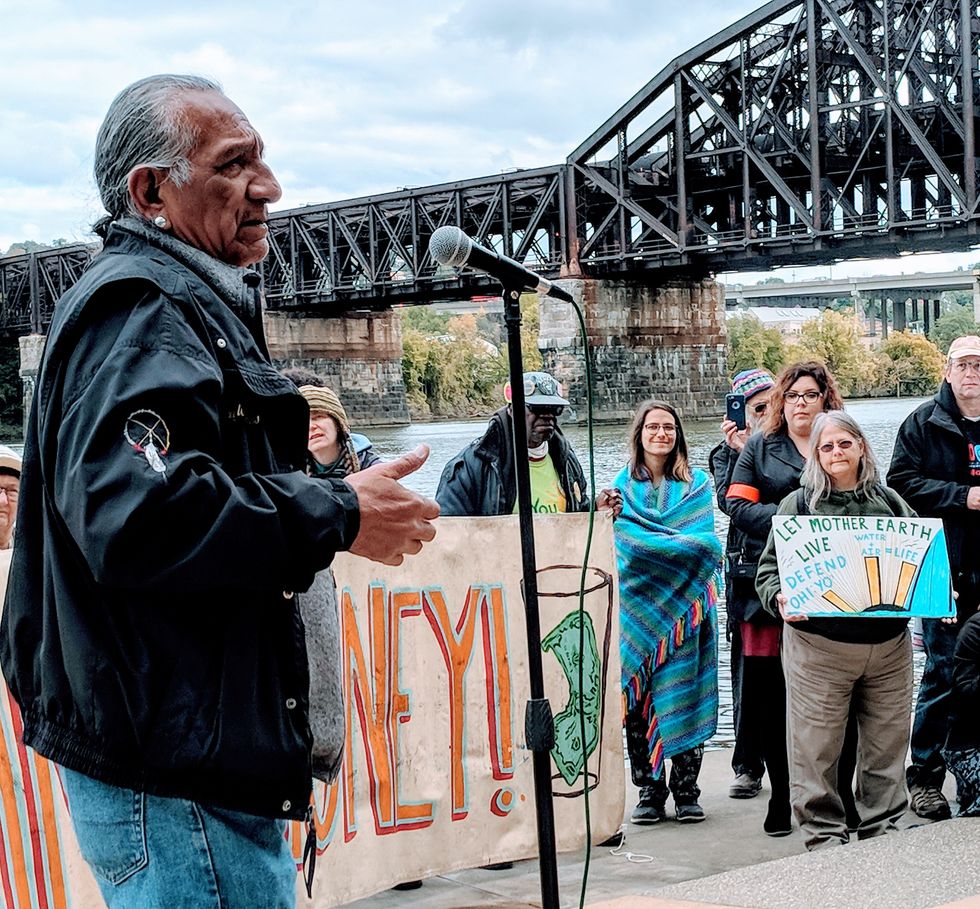
Peduto spoke about the original people of this land and referred to Trump's infamous "Pittsburgh, not Paris" tweet, saying that once again, Pittsburgh is "at the very heart of the environmental movement in the U.S. and far beyond."
He ended his remarks by saying, "The question is, what will we do to begin to play offense, instead of constantly playing defense? It begins with what we do with our air and our water."
Peduto speechyoutu.be
The mayor was heckled a number of times throughout his speech, with members of the crowd calling out things like,"Condemn the cracker plant!" They were referring to the massive Shell ethane cracker—one of five planned for the region—currently being built in neighboring Beaver County. To date, the mayor has declined to overtly speak out against the ethane cracker, stating that because it's being built outside his jurisdiction, it isn't appropriate.
Still, following his remarks, Peduto was warmly embraced by several members of the crowd.

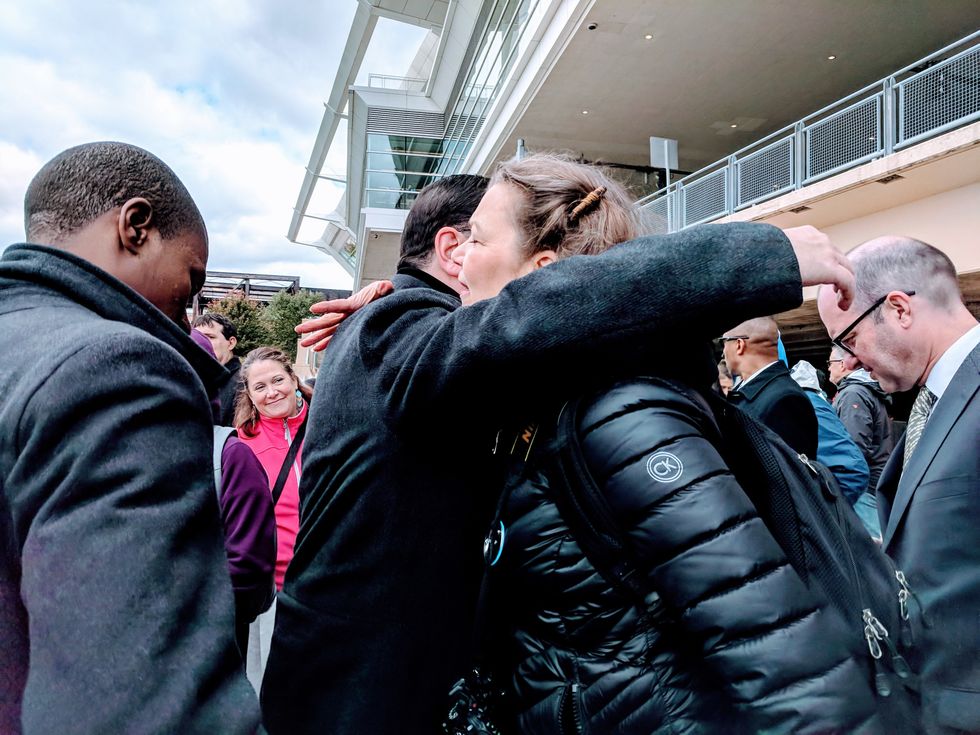
The 2018 Shale Insight Convention is still running through Thursday, and a number of other protests and several film screenings are planned. Representatives from the Shale Insight Convention did not return our requests for comment, and EHN's request for press credentials to attend the event were denied.
Editor's note: An earlier version of this story misidentified Degawenodas as a faithkeeper of the Seneca Nation.














